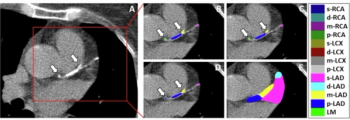
For segment-level coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a deep learning model had an accuracy rate of 73 percent for assigning calcifications to coronary artery segments and achieved a micro-average specificity of 97.8 percent.

Al-powered quantitative assessment of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) revealed that non-calcified plaque volume was over 3.5 times higher in patients who had major adverse cardiovascular events, according to multicenter research presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) conference.

For segment-level coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a deep learning model had an accuracy rate of 73 percent for assigning calcifications to coronary artery segments and achieved a micro-average specificity of 97.8 percent.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
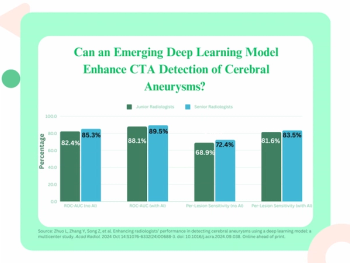
Adjunctive use of deep learning reportedly led to a 37 percent reduction of interpretation time for cerebral aneurysm assessment on computed tomography angiography (CTA) and greater than a 90 percent reduction in post-processing time.
Leveraging AI technology, the AiMIFY software reportedly facilitates double the contrast enhancement in comparison to gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) for brain MRI.
The new ultrasound platform reportedly offers a combination of enhanced imaging and AI-enabled tools to facilitate improved workflow efficiency.
Four Medicare administrative contractors (MACs) will provide coverage of AI-enabled coronary plaque analysis and quantitative coronary tomography assessment of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) for Medicare beneficiaries starting in November 2024.
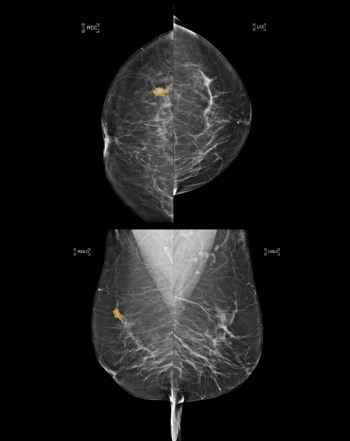
The combination of FDA-cleared AI software for mammography triage with a medical grade edge AI platform may allow the embedding of enhanced AI detection capability within existing mammography devices.
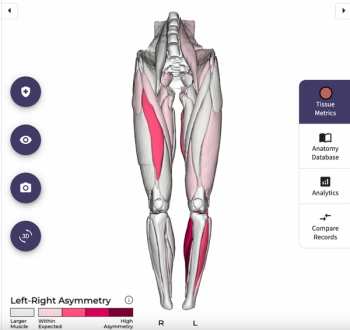
Based off rapid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the AI-enabled MuscleView reportedly offers 3D analysis of muscle volume, muscle asymmetry and intramuscular fat.

With the capability of identifying possible cases of aortic value stenosis (AVS) from existing electrocardiograms (ECGs), the AI-powered screening software from AccurKardia may facilitate earlier diagnosis of AVS, which is fatally missed in 50 percent of patient who have this condition.

Is it plausible that the current emphasis on spending what it takes to recruit and retain radiologists in a thriving job market shifts to more and more of a dependence on AI?
While staffing shortages in radiology continue to persist after the COVID-19 pandemic, current and emerging innovations powered by artificial intelligence (AI) may help facilities navigate these challenges and mitigate rising costs of health care.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
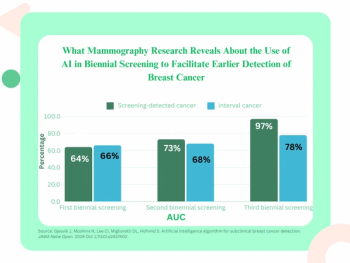
Mean artificial intelligence (AI) scoring for breasts developing cancer was double that of contralateral breasts at initial biennial screening and was 16 times higher at the third biennial screening, according to a study involving over 116,000 women with no prior history of breast cancer.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
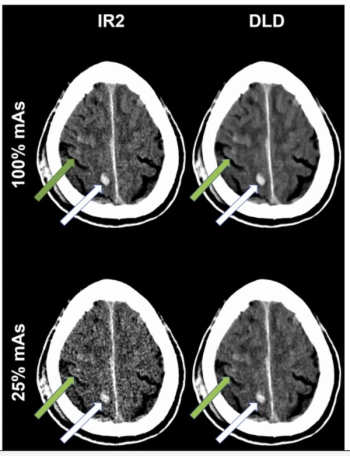
For patients who had neuroradiological trauma CT scans, researchers noted no significant visual differences between deep learning denoising at 25% mAs and iterative reconstruction at 100% mAs.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
The CINA-CSpine AI software reportedly demonstrated a 90.3 percent sensitivity rate for cervical spine fractures in validation testing on more than 300 non-contrast CT scans.
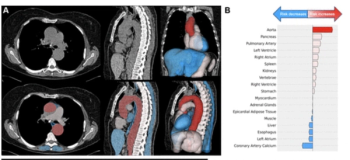
Emphasizing multi-structure segmentation and feature extraction from chest CT scans, an emerging AI model demonstrated an approximately 70 percent AUC for predicting significant incidental extrapulmonary findings as well as two-year and 10-year all-cause mortality.
Providing automated TI-RADS classifications and worksheets, the new AI-enabled software may facilitate improved efficiency with thyroid ultrasound exams.
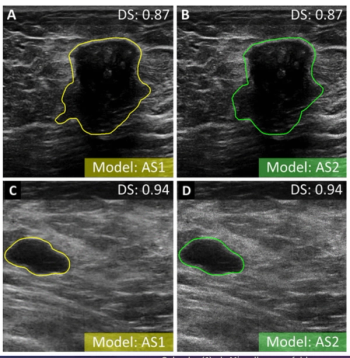
Developed with breast ultrasound data from nearly 1,200 women, a model with mixed radiomic and autoencoder features had a 90 percent AUC for diagnosing breast cancer, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
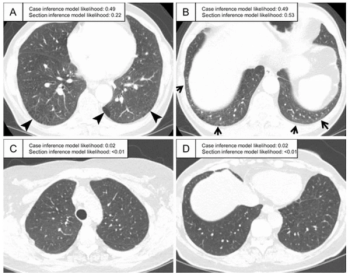
A machine-learning-based model demonstrated an 87 percent area under the curve and a 90 percent specificity rate for predicting interstitial lung abnormality on CT scans, according to new research.
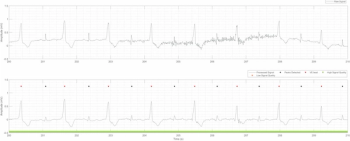
Geared toward ambulatory use, the HeartKey Rhythm suite reportedly offers enhanced signal clarity and rhythm detection algorithms.
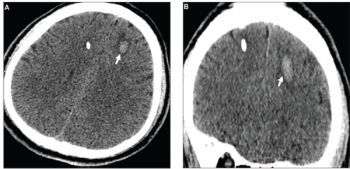
Adjunctive AI showed no difference in accuracy than unassisted radiologists for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) detection and had a slightly longer mean report turnaround time for ICH-positive cases, according to newly published prospective research.
Offering enhanced deep learning technology, the updated NeuroQuant 5.0 software reportedly bolsters segmentation capabilities for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.