
What options do you have when presented with cases that cannot be read “as-is?”

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
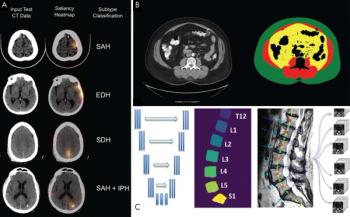
Brigham & Women’s Hospital has designed a data science pathway that can prepare radiology residents to lead the next era of artificial intelligence development and implementation.

CT can provide a diagnosis in a less invasive way and without a high false-positive rate.
Cerebral Aneurysms and CT Angiography; MammoScreen and Breast Cancer Detection; Low-Dose Lung Cancer Screening Program Performance; and Breast Cancer Screening Advocacy Efforts
In a study from China, there was no statistical significance in cancer detection rates between high-risk patients who were screened and those who were not.
Recognizing what matters to patients during the COVID-19 outbreak can help practices and hospitals meet patient needs and improve outcomes.

Open-source system makes it easier to merge clinical data with imaging files.
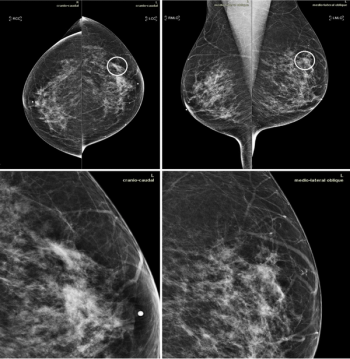
Study shows implementing the newly cleared software can slightly improve sensitivity and false negatives.

Certain parts of the brain respond differently to hot-button language found in campaign ads and speeches.
Purchasing vouchers for imaging services could present safety risks and set customer up for upselling attempts.
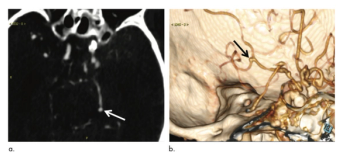
Deep learning tool improves cerebral aneurysm detection, specifically among radiologists with fewer years’ experience.

In this podcast episode, Dr. Shalom Kalnicki, from Montefiore and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, discusses the disparities minority patients face with cancer screenings and what can be done to increase access during the pandemic.

Among providers, including radiologists, who test positive for a sleep disorder, more than 90 percent have been undiagnosed and untreated.
Knowing the reasons behind your decisions – especially ones that affect patients – can be as important as the decision itself.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.

Imaging utilization has varied by socioeconomic factors during the COVID-19 outbreak.
A convolutional neural network can accurately measure skeletal muscles, helping predict patient survival.
Breast Cancer Screening in Indian & Pakistani Women; Fluciclovine PET for Prostate Cancer Imaging; Cardiac Ultrasound & COVID-19; and Improving Mammography Patient Experience

An analysis of the Dallas Heart Study from UTSW details how use of CAC scoring can help determine what patients would stand to benefit from aspirin use for primary prevention.
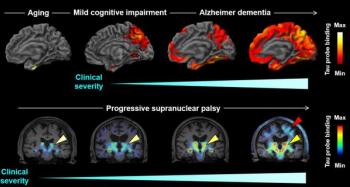
Modifying an existing imaging probe and labeling it with fluorine-18 improves providers’ ability to pinpoint protein accumulation – and differentiate between neurodegenerative conditions.
Study reveals favorable acute safety profile for macrocyclic gadolinium.

The scan, which is already part of the stroke management process, offers an opportunity for faster identification of patients with viral infection.
Research indicates patients who undergo a single 28-Gy session experience similar outcomes to those who have four 12-Gy sessions, pointing to safer, faster treatment.
3D technique manipulates radio waves and magnetic fields used for MRI to significantly increase tumor visualization on contrast-enhanced images.
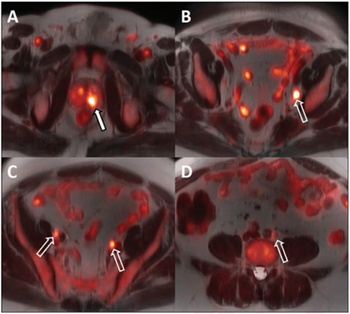
18F-fluciclovine PET/MRI can improve treatment guidance with better staging and evaluation of androgen deprivation therapy.
Adding the 18F radiotracer to MRI scans provides more detail, leading to better treatment planning and better disease-free survival rates in men with recurrent prostate cancer.

Ceiling-mounted system offers intelligent interface to guide technologists through exam.
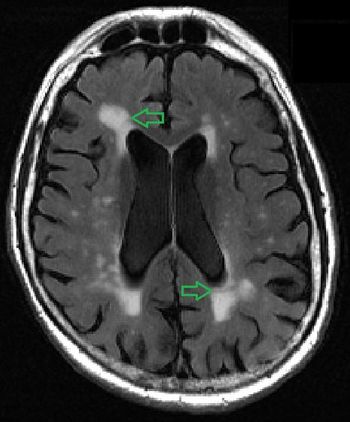
A tool that objectively measures the volume of white matter lesions can accurately pinpoint evidence of early dementia.
The modality is the only one that can be safely conducted at the bedside with patients on a ventilator.