
One-quarter of lung cancers found through CT screening are slow-growing or indolent, many of which may have been overdiagnosed, researchers say.

One-quarter of lung cancers found through CT screening are slow-growing or indolent, many of which may have been overdiagnosed, researchers say.

Increased use of MRI to evaluate newly diagnosed breast cancers has not resulted in an increase in contralateral prophylactic mastectomy.

Mammography screening overdiagnoses women who may never have had clinical symptoms, finds a study the ACR said is incorrect and misleading.

U.S. physicians ordered fewer non-emergency CTs in 2010 than in the previous nine years. Emergency CT use continues to grow.

Three-dimensional imaging with breast tomosynthesis increases diagnostic accuracy and reduces false positive recall rates.

Stereoscopic digital mammography, a new 3D technique, significantly improves the accuracy of breast cancer detection in high-risk women.

Unnecessary radiation exposure and burns during diagnostic radiology procedures ranked third on the ECRI Institute’s list of medical/technology hazards.

Physicians may be able to identify children at risk for epilepsy if they undergo EEG and MRI within days of having a febrile seizure.

Too many physicians are self-referring patients for advanced imaging services, resulting in increased costs, according to the GAO.

Researchers used PET to visualize binding sites of caffeine in the living human brain, making it possible to explore effects of caffeine consumption.

Women who undergo routine breast cancer screening have a lower risk of dying from breast cancer, according to an independent British panel.

A study in Japan found that low-dose chest CT screening may result in lower lung cancer mortality years after the screening introduction.

Minimally invasive musculoskeletal ultrasound provides a fast, accurate diagnosis of rheumatic diseases, among other benefits, researchers said.

Breast ultrasound is superior to mammography for initial evaluation in symptomatic women aged 30 to 39 and should be the primary imaging modality.

Use of coronary CT angiography can effectively reduce the number of invasive procedures, which supports CCTA’s role as a gatekeeper to coronary angiography.
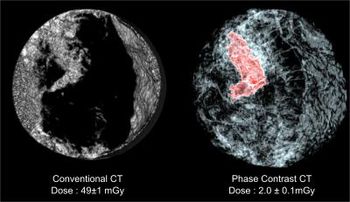
A new method using 3D CT in breast imaging provides a resolution two to three times higher with a radiation dose about 25 times lower.

Elevated beta amyloid in the brain, detected with PET imaging with PiB, may be better than genetic factors in predicting memory loss in healthy seniors.

Canadian C-spine rule is more accurate in screening for cervical spine injury compared with NEXUS, but more education is needed to curb imaging.
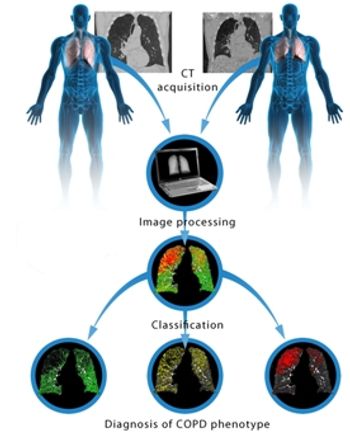
A new lung CT analysis technique, parametric response mapping, can help distinguish between early-stage damage and more serious damage to the airway.

Time-resolved multi-frame MRI provides better detects significant differences in coronary artery wall thickness, allowing docs to ID early-stage coronary disease.

Diffusion-weighted imaging performed with MRI for breast cancer screening may reduce the number of preventable breast biopsies.

Imaging study interpretations by subspecialty radiologists provide important clinical information about pediatric patients.

Dedicated breast MRI systems offer significant improvement in performance and diagnostic accuracy.

PET with F-18- fluorothymidine on patients with head and neck cancer prior to and during radiation therapy allows physicians assess early outcomes.

Magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate can help identify men who have low-risk prostate cancer and would likely benefit from active surveillance.

Adding digital breast tomosynthesis to digital mammography significantly increases the accuracy of the mammography, compared with full-field digital mammo.

Using computer-aided detection software to help find target areas in images may result in readers missing areas not marked for viewing.

Breast cancer mortality can drop significantly among women who undergo screening.

SPECT/CT scan can help detect positive sentinel lymph nodes and lead to higher rate of disease-free survival among patients with melanoma.

Women with mutations to the BRCA1/2 genes who undergo diagnostic chest radiation before age 30 are at a higher risk of developing breast cancer.