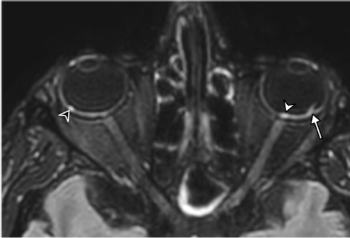
First brain MRI findings reveal dangerous COVID-19-related optical findings.

First brain MRI findings reveal dangerous COVID-19-related optical findings.

These radiopharmaceuticals are less expensive, and they offer longer half-lives.
Perivascular Spaces & Dementia; COVID-19 Loss of Smell and Taste; NAFLD & Multi-parametric CT; Plus, Point-of-Care Ultrasound in the Pandemic Era
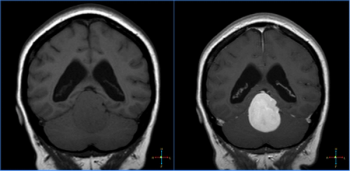
Can you diagnose this patient with dizziness?
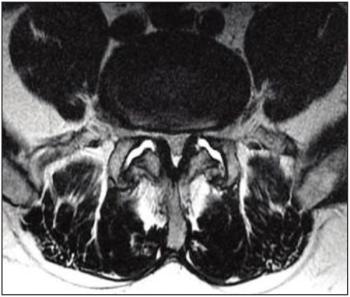
Pairing patient-reported data about pain symptoms with an MRI image can lead to better identification of pain’s origin.
Large numbers of perivascular spaces seen in the brain are more commonly found in patients who go on to develop cognitive problems or dementia.
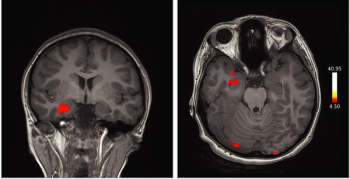
Images captured with fMRI in a case study reveal the role of the orbitofrontal cortex in patients infected with the virus who experience anosmia and ageusia.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.

Software provides annotated and segmented brain images captured by Hyperfine’s portable MRI system.
A new magnetic resonance spectroscopy technique can accurately measure how well the mitochondria are functioning in this patient group, potentially facilitating more effective therapies.
COVID-19 Damage, but No Virus in the Brain; Non-Ferromagnetic Bullets and the MRI; Six Trends to Watch in 2021; and AI and Ethics
These measurements can be used to predict at three months which patients will develop post-traumatic stress disorder after traumatic brain injury.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Study shows blood vessel damage and inflammation in the brain, but no evidence of SARS-CoV-2.
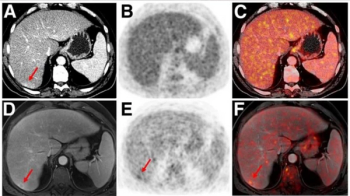
MRI reveals its wide utility this year, demonstrating improved performance in disease detection, as well as outperforming other modalities in providing clearer, more detailed images.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.

Brain regions that control memories and imagination are more tightly connected in people who get lonely.
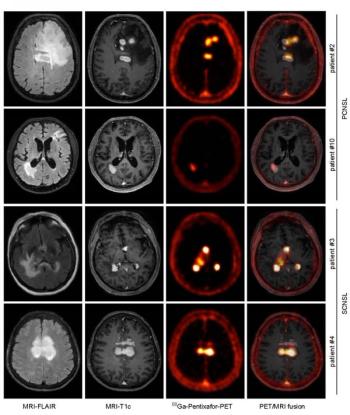
68Ga-pentixafor can clearly distinguish between healthy and malignant tissue on both CT and MRI scans.
A combination of acoustic imaging methods and algorithms offers a better method to explore the brain’s gray and white matter.
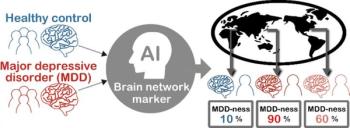
Machine learning can pinpoint specific activity patterns in the brain that could lead to more targeted therapies.

The 16-channel head adaptive image receive radiofrequency coil opens the door for greater comfort and future coil design improvements.
Differences in cortical thickness development correlates to cognitive differences and could be involved in increased risk for mental illness.
Novel deep learning model can provide needed information from multi-modal imaging even when some modalities are absent.
7T MRI and MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound present new clinical opportunities in the pipeline.
The mechanisms, magnitude, manifestations, and management of stroke during the pandemic.