
For National Mammography Day, Diagnostic Imaging offers a closer look at emerging news, current insights and recent research on mammography.
For patients undergoing stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for prostate cancer, the acute genitourinary (GU) toxicity rate associated with the procedure was 19 percent lower with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance in comparison to computed tomography (CT) guidance, according to new research presented recently at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.

For National Mammography Day, Diagnostic Imaging offers a closer look at emerging news, current insights and recent research on mammography.
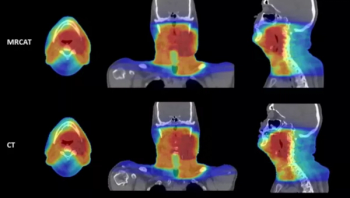
For physicians performing radiotherapy treatment of soft tissue tumors in the head and neck, the MRCAT Head and Neck offers an artificial intelligence (AI) application that allows the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as the primary or sole imaging for procedure planning.
While facilitating interdisciplinary colloaboration is a central objective with enterprise imaging platforms, this author says implementation of these platforms must ensure optimal patient privacy in sensitive cases involving abuse, assault and domestic violence.
In a recent letter to U.S. Rep. Rosa DeLauro (D-CT), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said a final rule on amendments to the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA), including an oft-delayed national standard for breast density notification in mammography reporting, may be published in the next couple of months.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
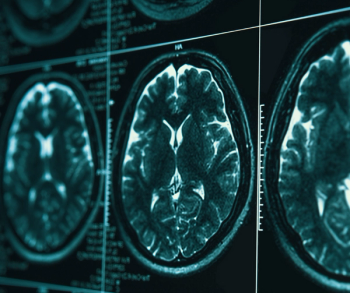
While current consensus guidelines do not recommend the use of brain MRI screening in patients with breast cancer, a new study shows significantly elevated risks for the development of central nervous system metastasis in patients with inflammatory breast cancer.
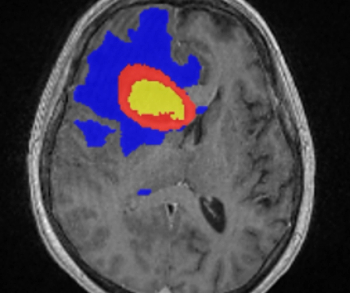
Incorporating artificial intelligence (AI)-based technology, Neosoma HGG reportedly demonstrated a 95.5 percent accuracy rate in measuring brain tumor volume on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans at various points during the treatment of patients with high-grade gliomas.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
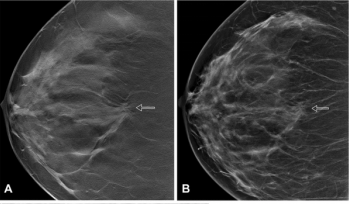
In a large study of nearly 100,000 women, researchers found that the combination of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and synthesized mammography had more than triple the detection rate for invasive breast cancer in extremely dense breasts in comparison to digital mammography alone.

In a thorough review of the literature, these authors discuss current approaches and emerging initiatives to increase the understanding of radiology reports by referring physicians as well as patients.
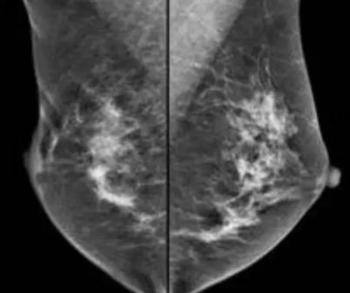
In a study involving nearly 700 patients with atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasia, or lobular carcinoma in situ, researchers found no difference in four-year breast cancer detection rates between women who had screening mammography and breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and women who only had mammography screening.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
AIR Recon DL, a deep learning-based image reconstruction software, will now be available with 3D sequences as well as PROPELLER motion-insensitive sequences on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners from GE Healthcare.
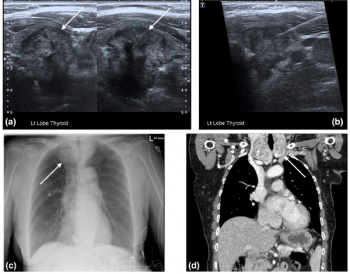
In light of recent shortages of iodinated contrast media, researchers from Australia suggest in a new publication that ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be viable first-line imaging options for a number of non-urgent presentations of the head and neck.
Assessing data from 386,590 women, researchers noted that women with extremely dense breast tissue have more than double the risk for breast cancer in comparison to women with average breast density and nearly four times the risk of women with extremely fatty breast tissue.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Requiring only half of the gadolinium dose of current non-specific gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs), gadopiclenol can be utilized with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help detect lesions with abnormal vascularity in the central nervous system and other areas of the body.
Emerging research suggests that combining pre-biopsy magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing more than triples the specificity rate for detecting clinically significant prostate cancer in comparison to sole reliance on a PSA level greater than or equal to 4 ng/mL.
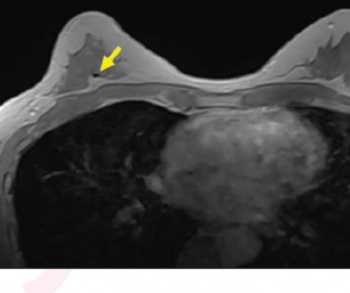
Emerging research suggests that the contrast-enhanced, in-phase Dixon sequence may be the most optimal sequence for detecting biopsy clips on breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
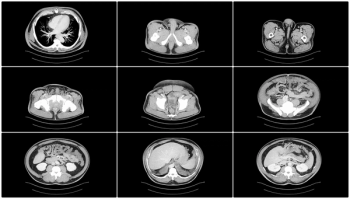
Greater imaging utilization has increased the prevalence of incidental findings or incidentalomas, but unclear clinical context and guidelines complicate management. Accordingly, these authors offer a thorough review of the literature and discuss new opportunities for improving interdisciplinary management strategies.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
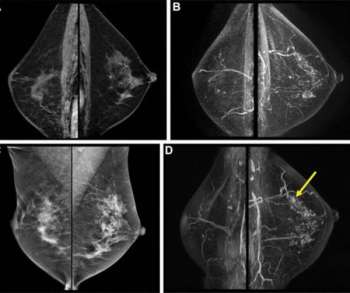
Mild, moderate, or marked background parenchymal enhancement on surveillance magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reportedly doubles the risk of second breast cancer in women who have had surgery for primary breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
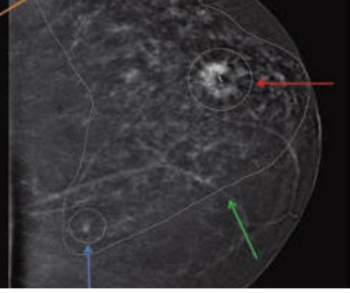
Researchers found the combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and contrast-enhanced mammography was nearly 22 percent more effective at detecting breast lesions than MRI-directed ultrasound.

Catch up on the top AI-related radiology content of the past month.