Images can pinpoint which women are at risk for ischemia and nipple necrosis.

Images can pinpoint which women are at risk for ischemia and nipple necrosis.
Fetal cardiac MRI and congenital heart defects; Survival tips for early radiology practice; Plus, Risk-based prioritization models for mammography during crises.
In more than 80 percent of referred cases, information gathered from fetal CMR can change clinical decision-making, and it can impact parental counseling, as well.
Supramolecular Amorphous-like Iron Oxide could provide less toxic, more biocompatible high-resolution imaging.
Dangers of missing one screening mammogram; Rise of cardiac CT and MRI; Strategies to improve financial stability; Plus, Talking to patient about COVID-19 vaccine-related adenopathies.
More radiologists are providing CT and MRI services, but these studies still fall behind echocardiography and nuclear medicine.

For better cardiology services, providers must look beyond the existing cardiology PACS.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
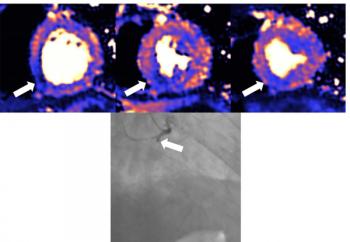
MRI scans reveal myocarditis, scarring, infarction, and ischemia in recovered patients with elevated troponin levels.
Using radiomics to assess impact of unconventional risk factors, including cocaine use and HIV infection, potentially introduces a “brave new world” of precision phenotyping in CAD.
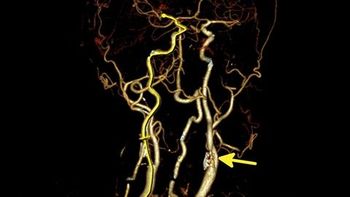
Using imaging to screen asymptomatic individuals can cause more potential harm than good, Task Force reiterates.
COVID-19 and Long-Term Lung Effects; Reduce Emergency Department Imaging Recalls; COVID-19, Myocarditis, and Athletes; Plus, New Recommendation for X-ray Gonad Shielding
New study, comparing recovered athletes to healthy controls, reveals a lower level of myocarditis that previously published research, but cardiac MRI is still important for safe return-to-play decisions.
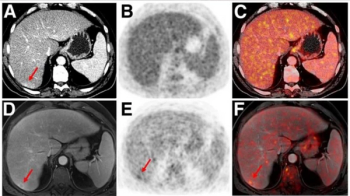
MRI reveals its wide utility this year, demonstrating improved performance in disease detection, as well as outperforming other modalities in providing clearer, more detailed images.
Study reveals favorable acute safety profile for macrocyclic gadolinium.
Study shows MRI exams can be safely performed with no adverse events in patients who have non-MR conditional devices, making the exams available for patients who frequently needs these studies the most.
A new technology overcomes the challenges to cardiac imaging presented by spontaneous fetal movement.
Rethinking CMR during COVID-19; Abdominal Imaging and COVID-19; Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19; African American and Lung Cancer Screening; Plus, African American Women and Disadvantages in Breast Cancer Screening
A group of cardiologists, imaging specialists, and general medicine providers offer a warning about using CMR with asymptomatic patients and entreat professional societies from radiology and other specialties to craft guidance on proper usage.

Scans identify evidence of the condition in 15 percent of athletes who have rebounded from viral infection.
Portable, Low-field MRI; COVID-19 and Cardiac MRI; High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound; Coronary CTA Guidance; and Pediatric Advanced Imaging Utilization
CT and heart attack prediction; lagging outpatient imaging volume recovery; equivalent thoracic MRI performance with COVID-19 pneumonia; and CT colonography during COVID-19
Abbreviated MRI; Low-Field Cardiac MRI; Contrast-Enhanced Breast Imaging; Obesity and Alzheimer's; and Neuroimaging and COVID-19
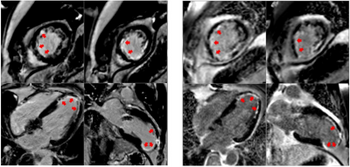
Performance of 0.55T MRI is comparable to 1.5T MRI in acquiring and interpreting late gadolinium enhancement in patients suspected of myocardial infarction, research shows.
Scans show cardiovascular impact lingers after the acute phase of viral infection and into recovery.