The indications for Gadobutrol injection, a generic substitute for Gadavist, include neurovascular and cardiovascular assessments as well as breast malignancy detection with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

The indications for Gadobutrol injection, a generic substitute for Gadavist, include neurovascular and cardiovascular assessments as well as breast malignancy detection with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
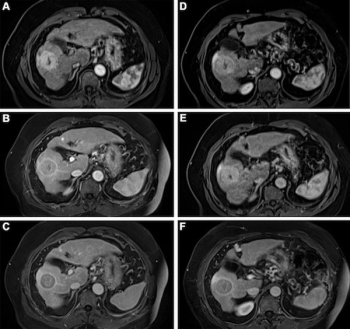
Newly published research suggests the use of gadopiclenol at 0.05 mmol/kg is non-inferior to gadobutrol 0.1 mmol/kg for all qualitative visualization parameters on full-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Superfluous pan scans have become standard for a vast majority of minor injury presentations in emergency room settings.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
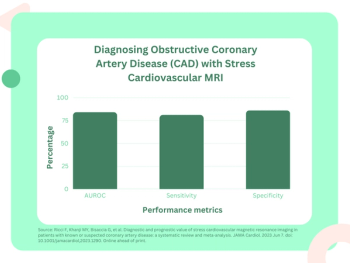
For the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a sensitivity rate of 81 percent and a specificity rate of 86 percent, according to a meta-analysis of 64 studies and data from 74,470 patients with stable chest pain.
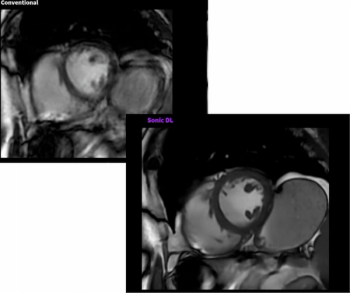
Powered by deep learning technology, Sonic DL reportedly facilitates the acquisition of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans at 12 times the speed of conventional MRI systems.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
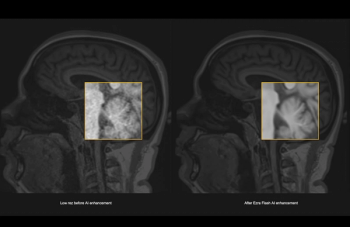
The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Ezra Flash reportedly enhances magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and enables significant reductions in scan times and costs for full-body MRI.

Conditional use of full-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is reportedly permitted for patients using any of the models for the remede® System, an implantable nerve stimulation therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe central sleep apnea.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent video interview, David Ouyang, M.D., shared insights from two recent studies he co-authored on the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to improve initial assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) on echocardiography and ascertain cardiac risks associated with changes in the left ventricle sphericity index seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Researchers suggested that overnight use of a power-save mode on outpatient magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices in the United States could reduce annual energy consumption by 76,288.2 megawatt hours (MWh) and add up to $10.7 million in cost savings.

Lamenting a lack of control over imaging requests from referring clinicians, this author suggests that a more collaborative approach between referrers and radiologists may facilitate more efficient use of imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Offering built-in safety features and independent verification of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) compatibility with cardiac devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillator systems, the MRI Care Pathway app may enhance the efficiency of radiology workflows for MRI scans in patients with these devices.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
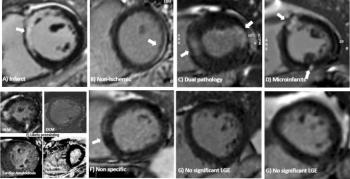
Consensus recommendations from the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance provide pertinent insights on the unique abilities of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide optimal characterization of myocardial tissue and diagnosis of COVID-19-related myocardial injuries.
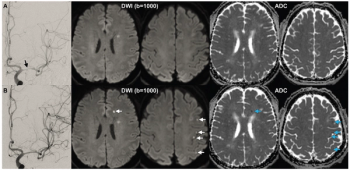
In the study of 119 patients who had endovascular treatment for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, multivariable analysis revealed that post-op ischemic brain lesions on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were 3.6 times more likely to occur in patients who smoke cigarettes and 2.9 times more likely in patients who had multiple operative attempts.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
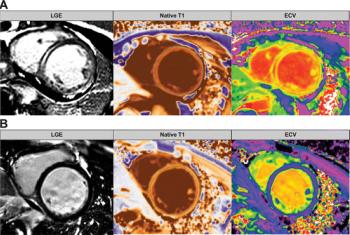
Emerging research suggests that cardiac MRI findings of late gadolinium enhancement, native T1 values and extracellular volume fraction may predict sudden cardiac death-related events in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy.
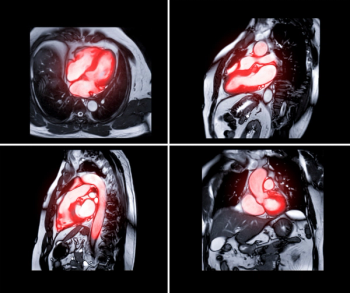
In a prospective study of over 600 patients, researchers found that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had no serious adverse effects upon the detection of tachyarrhythmias with non-MRI conditional implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs).