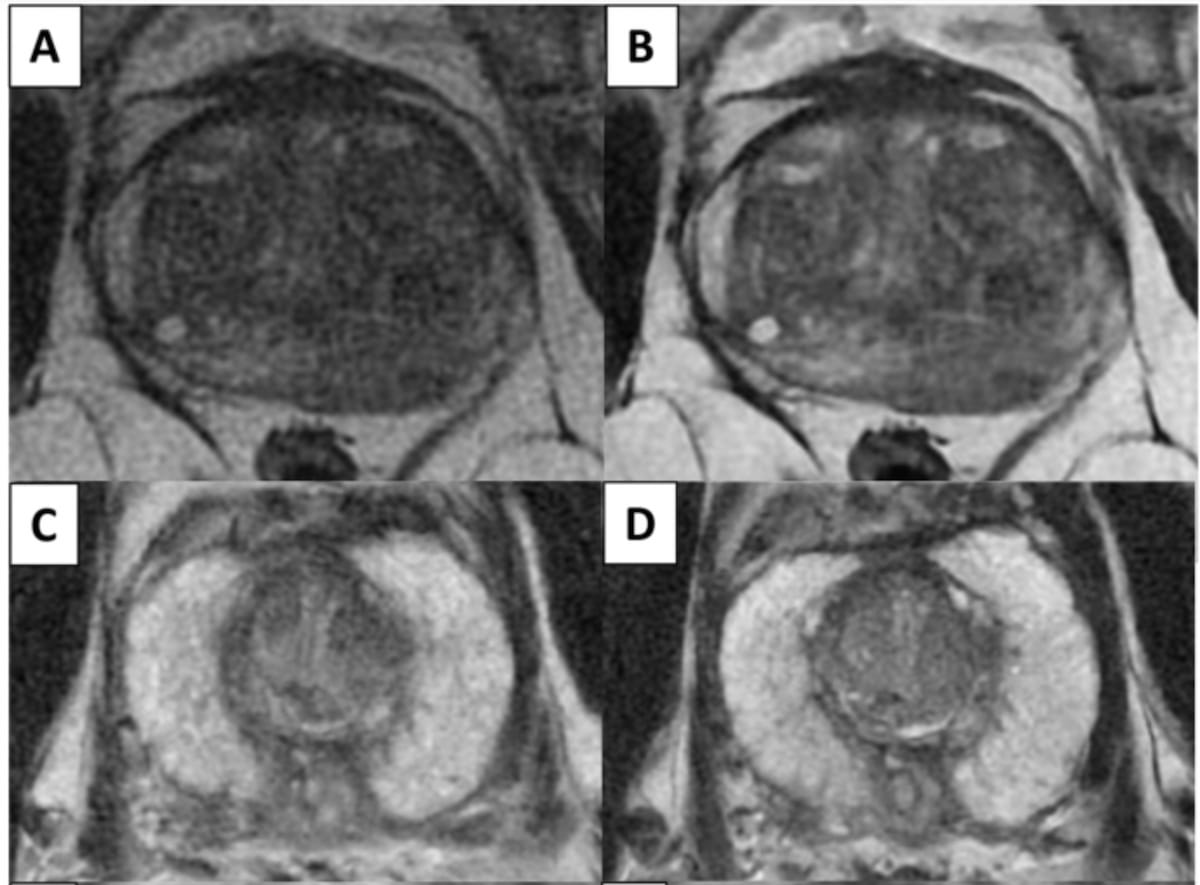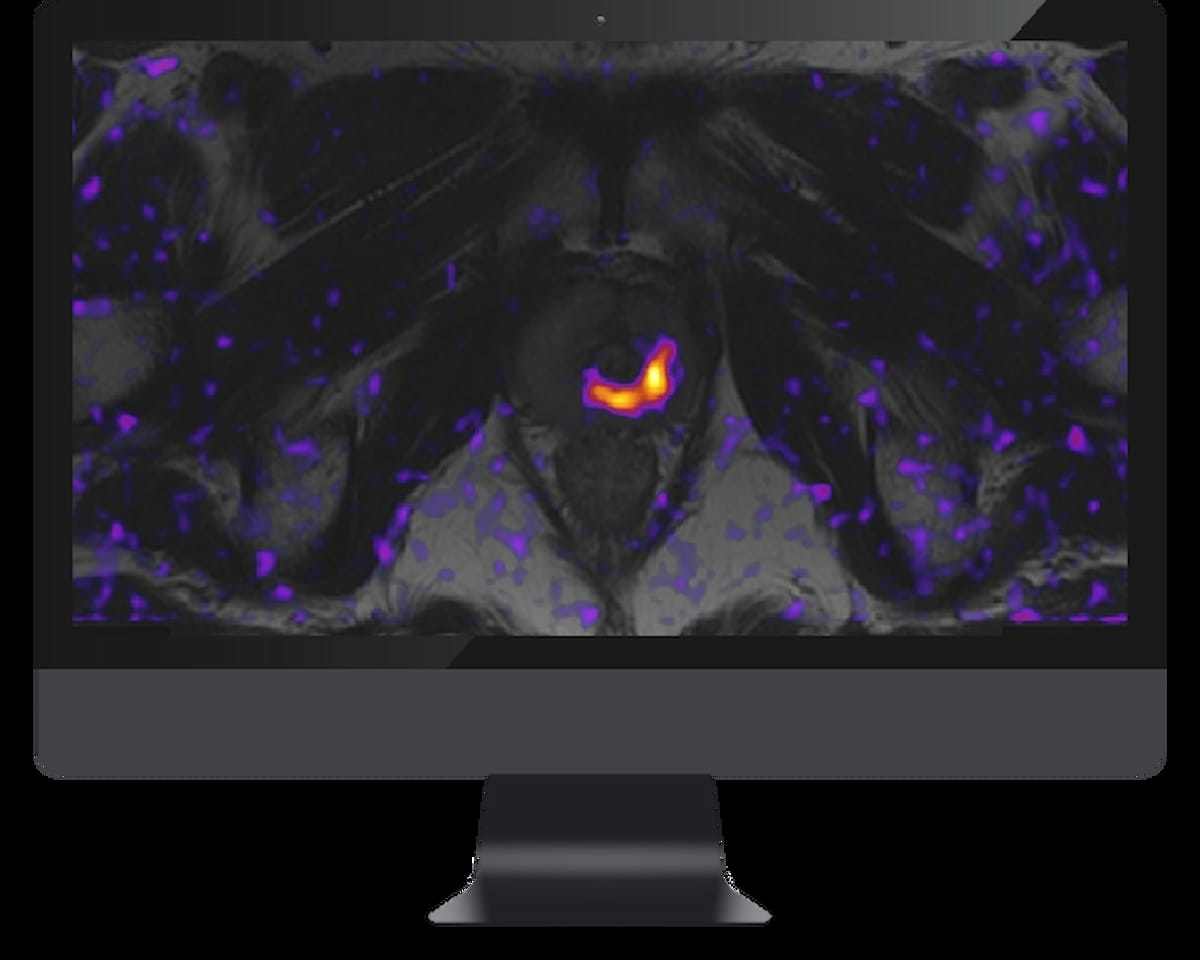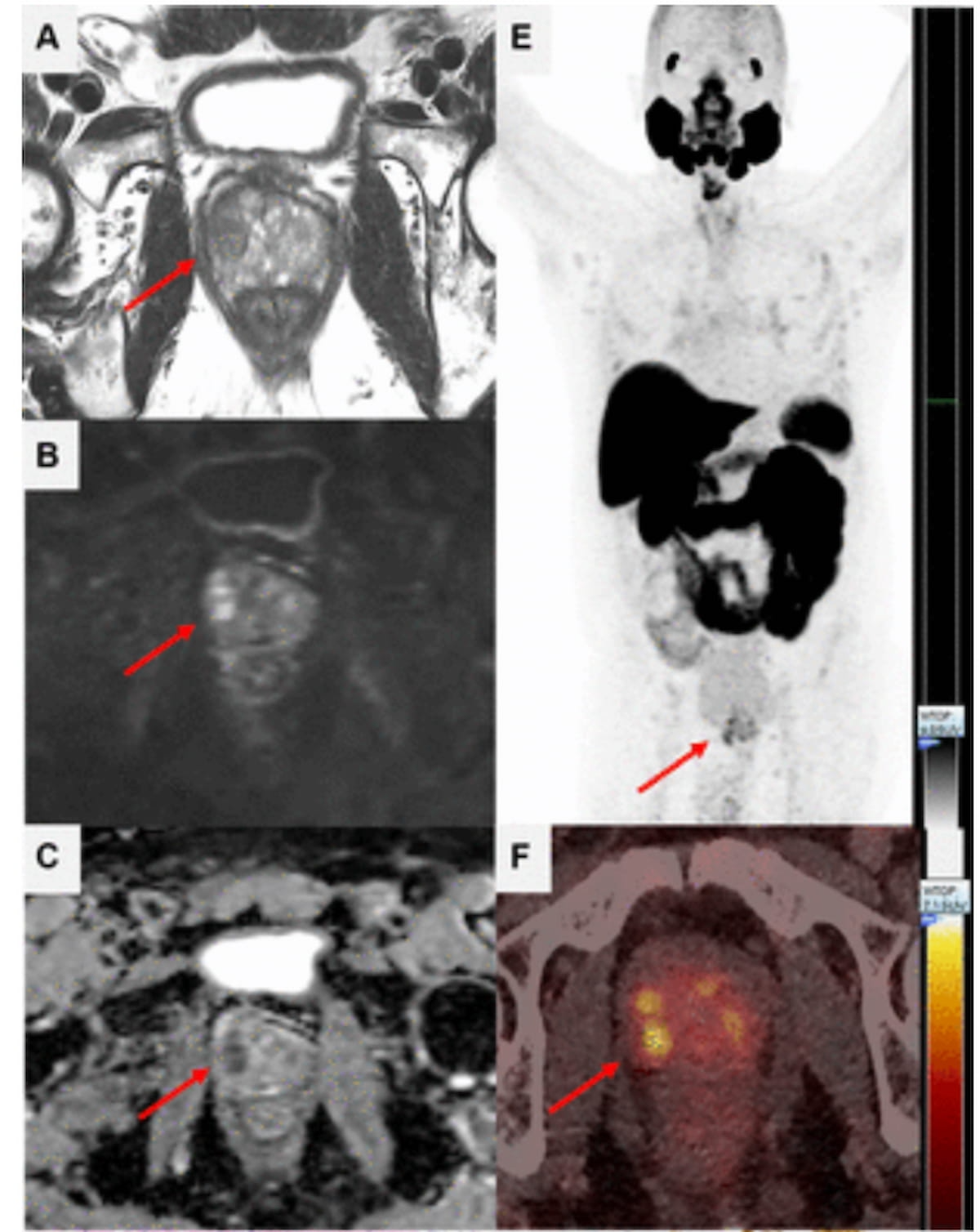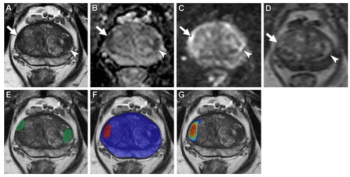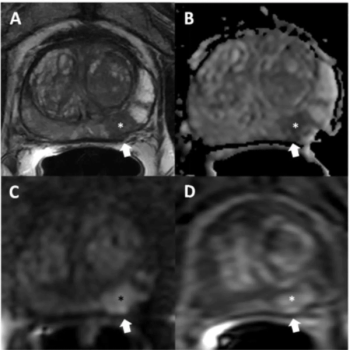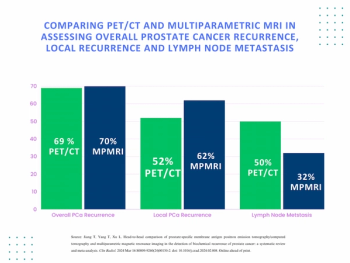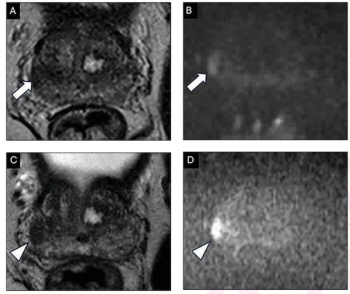