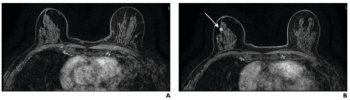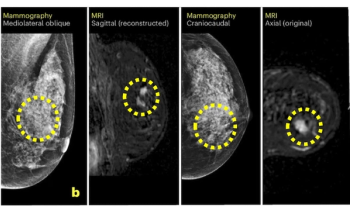
Can AI Facilitate Effective Triage for Supplemental Breast MRI After Negative Mammography Screening?
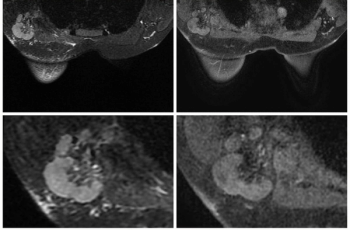
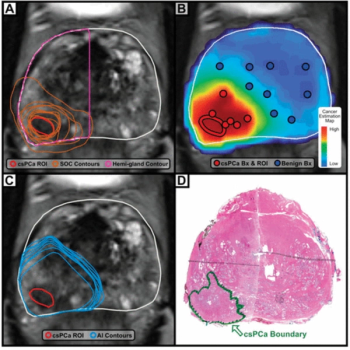
The AISmartDensity software facilitated a cancer detection rate (CDR) with breast MRI that was nearly four times higher than the CDR previously reported in trials involving traditional breast density assessment.