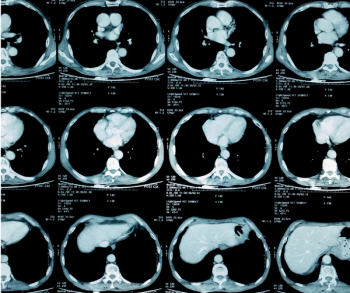
Emerging research suggests that strict adherence to the Lung-RADS classification may not lead to optimal detection of cancer.

Emerging research suggests that strict adherence to the Lung-RADS classification may not lead to optimal detection of cancer.
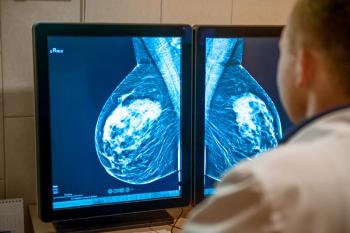
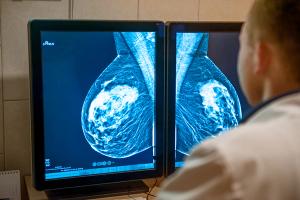
Given the broad range of fibrocystic changes, the authors of a recent study suggest that more precise diagnosis of breast MRIs could significantly reduce unnecessary biopsy procedures.
A new study suggests that patients with negative RT-PCR tests who are suspected of having COVID-19 may benefit from chest computed tomography (CT), which could help identify early stages of the disease.
Warning systems designed to streamline interpretation of screening mammograms may not benefit interpreting radiologists or patients, a new study suggests.

Patients said receiving radiology results and reviewing the images and findings directly with a radiologist after completion of a neck ultrasound was beneficial, according to a new study.

Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital proposed an algorithm for appropriate axillary nodal imaging to better align with changes in treatment algorithms for axillary nodal disease in patients with breast cancer.

A recent article in Clinical Imaging suggests a three-pronged education approach to address healthcare disparities in radiology.
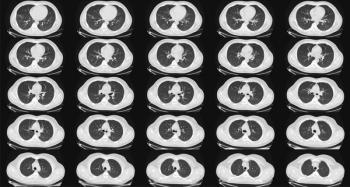
A recent study showed how using artificial intelligence to retrieve reference images could improve diagnosis of interstitial lung disease with chest CT.
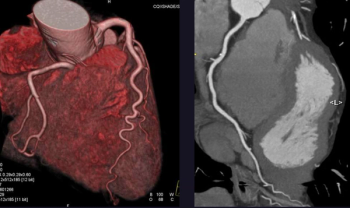
Cardiac CTA before transcatheter aortic valve replacement can be used to better determine risk by assessing left atrium functional parameters that are predictive of mortality.
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma may benefit from early PET/CT imaging after transarterial radioembolization to predict treatment response and survival, a new study found.
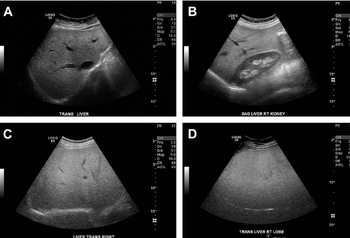
Investigators in Japan developed a statistical model to identify patients with high-risk nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using three ultrasound-based markers, which yielded an 86.5% positive predictive value.
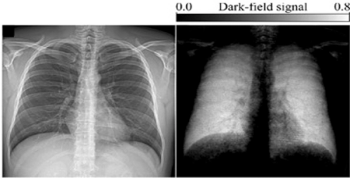
X-ray dark-field chest imaging may generate detailed imaging of lungs without interference from surrounding tissue or influence by characteristics such as age, gender or weight.
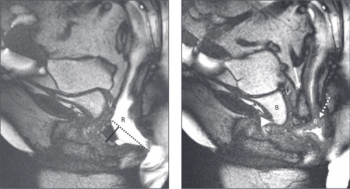
The report provides a universal set of recommendations and language for technique, interpretation and reporting of magnetic resonance defecography and is endorsed by six medical societies.

Patients suspected of having coronary stenoses may benefit from ultra-high-resolution CT, according to a recent study that showed high diagnostic confidence in severely calcified coronary atherosclerotic disease.
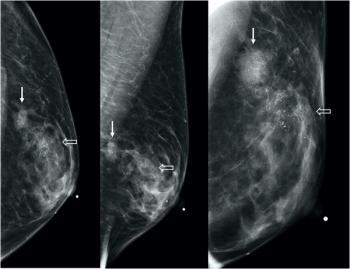
Feminizing hormone therapy may increase the risk of breast cancer in transgender women, a growing body of research suggests, underscoring a need for health care providers to understand the risks, breast imaging features, and health care needs of this demographic.
The post-processing software platform can reduce brain imaging acquisition time by 40%.

Computed tomography (CT) abnormalities are reported among a substantial proportion of patients after hospitalization with COVID-19.
The combination approach may significantly reduce over-detection while providing noninferior detection of clinically significant prostate cancer.
A nuanced approach is needed to weigh the risk of vaccination-associated axillary lymphadenopathy against the risk of delaying breast cancer screening.
A tailored educational intervention involving collaboration among mental health, primary care and radiology clinicians may help overcome challenges to lung cancer screening among individuals with serious mental illness.

Published: November 3rd 2021 | Updated:
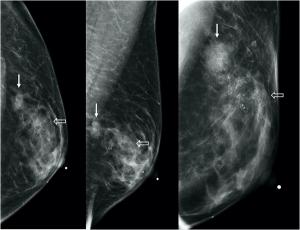
Published: September 9th 2021 | Updated:
Published: December 7th 2021 | Updated: