Study finds basing screening recommendations on age does not maximize the benefit – using different factors to design targeted testing would be better.

Study finds basing screening recommendations on age does not maximize the benefit – using different factors to design targeted testing would be better.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.

While the pandemic raged, work continued to advance the development of AI tools with breast imaging services.

The December 2020 Diagnostic Imaging eBook.
Younger and African American patients face significantly increased odds of having their symptoms associated with radiation therapy under-treated by providers.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
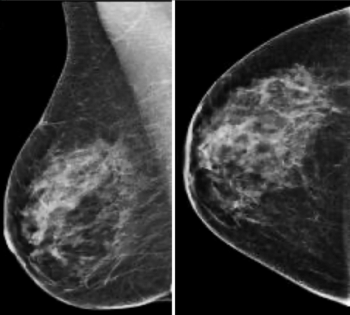
The improved cancer detection rate that catches more cancers with favorable prognoses and the lower false negative rates, improves patient outcomes and puts DBT on track to replace 2D mammography as the gold standard for screening.
Hologic’s Jennifer Meade, division president of breast and skeletal care, discusses the focus for breast imaging in the near future and some latest technologies.

Conducting screening mammography on men with a genetic risk for breast cancer can increase early detection, but clinical guidance and recommendations remain inconsistent.

Implementing artificial intelligence tools with breast imaging can pinpoint overlooked interval cancers and decrease provider workload in screening mammography programs.

A model that uses biomarkers pulled from a woman’s mammogram does produce a more accurate breast cancer risk assessment.

Women who experience food or housing insecurities are more likely to take longer between imaging and follow-up, putting them at greater risk for undiagnosed breast cancer.
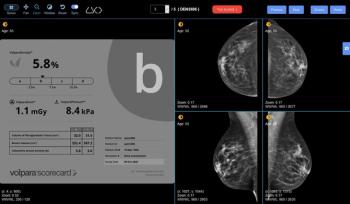
Volpara Health and DetectED-X are collaborating to make a breast density categorization training tool available to radiologists worldwide.
Diagnostic Imaging and Testicular Cancer Risk; Digital Breast Tomosynthesis/Synthetic Mammography Combination for Breast Cancer Screening; Efficacy of Low-Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening; and the Evolving Role of the Radiologic Technologist
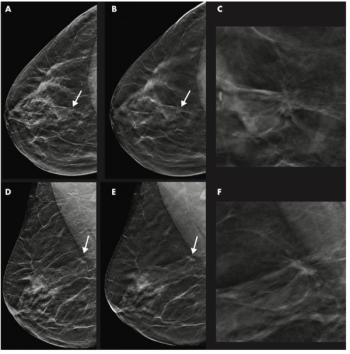
Not only did this combination improve breast cancer detection, but it could also catch more potentially invasive cancers earlier.

Together with integrated cancer care provider GenesisCare, the imaging provider looks to attack the two biggest global health problems.
Cerebral Aneurysms and CT Angiography; MammoScreen and Breast Cancer Detection; Low-Dose Lung Cancer Screening Program Performance; and Breast Cancer Screening Advocacy Efforts
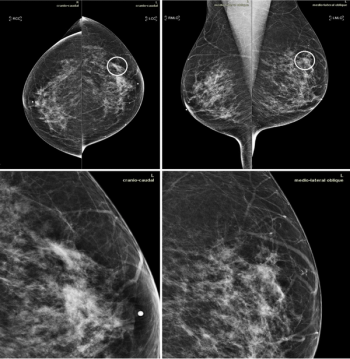
Study shows implementing the newly cleared software can slightly improve sensitivity and false negatives.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Breast Cancer Screening in Indian & Pakistani Women; Fluciclovine PET for Prostate Cancer Imaging; Cardiac Ultrasound & COVID-19; and Improving Mammography Patient Experience

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
More culturally relevant screening strategies could improve preventive healthcare in these groups.
Screening mammography begins to reduce breast cancer mortality at an age earlier than when most women begin screening.

MRI catches more malignant lesions in women with dense breasts who undergo digital breast tomosynthesis than those who have digital mammography alone.

Serena Bright™ shortens time to biopsy results, a critical capability during the COVID-19 pandemic.