
Coronary CT angiography is a useful tool in detecting prevalence and type of coronary artery fistulas.

Coronary CT angiography is a useful tool in detecting prevalence and type of coronary artery fistulas.

CCTA may be effective in screening CAD in adult survivors of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.

Cardiac imaging with PET and MRI shows excellent diagnostic accuracy compared with SPECT-MPI.

High resolution coronary CT angiography provides better results among patients at high risk for CAD than does standard resolution coronary angiography.

Incidental findings from diagnostic chest CT may help physicians identify patients at risk for cardiovascular disease.

The now FDA-approved angiography system by Siemens Healthcare has been optimized for extensive clinical utilization.
The latest dual source CT includes features that provide low dose imaging for patients with renal insufficiency, difficulty holding their breath and more.
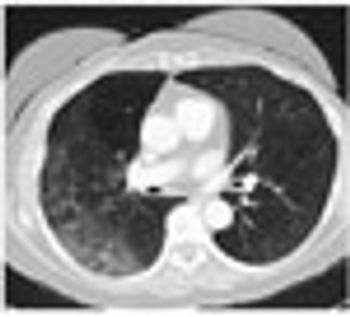
Patients undergoing low dose CT chest screening for lung cancer may also be assessed by automated coronary artery calcification scoring.

Pulmonary CT angiograms that detect coronary artery calcification can help predict acute coronary syndrome in some patients

As clinicians order more noninvasive cardiac imaging for patients with suspected ischemia, hospital admission rates and angiography rise.

Imaging with CT and coronary CT angiography shows prevalent and extensive presence of coronary artery plaque among men infected with HIV.

Use of nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging exams dropped sharply between 2006 and 2011, but substitute imaging studies haven’t increased.

Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging may help clinicians predict future cardiac events among patients with coronary artery disease or recent MI.

CT angiography and SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging improves with the use of synchronized multimodal heart visualization software.

Using CT to measure coronary artery calcium may aid physicians in predicting the chances of incident cardiovascular events.

Cardiologists should review cardiac imaging use for their patients in an effort to reduce patient radiation exposure.

PET-CT with the radioactive tracer 18F-NaF PET-CT helps clinicians detect ruptured and high-risk coronary plaques.

A new technique, quantitative T1 mapping with cardiovascular MRI, can help clinicians detect Fabry disease and the severity of heart damage.

Low-dose ionizing radiation from cardiac imaging after heart attack poses a greater cancer risk for women than men.

Transthoracic echocardiography results do not frequently change active treatment among patients.

CT scans of mummies show that plaque build-up and clogged arteries occurred among people 4,000 years ago, as well as today.

Most men with small abdominal aortic aneurysms, 3.0 cm to 5.4 cm, could be safely monitored with ultrasound at longer intervals.

Imaging the loss of nerve function in the heart may better identify patients who would benefit from receiving implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICD) than current testing methods.

PET imaging agent CardioGen-82 is returning to the U.S. market with a revised label warning of unintended radiation exposure risk.

The problems lead to unexpectedly high patient radiation exposure and voluntary recall of the PET imaging agent.