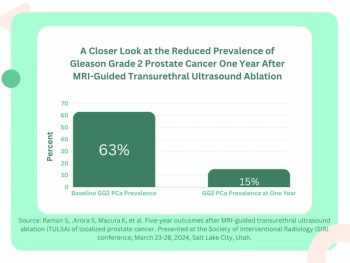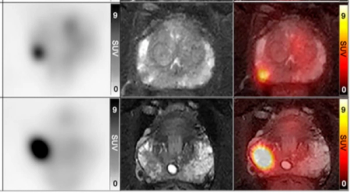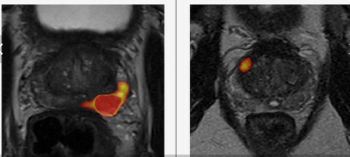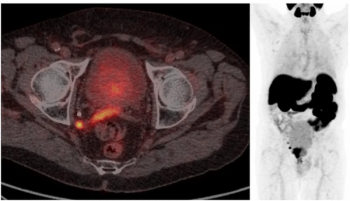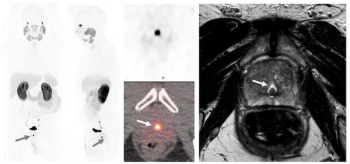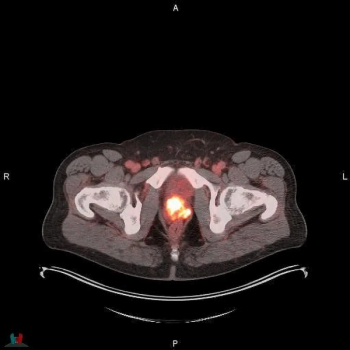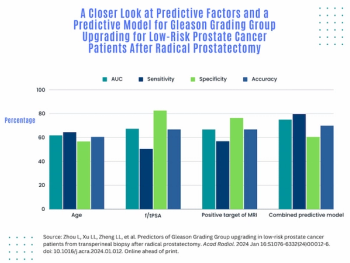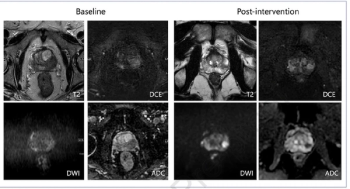
Using a learning network model to discuss challenges and share insights among radiology departments from five different organizations, researchers noted that 87 percent of audited prostate MRI exams had PI-QUAL scores > 4 at the conclusion of the collaborative program.