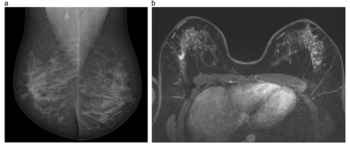
One of the recommendations from the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) is annual breast MRI exams starting at 25 years of age for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer.
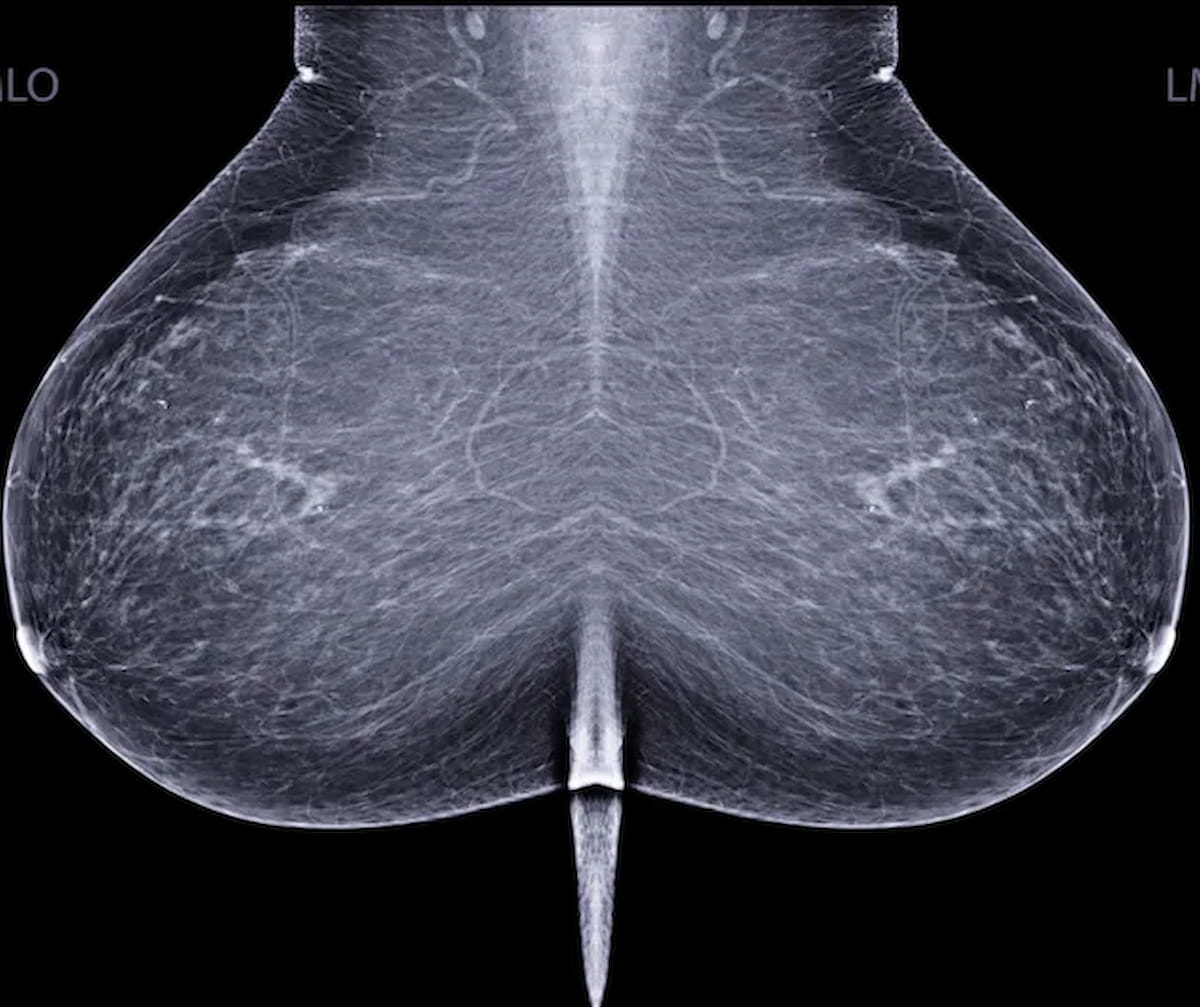
In finalized updates to breast cancer screening recommendations, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) advocates biennial mammography screening for women 40 to 74 years of age and notes insufficient evidence for the use of supplemental MRI in women with dense breasts.

One of the recommendations from the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) is annual breast MRI exams starting at 25 years of age for women deemed to be at high risk for breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
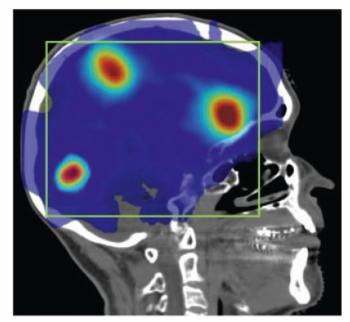
Examining current trends in brain cancer diagnostics, these authors discuss diagnostic imaging advances, pathways with adaptive radiotherapy and the ongoing quest to provide optimal precision with dosimetry.
