USPSTF lung cancer screening recommendation update; Cancer screenings and COVID-19; and CT and unintentional weight loss.

USPSTF lung cancer screening recommendation update; Cancer screenings and COVID-19; and CT and unintentional weight loss.
Revised guidelines support low-dose CT screening for patients between ages 50 and 80 with 20-pack year smoking histories – a move that lowers the screening age and, potentially, incorporates more high-risk individuals.
The impacts of the pandemic have been long-lasting – what has the effect been, and what prompts patients to return.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
CT Colonography & Tumor Differentiation; COVID-19 & Leukoencephalopathy; MRI, the Angiography Suite, and Acute Ischemic Stroke; Plus, DBT, African American Women, & Decreased Access
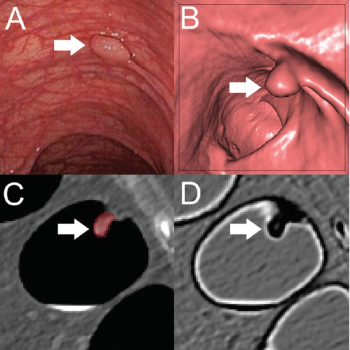
Implementing a radiomics-based machine learning algorithm allows CT colonography to differentiate between benign and pre-cancerous polyps with high sensitivity and specificity.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Mammography "Sweet Spot" Recall Rate; MRI for Early-Stage Testicular Cancer Follow-Up; COVID-19 and Body Self-Attack; Plus, Global Radiology
Using MRI – rather than CT – for post-surgical monitoring can effectively detect cancer relapse without exposing men to unnecessary radiation.
COVID-19 Vaccine-Related Adenopathies on Breast MRI; Baseline Mammography at 40; Cherenkov Imaging to Improve Radiation Therapy Improvement; and Sexual Harassment and Gender Discrimination in Radiology
Not all radiologists adhere to practice guidelines that direct providers how to respond to the presence of pulmonary nodules.

Cherenkov imaging uses special BeamSite cameras to capture radiation beam interaction with tissue, making radiation oncology treatments a visual process.
Female breast cancer diagnosis is now the most common cancer diagnosis globally, largely affecting women in transitioning countries.
Low-Dose CT Screening for Never Smokers; PET Imaging and Hormone Therapy; Opportunities, Responsibilities, and Challenges for Women in Radiology; and Advances in Thyroid Cancer Imaging
Hormone therapy is only effective in roughly half of estrogen receptor-positive cancers. Being able to identify patients that will not respond could save valuable treatment time.
Research data reveals using LDCT with patients who have never smoked – but who are still at high risk – is effective for lung cancer screening.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Perivascular Spaces & Dementia; COVID-19 Loss of Smell and Taste; NAFLD & Multi-parametric CT; Plus, Point-of-Care Ultrasound in the Pandemic Era
Whole-body MRI was able to detect more lesions and identify more patients for earlier treatment.
COVID-19 Vaccine Adenopathies Mimic Breast Malignancies; Appendicitis, CT Exposure and Increased Cancer Risk; and MRI AI Tool for Prostate Cancer Recurrence Prediction
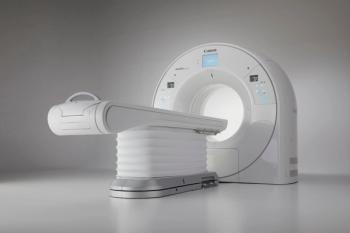
Aquilion system offers industry’s largest bore and widest field-of-view, potentially augmenting radiation therapy planning.
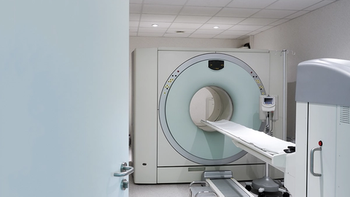
The number of CT scans corresponds to an increase in risk of hematologic malignant neoplasms, especially in children under age 16.

An early analysis shows that low-dose CT screening for lung cancer has still not fully rebounded, leading to later detection of cancers.

Low-dose CT screening for lung cancer does present risks of false-positives and over-diagnosis, but for heavy or ex-smokers, it is worth it.
DECT and electron density offers more accurate differentiation between metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes when compared to FDG PET/CT.