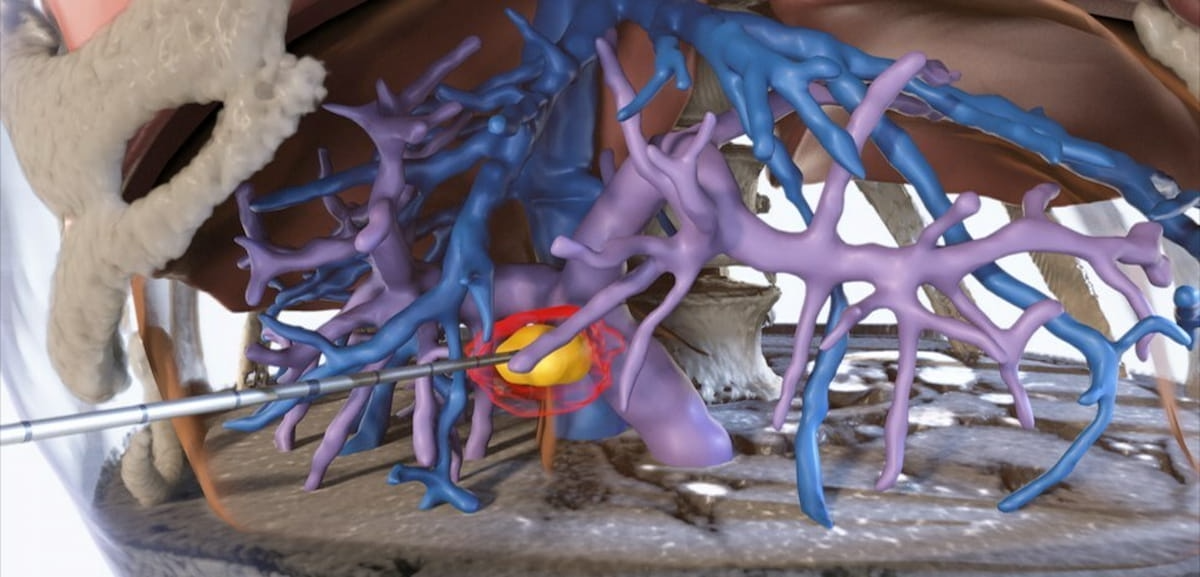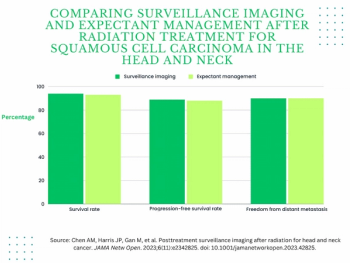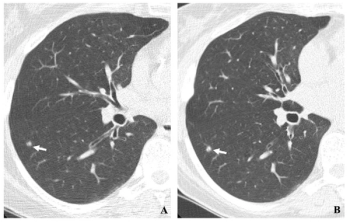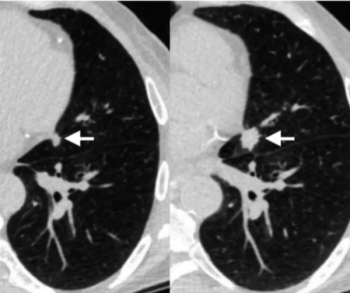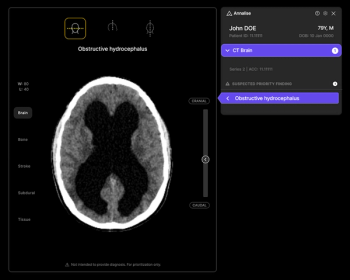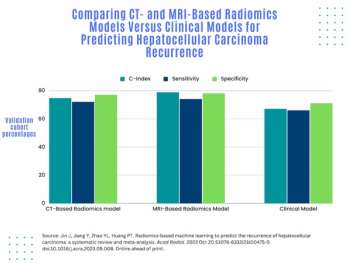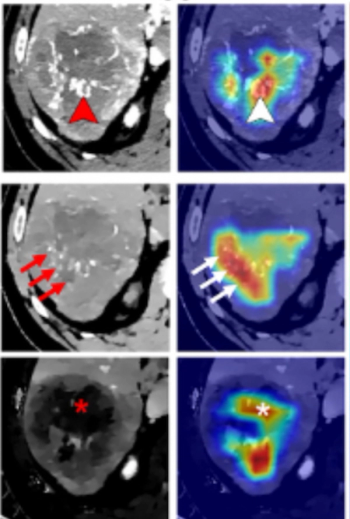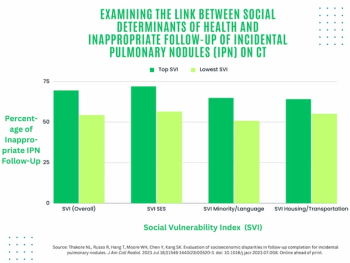
In a study examining the potential of the large language models ChatGPT-4 and Bard to follow ACR Appropriateness Criteria for breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer screening, researchers noted “impressive accuracy in making radiologic clinical decisions.”