Contrast-Enhanced US Differentiates Between Malignant/Benign Renal Lesions
Largest study in Europe for the evaluation of renal lesions using CEUS with a histopathological validation.
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) helps differentiate between malignant and benignant renal lesions, according to a study published in the journal
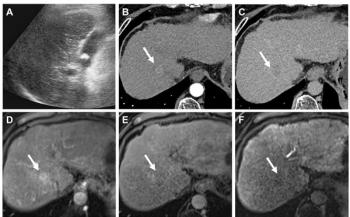
Researchers from Germany sought to investigate the usefulness of CEUS in the evaluation of renal masses. A total of 225 patients with renal masses, ranging in age from 18 to 86 years, were included in the study. CEUS was used for determining malignancy or benignancy and findings were correlated with the histopathological outcome. Out of 255 lesions, 212 lesions (83.1%) were malignant and 43 (16.9%) were benign. Diagnostic accuracy was tested using the histopathological diagnosis as the gold standard.
Related article:
The results showed that CEUS had a sensitivity of 99.1%, a specificity of 80.5%, a positive predictive value of 96.4% and a negative predictive value of 94.3%. Kappa for diagnostic accuracy was κ = 0.85. Of 212 malignant lesions, 200 renal cell carcinomas and 12 other malignant lesions were diagnosed. Out of 43 benign lesions, 10 angiomyolipomas, 3 oncocytomas, 8 renal cysts and 22 other benign lesions were diagnosed.
The researchers concluded that CEUS is an useful method to differentiate between malignant and benignant renal lesions.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.