Report from SNM: PET/CT produces Image of the Year
The ability to simultaneously display 3D anatomic and molecular information to evaluate lung cancer earned Dr. Andrew Quon recognition for the Society of Nuclear Medicine’s Image of the Year.
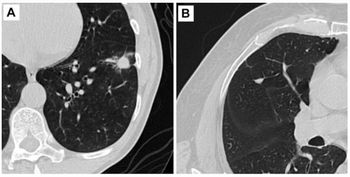
The ability to simultaneously display 3D anatomic and molecular information to evaluate lung cancer earned Dr. Andrew Quon recognition for the Society of Nuclear Medicine's Image of the Year. Dr. Henry Wagner singled out an example of 3D FDG-PET/CT bronchoscopy produced by Quon, an assistant professor of radiology at the Institute for Molecular Imaging at Stanford University. The image employs metabolic FDG-PET to identify the position of a primary cancer lesion in a lung and an avid mediastinal lymph node partially obscured by the bronchus. Three-D-rendered multislice CT contributes a stunning view of surrounding anatomy. It allows the physician to rule out endobronchial involvement. Wagner, a professor of environmental health sciences at Johns Hopkins University, announced the selection Monday at the SNM meeting in Toronto.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.














