MRI
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
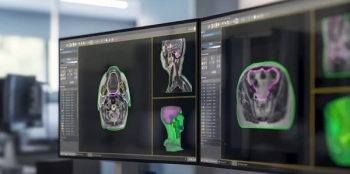
Capable of segmenting over 37 organs and structures in the head, neck and pelvis, the MR Contour DL software is currently being showcased at the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) conference.
Emerging MRI research suggests that brain age is nearly two years older than chronological age for people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and increased alcohol intake.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in April 2025.
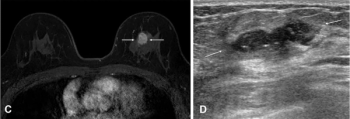
Preoperative breast MRI had no impact upon recurrence-free survival and overall survival for women with HER-2 positive, hormone receptor-negative breast cancer, according to a multivariable analysis of a new study involving nearly 1,100 women.
In a recent interview, Wayne Brisbane, M.D., discussed new research, presented at the American Urological Association (AUA) conference, which revealed a 15 percent higher AUC for an emerging AI software in detecting seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) in comparison to prostate MRI alone.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
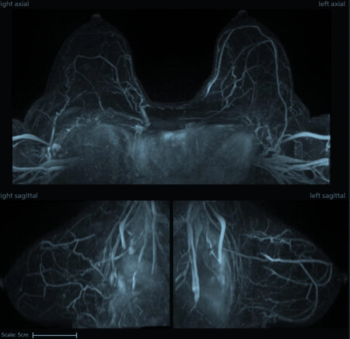
An artificial intelligence algorithm for dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI offered a 93.9 percent AUC for breast cancer detection, and a 92.3 percent sensitivity in BI-RADS 3 cases, according to new research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
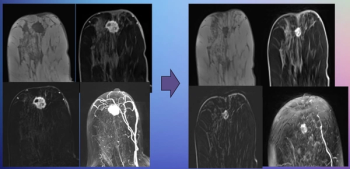
New research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference suggests that abbreviated MRI is comparable to full MRI in assessing pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
In a recent interview, Benjamin Kann, M.D., discussed the use of an emerging AI model that can assess longitudinal MR imaging to help predict postoperative recurrence risk for gliomas in pediatric patients.
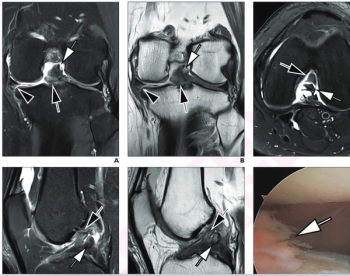
Employing deep learning image reconstruction, parallel imaging and multi-slice acceleration in a sub-five-minute 3T knee MRI, researchers noted 100 percent sensitivity and 99 percent specificity for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears.
In a recent interview, Arjun Sahgal, M.D., discussed current and emerging research examining the potential of MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy for treating glioblastomas.
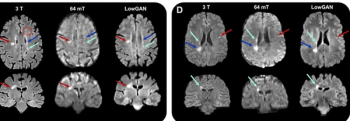
In comparison to native 64-mT MRI, the deep learning generative model LowGAN offered enhanced white matter lesion conspicuity and image quality in a study involving patients with multiple sclerosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
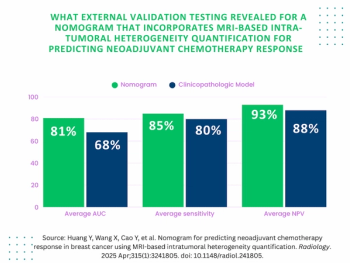
An emerging nomogram model for intra-tumoral heterogeneity quantification with breast MRI demonstrated an average 85 percent sensitivity in external validation testing for predicting pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
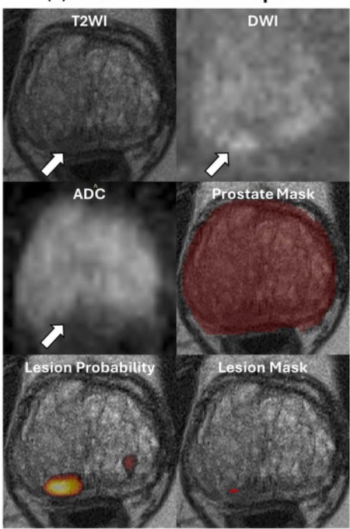
Demonstrating no significant difference with radiologist detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), a biparametric MRI-based AI model provided an 88.4 percent sensitivity rate in a recent study.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
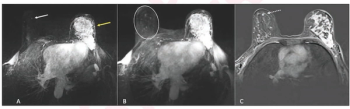
In a new study involving over 120 women, nearly two-thirds of whom had a family history of breast cancer, ultrafast MRI findings revealed a 5 percent increase in malignancy risk for each second increase in the difference between lesion and background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) time to enhancement (TTE).
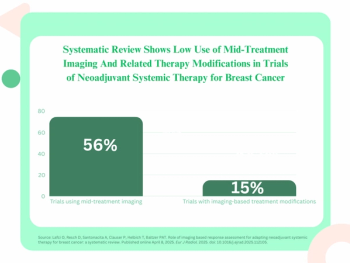
A systematic review of 147 clinical trials assessing neoadjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer also revealed that mid-treatment imaging was utilized in 56 percent of the studies.
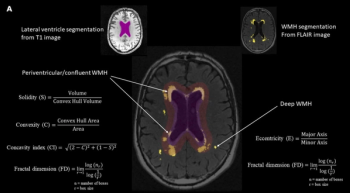
Emerging research demonstrated that cognitive declines in memory, executive function and processing speed domains were associated with irregular shape of periventricular/confluent white matter hyperintensities.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
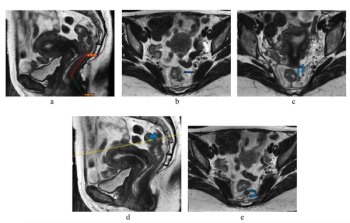
Abbreviated MRI demonstrated a 95.3 percent specificity for rectal cancer and provided strong agreement with the full MRI protocol for T staging and detection of extramural venous invasion, according to newly published research.
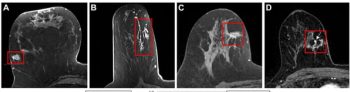
New multicenter research suggests that radiomic features derived from breast MRI may enhance prognostic capabilities with disease upstaging for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
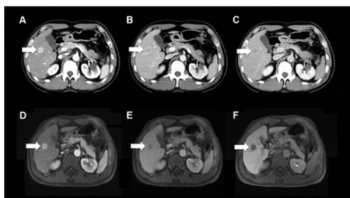
LI-RADS category 5 (LR-5) assessment had an 11 percent higher AUC for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with non-cirrhotic chronic hepatitis C (CHC) in comparison to those with cirrhotic CHC.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.