MRI
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
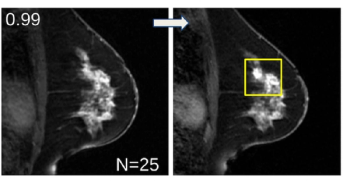
An artificial intelligence (AI) model demonstrated a 72 percent AUC for predicting breast cancer one year before a subsequent MRI.
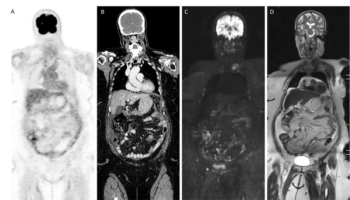
In newly published guidelines, researchers discuss the utility of CT, MRI and PET/CT in the diagnosis, staging, treatment monitoring and follow-up imaging for peritoneal metastases in patients with ovarian or colorectal cancer.

In recent interviews, Eric Rohren, M.D., and Krishna Nallamshetty, M.D., discuss the potential of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) to progress into life-threatening consequences and an emerging AI-powered tool that may bolster adherence to best practice recommendations in radiology reporting of incidental AAA findings on CT and MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent interview, Stamatia Destounis, M.D., discussed the impact of national breast density notification for mammography reports and key considerations with staffing and ongoing education for patients, staff and referring providers on the merits of supplemental breast imaging.
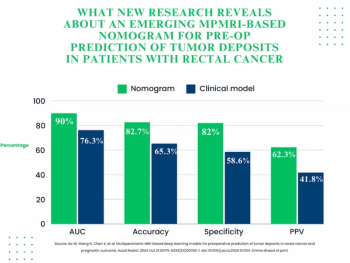
For patients with rectal cancer, an emerging nomogram that combines deep learning and clinical factors had greater than 16 percent and 23 percent increases in accuracy and specificity, respectively, for pre-op prediction of tumor deposits in comparison to clinical factors alone.
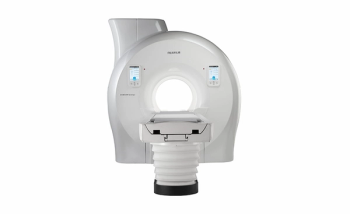
Emerging technologies included with the 10th version of the 1.5T MRI platform include Synergy DLR Clear and Synergy Vision that are geared toward mitigating common challenges with artifacts.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in October 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
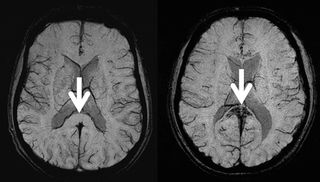
New research revealed no significant difference between gadolinium-free MRI and GBCA-enhanced MRI in preoperative predictive accuracy for the grading of diffuse gliomas in adults.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
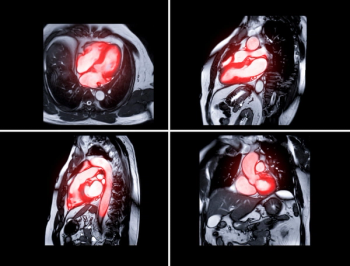
The updated software reportedly provides access to more than 200 enhanced features including optimized hanging protocols with a cardiac MRI viewer and perfusion quantification analysis.
A model emphasizing time-dependent diffusion MRI was 15 percent more effective than apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements at predicting pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for women with breast cancer, according to new research.
The Ezra Blueprint scan reportedly includes quantitative brain measurements, coronary calcium scoring (CAC) and a full-body MRI that provides screening for over 500 conditions.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Leveraging AI technology, the AiMIFY software reportedly facilitates double the contrast enhancement in comparison to gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) for brain MRI.
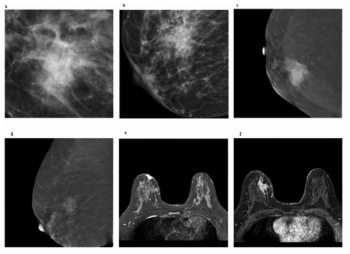
Is the Kaiser Score More Effective than BI-RADS for Assessing Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and MRI?
For women with breast-enhanced masses, Kaiser scoring (KS) demonstrated a 20 percent higher AUC than BI-RADS classification for contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) and was comparable to KS for breast MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
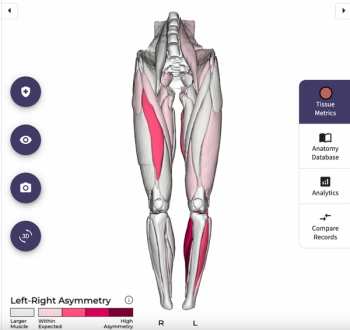
Based off rapid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the AI-enabled MuscleView reportedly offers 3D analysis of muscle volume, muscle asymmetry and intramuscular fat.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
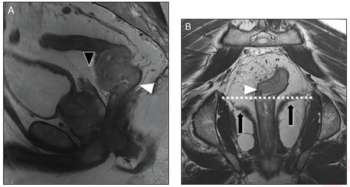
Noting a rapidly changing paradigm for the treatment of rectal cancers, the authors of a new literature review discuss current and emerging principles in MRI assessment and staging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in September 2024.
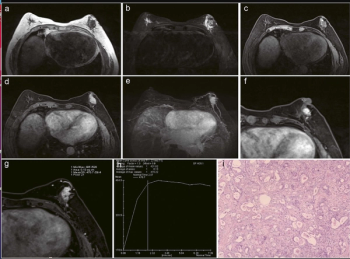
The addition of parameters such as patient age, MIP sign and associated imaging features to the Kaiser score demonstrated a 95.6 percent AUC for breast cancer detection of enhancing lesions on breast MRI in recently published research.

Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in September 2024.