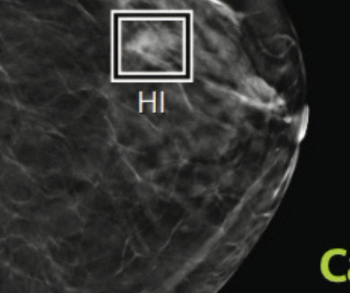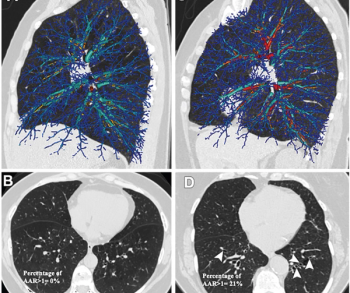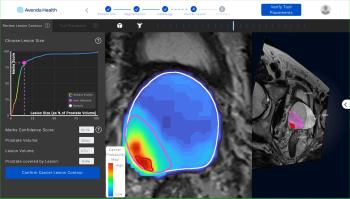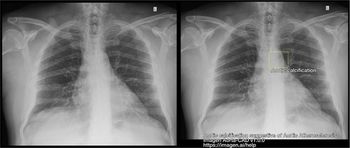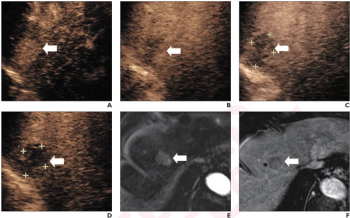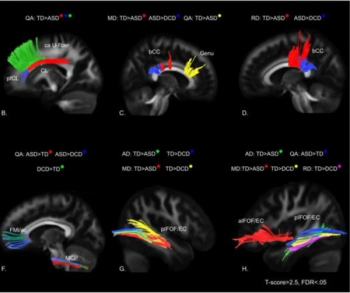
In a video interview discussing one of her recent lectures at the Radiological Society for North America (RSNA) conference, Nina Kottler, M.D., M.S., noted how the combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and radiologist experience can help mitigate bias limitations with the development of AI algorithms as well as educational biases inherent to a radiologist’s training and experience.