
Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
The injectable authorized generic reportedly facilitates gallbladder imaging as well as X-ray imaging of the intestinal tract.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
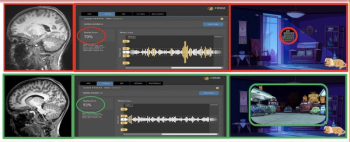
FIRMM-pix, a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) software module recently launched at the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) conference, reportedly employs visual biofeedback and gamification that coaches patients to stay still during brain MRI exams.
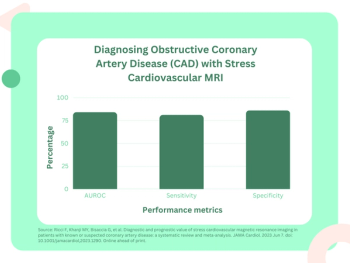
For the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a sensitivity rate of 81 percent and a specificity rate of 86 percent, according to a meta-analysis of 64 studies and data from 74,470 patients with stable chest pain.
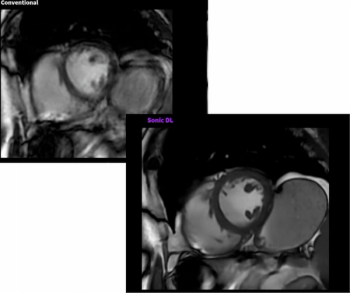
Powered by deep learning technology, Sonic DL reportedly facilitates the acquisition of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans at 12 times the speed of conventional MRI systems.
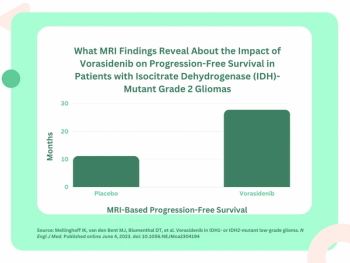
For patients with residual or recurrent grade 2 isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-mutant gliomas, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed that daily dosing of vorasidenib, an inhibitor of mutant IDH1 and IDH2 enzymes, led to a median progression-free survival of 27.7 months in comparison to 11.1 months in a placebo group, according to new research presented at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting in Chicago.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
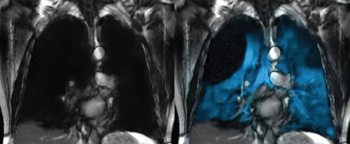
The combination of Philips’ MR 7700 multi-nuclei scanner with the FDA-approved Xenoview hyperpolarized Xenon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent may facilitate earlier diagnosis and intervention for patients with obstructive lung diseases.
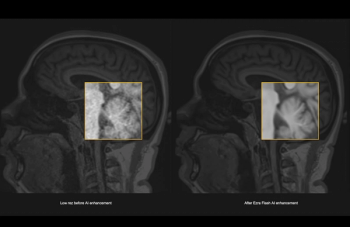
The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Ezra Flash reportedly enhances magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and enables significant reductions in scan times and costs for full-body MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Conditional use of full-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is reportedly permitted for patients using any of the models for the remede® System, an implantable nerve stimulation therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe central sleep apnea.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recently published review, radiology researchers from the University of Wisconsin discussed the potential and key considerations for applying accelerated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols in the assessment of emergent and urgent conditions.
Through artificial intelligence (AI), Neurophet AQUA reportedly provides segmentation and analysis of brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for possible brain atrophy in five minutes.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent video interview, David Ouyang, M.D., shared insights from two recent studies he co-authored on the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to improve initial assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) on echocardiography and ascertain cardiac risks associated with changes in the left ventricle sphericity index seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
While calling for a universal breast cancer risk assessment by the age of 25, the American College of Radiology (ACR) emphasized that ascertaining screening needs prior to the age of 40 is particularly important in high-risk populations such as Black women, who are 42 percent more likely to die from breast cancer in comparison to non-Hispanic White women.

In a review of the literature, this author discusses the viability of artificial intelligence (AI), parallel imaging, compressed sensing and simultaneous multi-slice excitation for improving the scan times and use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to facilitate CyberKnife treatment.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Neuro Suite reportedly enables radiologists to access leading neurological AI algorithm solutions in the field, including the brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) segmentation capabilities of the Combinostics’ algorithm that can help differentiate degenerative pathologies such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
Researchers suggested that overnight use of a power-save mode on outpatient magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices in the United States could reduce annual energy consumption by 76,288.2 megawatt hours (MWh) and add up to $10.7 million in cost savings.

Lamenting a lack of control over imaging requests from referring clinicians, this author suggests that a more collaborative approach between referrers and radiologists may facilitate more efficient use of imaging.