Diagnostic Imaging and Testicular Cancer Risk; Digital Breast Tomosynthesis/Synthetic Mammography Combination for Breast Cancer Screening; Efficacy of Low-Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening; and the Evolving Role of the Radiologic Technologist

Diagnostic Imaging and Testicular Cancer Risk; Digital Breast Tomosynthesis/Synthetic Mammography Combination for Breast Cancer Screening; Efficacy of Low-Dose CT Lung Cancer Screening; and the Evolving Role of the Radiologic Technologist
Even potential for over-diagnosis does not appear to increase other causes of mortality.
Cerebral Aneurysms and CT Angiography; MammoScreen and Breast Cancer Detection; Low-Dose Lung Cancer Screening Program Performance; and Breast Cancer Screening Advocacy Efforts

In a study from China, there was no statistical significance in cancer detection rates between high-risk patients who were screened and those who were not.

In this podcast episode, Dr. Shalom Kalnicki, from Montefiore and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, discusses the disparities minority patients face with cancer screenings and what can be done to increase access during the pandemic.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Breast Cancer Screening in Indian & Pakistani Women; Fluciclovine PET for Prostate Cancer Imaging; Cardiac Ultrasound & COVID-19; and Improving Mammography Patient Experience
Research indicates patients who undergo a single 28-Gy session experience similar outcomes to those who have four 12-Gy sessions, pointing to safer, faster treatment.
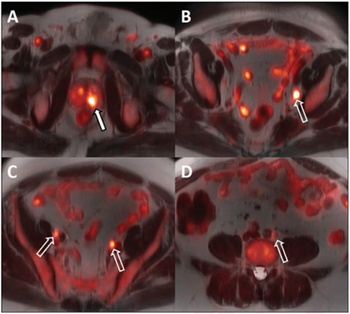
18F-fluciclovine PET/MRI can improve treatment guidance with better staging and evaluation of androgen deprivation therapy.
African American, as well as other racial and ethnic minority, patients likely have lower levels of CTC screening due to out-of-pocket costs.

In this podcast, Dr. Anupam Basu from Cook County Health in Chicago discusses the 30-pack-year threshold for lung cancer screening that overlooks at-risk African American smokers.

What to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
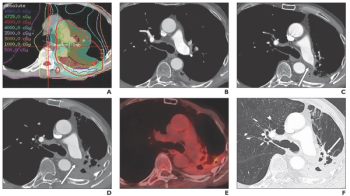
Pulmonary artery thrombosis presents differently from acute pulmonary embolism on CT scans.
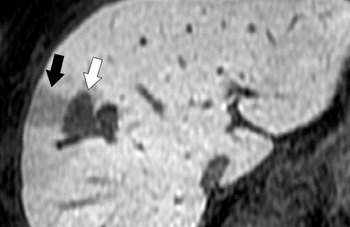
Results indicate radiologic findings are better survival predictors than pathologic vessel invasion.

Michael Gotway, M.D., cardiopulmonary radiologist with the Mayo Clinic, discusses the signature signs of EVALI on CT scans in this podcast.
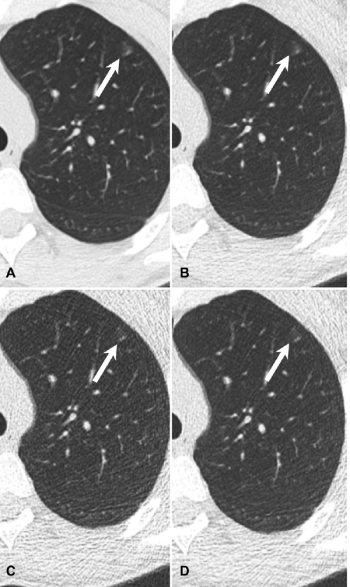
Dropping National Lung Cancer Screening radiation dose by two-thirds can yield images of diagnostic quality of solid lung nodules.
Men in this patient group are less likely to have a PET scan with the radiotracer that performs the best.
PET/MRI vs. PET/CT; Abdominal CT and COVID-19; Chest MRI vs Chest CT; Expert Interpretations of Endometriosis; and Delayed Breast Cancer Treatments for African American Women
CEUS is a safer, less expensive option for diagnosing focal liver disease.
Azurion Lung Edition is supports precision diagnosis and minimally invasive therapy in one room.
Treatment does not significantly change three-year disease-free survival rates.
States with expanded coverage saw an increase in cancer diagnosis for covered adults, as well as the overall population.
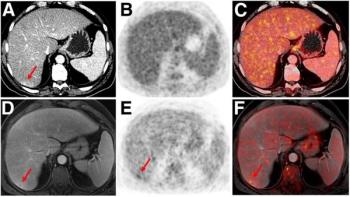
PET/MRI detects more lesions with less radiation, making it a great option for pediatric patients.
Rethinking CMR during COVID-19; Abdominal Imaging and COVID-19; Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19; African American and Lung Cancer Screening; Plus, African American Women and Disadvantages in Breast Cancer Screening
Low-dose CT scans could catch more cancers if the lung cancer screening threshold were dropped to a history of 20-pack-years.