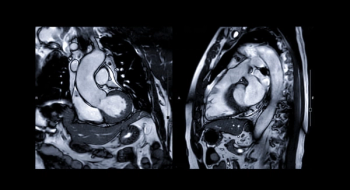
While noting inconsistencies with the diagnostic yield of cardiac MRI in patients who survived sudden cardiac arrest, researchers cited unique advantages in characterizing ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) and facilitating alternate diagnoses.
The use of continuous ofatumumab in patients within three years of a relapsing multiple sclerosis diagnosis led to substantial reductions in associated lesions on brain MRI scans, according to research recently presented at the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) conference.
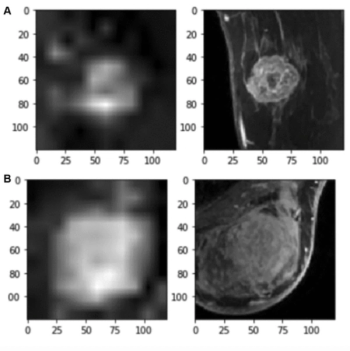
For the prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer, an MRI-based, 4D convolutional neural network model demonstrated an AUC of 87 percent and sensitivity of 89 percent, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Discussing findings from a new study presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference, Shahrzad Tavana, M.D., detailed the significant impact of training sessions for MRI technologists in improving breast positioning, optimal field of view and accuracy of sequence submissions to PACS for breast MRI exams.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
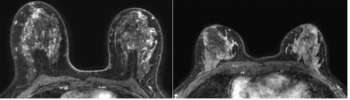
An MRI-based machine learning model demonstrated a comparable background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) hazard ratio to that of manual BPE assessment for breast cancer, according to a study of over 4,500 women with dense breasts.
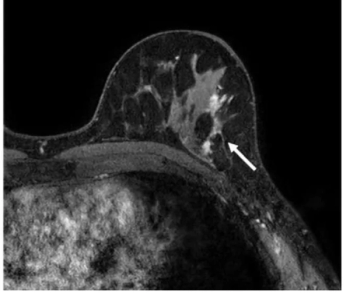
In a new literature review, researchers noted key findings on the use of breast MRI in facilitating breast cancer detection for women with dense breasts and others at high-risk for breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in March 2024.
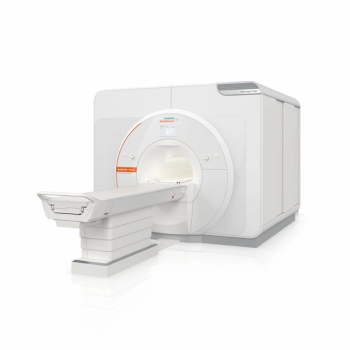
Offering improved image clarity capable of capturing details of subtle pathology, the Magnetom Terra.X 7T MRI system reportedly features the first eight-channel parallel transmit architecture for clinical use.
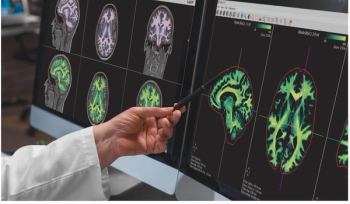
SyMRI 3D reportedly combines precise estimates of regional brain volume with improved resolution bolstering accuracy with lesion analysis.

The multimodality system nCommand Lite reportedly facilitates real-time remote imaging guidance on scanning parameters and procedure assessments to licensed technologists for a variety of imaging modalities including CT and MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
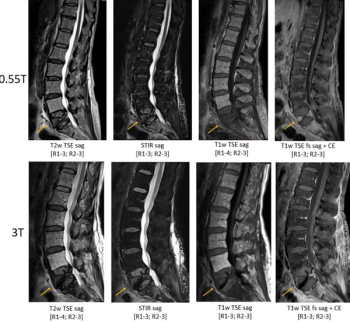
In a study of patients who had lumbar spine MRI exams at 0.55T, 1.5T and 3T, researchers found that 0.55T MRI provided acceptable diagnostic quality across all sequences for varying pathologies including degenerative joint disease, compression fractures and osseous metastatic disease.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Emphasizing optimal balancing of patient safety and image quality, these authors discuss the impact of the specific absorption rate and B1+rms parameters upon radiofrequency exposure with MRI exams.
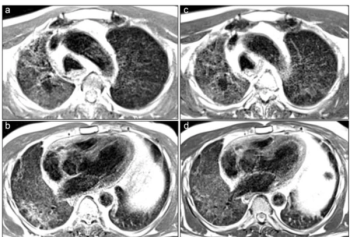
Emerging research with low-field MRI shows that persistently moderate to severe opacities were a common finding in patients up to two years after having acute COVID-19 pneumonia.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a study of nearly 2,500 women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 sequence variations, researchers found that MRI surveillance led to a 3.2 percent breast cancer mortality risk at 20 years in contrast to a 14.9 percent mortality risk for those who did not have MRI surveillance.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in February 2024.
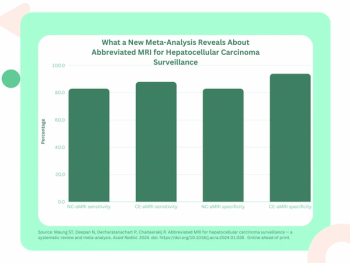
A new meta-analysis noted pooled sensitivity and specificity rates of 83 percent and 91 percent, respectively, for the use of non-contrast abbreviated MRI in surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).