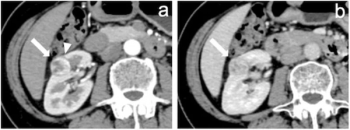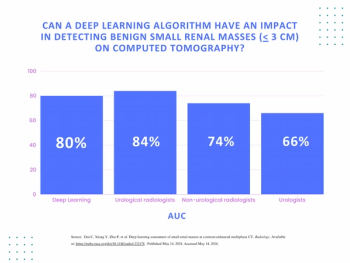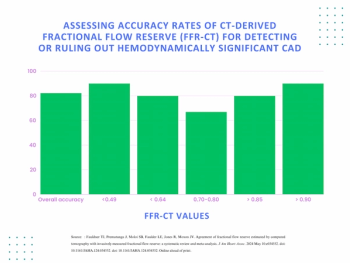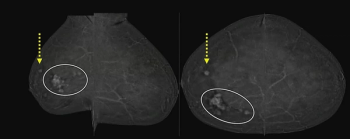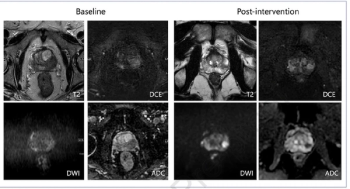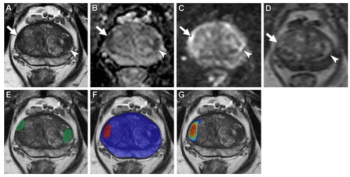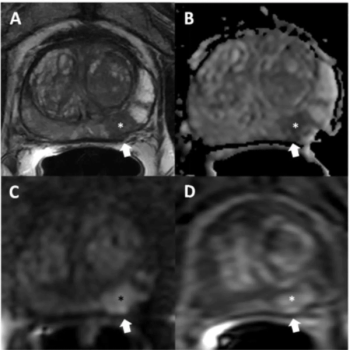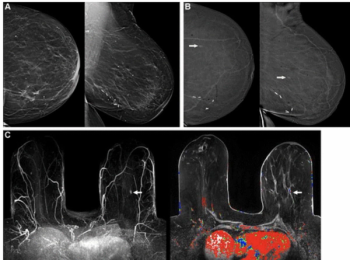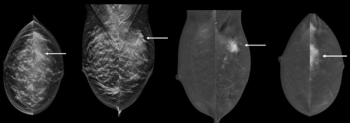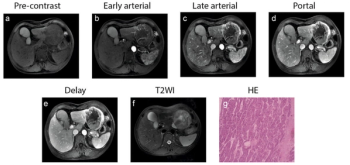
Incorporating dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, a deep learning model demonstrated a 20 percent higher AUC in external validation testing than clinical factors alone and over a 17 percent higher AUC than radiological factors alone in predicting proliferative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).