
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on a variety of new FDA clearances in radiology from the past week.

Flagging DBT images that may warrant a more expedited review, the CogNet AI-MT+ platform can reportedly be integrated into existing IT systems to facilitate workflow efficiencies for radiologists.

In a recent interview from the International Stroke Conference, Jeremy Heit, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research suggesting that AI may offer better assessment than neuroradiologists of aneurysm growth on computed tomography or magnetic resonance angiography scans.

The Ascent3T Neonatal Magnetic Resonance Imaging System is reportedly the first high-field 3T system geared to neonatal applications.

Wendie Berg, M.D., Stamatia Destounis, M.D., and Amy Patel, M.D., share their thoughts and perspectives on key findings from the Lancet mammography study on AI and interval breast cancer, and how they have incorporated AI into their practices.

A high SUVmean on PSMA PET imaging was associated with 95 more days of mean progression-free survival (PFS) in contrast to those with a low median SUVmean, according to a new study of patients with mCRPC treated with (225Ac)Ac-PSMA-I&T.

The CT-based RevealAI-Lung software reportedly offers a Malignancy Similarity Index score to facilitate evaluation of incidental lung nodules.

In addition to significantly reduced radiation dosing in comparison to energy-integrating detector CT (EID-CT), photon-counting CT provided higher detection of enhancement-related malignant features, according to new prospective research involving 200 patients with lung cancer.

The Brainomix 360 Stroke Next Generation software reportedly includes automated assessment of net water uptake (NWU), a CT-based biomarker that may improve risk stratification for patients with severe strokes.

In a recent interview, Amy Patel, M.D., discussed key targets in legislation for breast imaging in 2026 and offered advice for breast radiologists seeking to get more involved in advocacy.
The Allia Moveo C-arm platform reportedly offers ergonomic maneuverability, enhanced artifact reduction and flexibility with the use of cone-beam CT.

Are non-physicians playing around with your radiology reporting macros?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a comparative study involving over 105,000 women, researchers found the use of adjunctive AI for mammography triage resulted in a 16 percent lower rate of invasive interval cancers in comparison to double reading by radiologists without AI.

The Biograph One PET/MRI system may facilitate accelerated scan times, improved visualization and more efficient assessments of theranostic approaches for patients with oncologic and neurological diseases.

In a new podcast episode, Kernesha Weatherly, DHA, emphasized the importance of communication with radiologists, ordering providers and patients to identify challenges with follow-up of incidental imaging findings, and how AI helped bolster data and “line of sight” in these cases at Ochsner Health.

Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in January 2026.

Employing AI-powered automation, the MIM LesionID™ Pro reportedly bolsters the efficiency of whole-body tumor burden analysis with PSMA PET/CT and SPECT/CT.
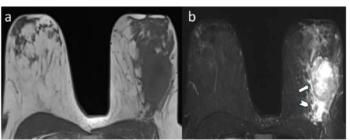
For young women with breast cancer, peritumoral edema on pre-op breast MRI was associated with over a 3.6-fold higher likelihood for reduced disease-free survival, according to new research.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in January 2026.
Employing latent profile analysis (LPA) to help assess body fat distribution patterns, researchers found that a pancreatic-predominant profile with elevated proton density fat fraction derived from MRI was associated with extensive gray matter atrophy and cognitive decline.
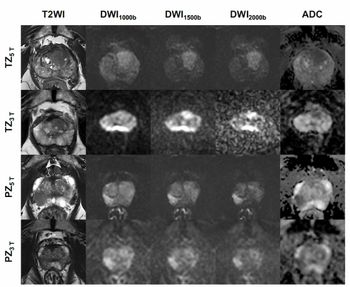
The use of 5T prostate MRI offered significantly higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) than 3T prostate MRI as well as enhanced delineation with T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging, according to newly published comparative research.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Whether it’s a home gym, a healthy diet or a prudent approach to savings and eventual retirement, there are key ‘assets’ that can help sustain a strong quality of life.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on a variety of new FDA clearances in radiology from the past week.

Sharing his insights as well as findings from recent research, Mina Makary, M.D., discussed pertinent challenges with diversity and resident attrition rates in interventional radiology and possible approaches to address these issues.
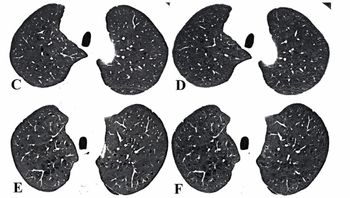
A prospective research comparison of ultra-low-dose (ULD) PCCT and low-dose (LD) PCCT protocols yielded comparable image quality and strong agreement on emphysema severity assessments with ULD PCCT offering significantly reduced radiation dosing.

Employing low pressure ultrasound treatment to break up kidney stones, the Break Wave lithotripsy device offers a non-invasive, anesthesia-free alternative