
Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
Superfluous pan scans have become standard for a vast majority of minor injury presentations in emergency room settings.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
While it stands to reason that referring physicians would prefer a condensed summary of relevant imaging findings, vagaries with insurers, patients and other possible readers of the radiology report may warrant an inefficient minutiae-cluttered approach.
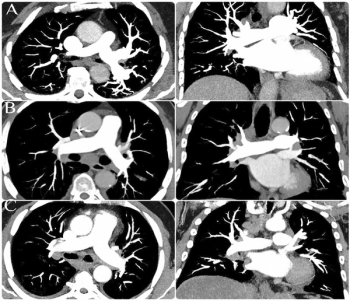
New research suggests the use of high-pitch photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) facilitates similar image quality and attenuation in the pulmonary trunk at lower iodinated contrast media (ICM) dosing levels ranging from 35 to 60 ml.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
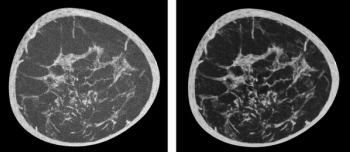
The artificial intelligence (AI) software facilitates high-resolution three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) images of the breast.
There are cases that warrant verbal communication with referring clinicians, but making that communication happen can, at times, be a challenging responsibility.
The InterView Fusion and InterView XP reportedly improve image quality for single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and offer imaging tools specifically geared to common nuclear medicine studies ranging from bone imaging to cardiac assessment and lung imaging.
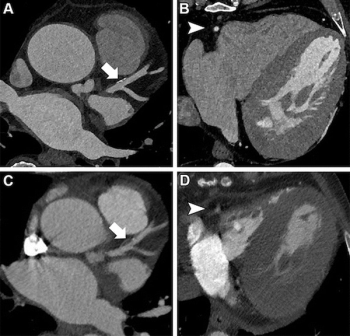
In a study cohort of patients undergoing pre-operative workup for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), researchers found the use of photon-counting CT for ultra-high resolution coronary CT angiography had a 96 percent sensitivity rate and an 84 percent specificity rate for the detection of coronary artery disease (CAD).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recent video interview from the Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine (SIIM) conference, Ali Tejani, M.D., discussed pertinent insights on leveraging the value of adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled triage software for computed tomography (CT) scans with radiology workflow improvements to achieve “clinically meaningful change” for patients with incidental pulmonary emboli findings.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
When reviewing radiographs, computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, do you still turn to mnemonics every now and then to jog your short-term memory?
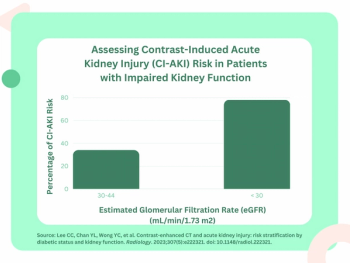
The use of contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) was associated with more than double the risk of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) in patients with diabetes and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 in comparison to the use of non-contrast CT in this population.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
Whether it’s attempting to get appropriate clinical histories from referring physicians or getting a tech to split up a multiphasic contrast study into separate image series, consistently striving to fight the good fight for optimal image interpretation is worth the effort.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
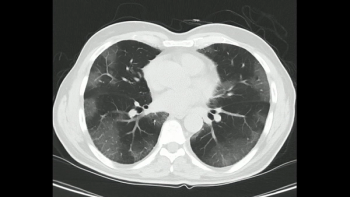
In a review of patient data from 42 countries, researchers found that standardized typical findings on computed tomography (CT) for COVID-19 had a pooled sensitivity rate of 70 percent and a pooled specificity rate of 90 percent.
Catch up on the top five most viewed content at Diagnostic Imaging for the month of May 2023.
Precision DL, a deep learning-based software which will be available on GE HealthCare’s Omni Legend PET/CT device, reportedly increases the detectability of small, low-contrast lesions by 42 percent.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
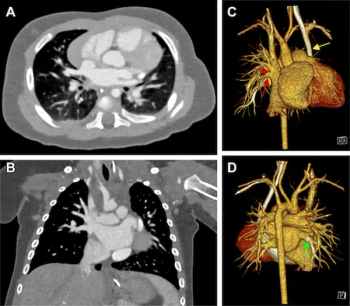
Photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) significantly increased the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) in comparison to dual-source CT (DSCT) at similar radiation dosing, according to a new study of over 100 children with suspected congenital heart defects.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.