Older women exposed to higher levels of air pollution can experience a 24-percent increase in Alzheimer’s risk.

Older women exposed to higher levels of air pollution can experience a 24-percent increase in Alzheimer’s risk.
Approximately half of all patients who experience stroke, brain bleeds, or blocked blood vessels, identified on MRI or head CT in this study, had high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes.
New scanner is designed to augment neurological and musculoskeletal imaging functions.
Identification of facial nerves impacted by this condition increases dramatically with DCE-MRI.

Certain parts of the brain respond differently to hot-button language found in campaign ads and speeches.
A convolutional neural network can accurately measure skeletal muscles, helping predict patient survival.
Interventional radiologists are uniquely positioned to practice stroke intervention.
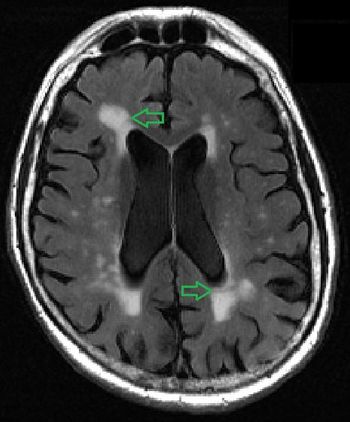
A tool that objectively measures the volume of white matter lesions can accurately pinpoint evidence of early dementia.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
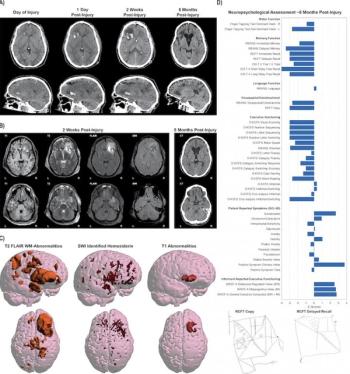
Worldwide effort will amass large datasets from institutions that can be used to identify long-term traumatic brain injury and augment therapies.
Opposition to AI in Mammography; Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dysfunction; Clear & Present Danger for The Match; Trends & Innovations in Breast Imaging
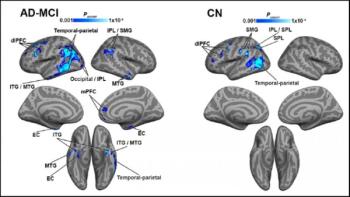
As Alzheimer’s disease progresses, more brain regions exhibit evidence of this link.
MRI and PET Reveal Parkinson's disease Duality; MRI Shows More Aggressive MS in Hispanic Patients; Radiation Dose Misconceptions; and Challenges for Racial and Ethnic Minorities in Cancer Screening
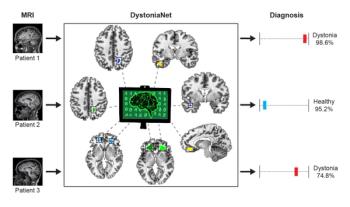
The platform, dubbed DystoniaNet, was able to identify 3 varieties of focal dystonia in a matter of 0.36 seconds with almost 100-percent accuracy.
Volumetric MRI shows Hispanic patients are at a greater risk of experiencing more aggressive disease, leading to sustained disability.
Advanced imaging shows Parkinson’s can begin as brain-first or body-first.
Portable, Low-field MRI; COVID-19 and Cardiac MRI; High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound; Coronary CTA Guidance; and Pediatric Advanced Imaging Utilization

Point-of-care, 64mT MRI performs as well as conventional CT and MRI while improving patient safety.

By capturing changes to the hippocampus, MRE can pinpoint brain damage early before epilepsy becomes medication resistant.
Cerebral infarction and hemorrhage are more common in severe cases while cranial nerve abnormalities affect patients with milder disease.
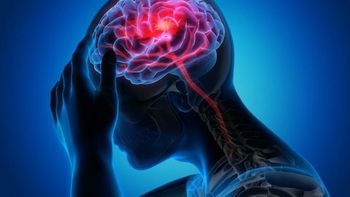
Images reveal hypertension can be significant risk factor for CSVD.

Products focus on Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and accelerating clinical translation.

Emergency providers are utilizing more ultrasound and MRI scans, fewer CTs.
COVID-19, Stroke, and Heart Damage; Limitations of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis; Guidance for Pediatric CTA; and Micro-Ultrasound and Prostate Cancer
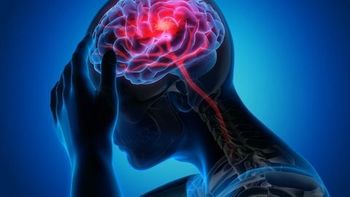
Clinicians should adopt a lower threshold for evaluating patients for stroke and providing care.