
Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Based on a review of 3,495 echocardiographic studies to evaluate left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), researchers found that cardiologists changed initial artificial intelligence (AI) assessment 16.8 percent of the time and initial sonographer assessment 27.2 percent of the time.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
In a recent video interview, Kathy Schilling, M.D., discussed findings from a study of ProFound AI, an adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) software for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), that demonstrated a 23 percent increase in breast cancer detection in comparison to DBT alone.

In recent video interviews, Tessa Cook, MD, PhD, Nina Kottler, MD, MS, and Sonia Gupta, MD shared their insights and perspective on potential benefits and drawbacks of ChatGPT in radiology.
Viz AAA is reportedly the first artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled algorithm to garner FDA 510(k) clearance for the detection of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
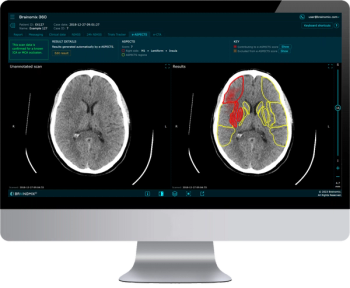
Through artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scans, the Brainomix 360 e-ASPECTS software provides an automated ASPECTS score and heatmap to enhance stroke imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a review of 555 neuroimaging-based artificial intelligence (AI) models for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders, researchers found that nearly 72 percent of the AI models had an inadequate sample size and over 99 percent were insufficient at handling data complexity.
The artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software, which has a documented 91 percent sensitivity rate for detecting pediatric fractures, is reportedly the first AI fracture detection modality to receive FDA 510(k) clearance for use in the pediatric population.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
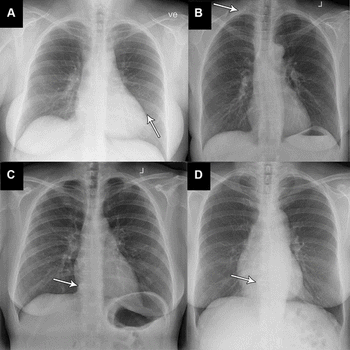
In a study of over 1,500 patients, researchers found that an emerging artificial intelligence (AI) modality had significantly higher sensitivity rates for abnormal posteroanterior chest radiographs and critical finding radiographs than radiology reports.
Comparing year-long findings with and without adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) at a breast cancer screening program in Spain, researchers found the combination of digital breast tomosynthesis and AI had a 92.5 percent accuracy for diagnosing cancer in patients with elevated risk.
The new launches include the 80/160-slice computed tomography (CT) scanner Aquilion Serve, which allows simultaneous previews of axial, lateral and AP views, and Celex, a multipurpose X-ray system that offers automated and customizable features to help maximize workflow efficiencies.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
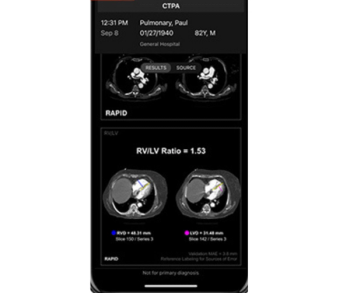
Facilitating expedited assessment of pulmonary embolism severity, the emerging artificial intelligence (AI) tool Rapid RV/LV reportedly calculates the right ventricle/left ventricle (RV/LV) ratio within minutes of a computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The upgraded, artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software for the Swoop® Portable MR Imaging System reportedly enhances the device’s signal-to-noise ratio for diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences.

In a recent video interview, Sonia Gupta, MD discussed a number of ongoing developments with artificial intelligence (AI) in radiology, ranging from market consolidation of AI vendors to maximizing automation and efficiency with patient triage, reporting and follow-up of incidental findings.

The HERA W10 Elite ultrasound platform provides enhanced visualization features and artificial intelligence (AI)-aided measurement capabilities.
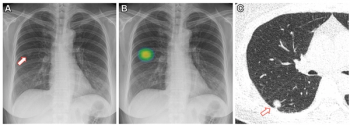
In newly published research, researchers found that an artificial intelligence (AI) computer-aided detection (CAD) system was more than twice as likely as non-AI assessment to diagnose actionable lung nodules on chest X-rays.
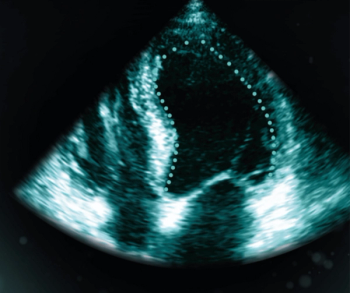
Employing an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered scoring system, LVivo IQS reportedly provides real-time assessment of the quality of cardiac ultrasound images.
From enhanced image quality and workflow efficiencies to an improved patient experience and potential synergies wih enterprise cloud services, artificial intelligence continues to redefine possibilities in radiology.
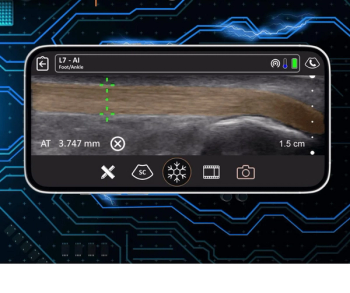
In what is reportedly the first Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance for the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for musculoskeletal ultrasound, the model provides automated measurements of tendons in the knee, ankle, and foot.
In an external validation data set for a deep learning bone-suppressed (DLBS) model, researchers found that adjunctive use of the DLBS model led to a nearly 15 percent increase in sensitivity for detecting pulmonary nodules on chest X-rays in comparison to radiologist assessment.
Researchers showed that adjunctive use of a deep learning algorithm resulted in an eight percent increase in sensitivity and a nearly 10 percent increase in specificity for differentiating between colon carcinoma and acute diverticulitis on computed tomography (CT) scans.