
Joseph Cavallo, MD, MBA, and Dushyant Sahani, MD, discuss generic agents iodixanol injection and gadoterate meglumine injection for the use in imaging modalities.

Joseph Cavallo, MD, MBA, and Dushyant Sahani, MD, discuss generic agents iodixanol injection and gadoterate meglumine injection for the use in imaging modalities.

Catch up on the top five most viewed content at Diagnostic Imaging in August 2023.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
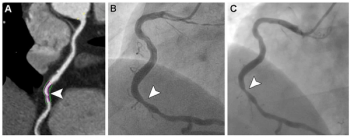
A high lipid core burden in non-revascularized plaque is associated with nearly a 13-fold higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) such as cardiac death and myocardial infarction (MI), according to new research based on coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) findings.
Experts discuss the concept of generics and how they have traditionally been utilized in the healthcare space.
Joseph Cavallo, MD, MBA, and Dushyant Sahani, MD, provide an overview of the different imaging technique protocols needed for contrast agents.
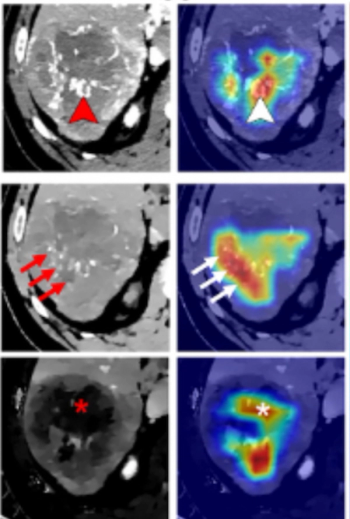
In comparison to clinical-radiologic assessment, a deep learning CT radiomics nomogram had a 10 percent higher AUC and a 27 percent higher specificity for predicting the macrotrabecular massive subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma in external data testing.
When facilities routinely forward X-rays for “pain,” vascular ultrasound studies without Doppler or chest computed tomography (CT) scans devoid of breath holding, patient care suffers.
Radiology experts discuss the role of contrast agents in imaging and the impact these agents have on image quality.

Joseph Cavallo, MD, MBA, and Dushyant Sahani, MD, provide a brief overview of imaging modalities and their importance in medical diagnosis and treatment.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Does access to prior imaging results have to be mission impossible for teleradiologists?

The controversial Independent Dispute Resolution (IDR) process of the No Surprises Act was temporarily suspended by the CMS on August 4 due to a federal court ruling that vacated a substantial administrative fee increase and batching rule from the CMS that reportedly curtailed challenges of claim reimbursement by radiologists and other providers.
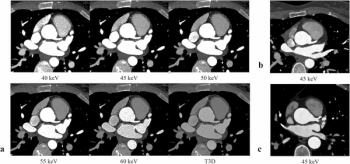
Emerging research suggests that achieving an optimal virtual monoenergetic image (VMI) energy level with photon-counting computed tomography (CT) may allow up to a 40 percent reduction of contrast media dosing for coronary CT angiography.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
Catch up on the most viewed content at Diagnostic imaging in July 2023.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
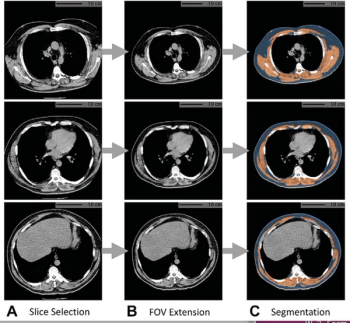
In a study of over 20,700 people, researchers found that artificial intelligence (AI) analysis of body composition measurements via lung cancer screening computed tomography (CT) exams improves the prediction of mortality risks for lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
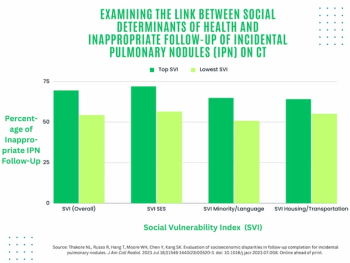
In a study of nearly 2,500 patients with incidental pulmonary nodules (IPN) on chest computed tomography (CT) exams, 69.5 percent of those in the highest quartile of the CDC’s Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) had inappropriate IPN follow-up in comparison to 54.3 percent of those in the lowest quartile of the CDC SVI.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
The notion of non-physician practitioners (NPPs) attempting to do radiologist-level work is a very slippery slope and what this author refers to as the “bargaining” stage of grief.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.