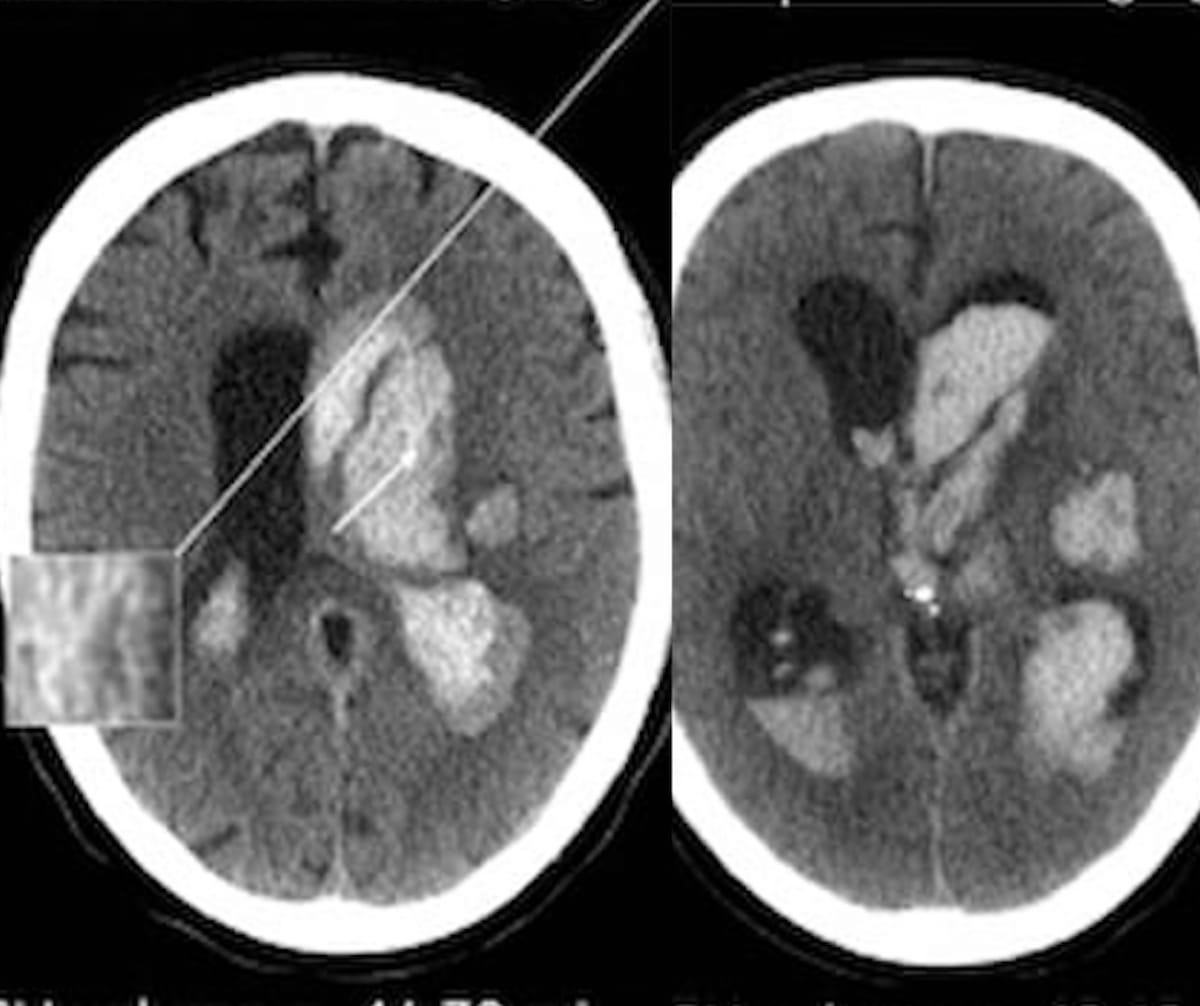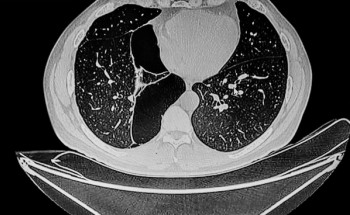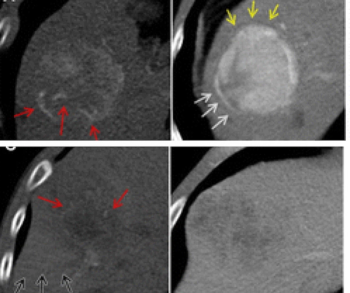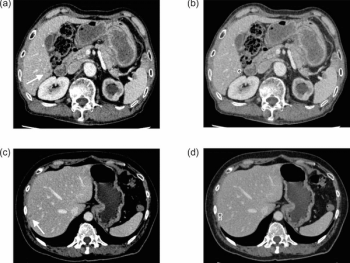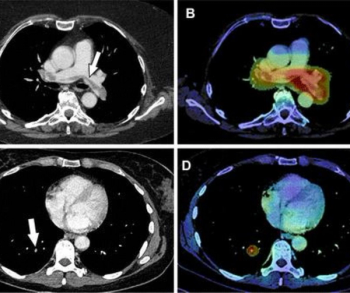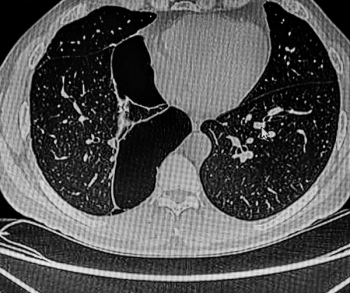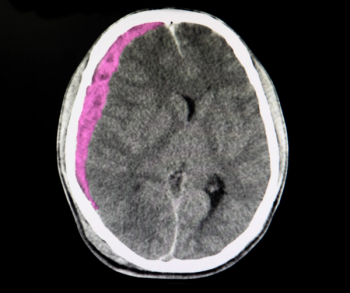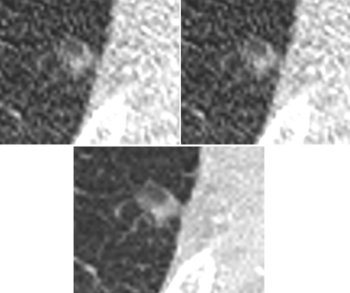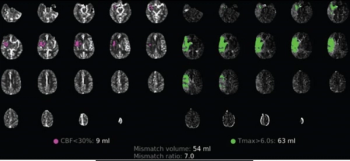
Unvaccinated people with COVID-19 who undergo angiographic reperfusion after acute ischemic stroke may have a greater than fivefold risk of continued infarct growth in comparison to unvaccinated people without COVID-19, according to computed tomography perfusion (CTP) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings from a recently published study.