
Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
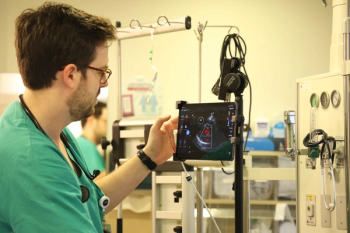
Combining four CAD modules for valvular pathologies with a variety of automated measurements, the AI-enabled AISAP Cardio ultrasound system reportedly facilitates up to a 90 percent accuracy rate in detecting common cardiac conditions.
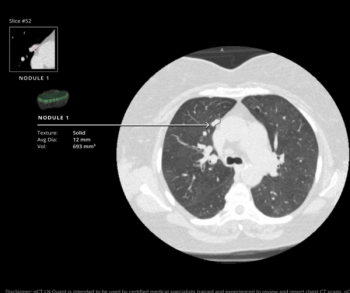
The AI-powered qCT LN Quant software reportedly generates 2D and 3D reconstructions and facilitates assessment of morphologic data across multiple thoracic studies.
Key features of the HealthCCSng V2.0 software include numerical coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a new zero CAC category and user customization of upper and lower limits for CAC scoring categories.
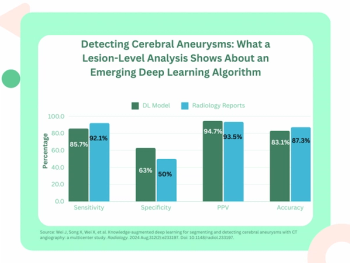
Providing an 85.7 percent sensitivity rate for detecting cerebral aneurysms on computed tomography angiography (CTA), the deep learning model also offered a similar AUC (93 percent) in comparison to radiology reports (91 percent).
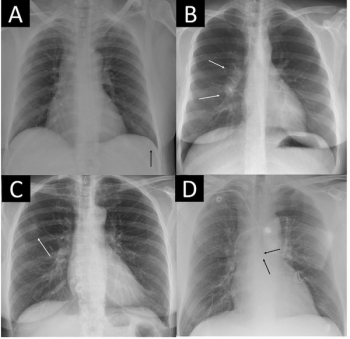
New research suggests the use of an AI software may help rule out pathology on over 50 percent of unremarkable chest X-rays with a 98 percent sensitivity threshold.
Offering a variety of AI features for streamlined workflow and enhanced visualization, the Acuson Origin ultrasound system also features the newly FDA-cleared AcuNav Lumos 4D ICE (intracardiac echocardiography) catheter.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
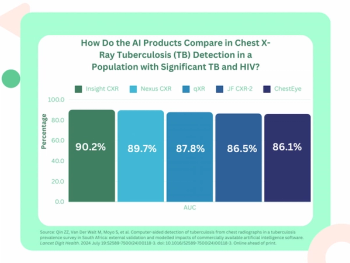
At a 90 percent threshold for sensitivity, Lunit’s Insight CXR and the Nexus CXR software from Nexus demonstrated the highest specificity rates for tuberculosis (TB) detection in a patient population with a high prevalence of TB and HIV.
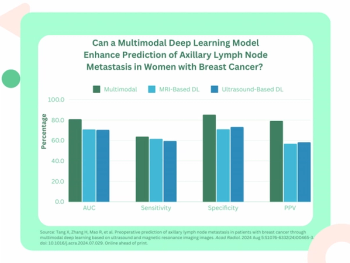
External validation testing revealed a deep learning combination of breast MRI, ultrasound and clinical factors had a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis than sole use of MRI- or ultrasound-based deep learning models in patients with breast cancer.
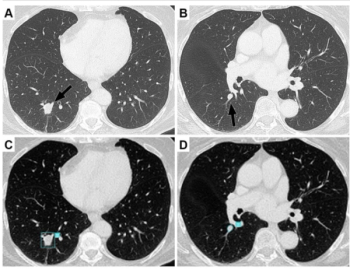
New research shows the use of adjunctive AI resulted in a 12 percent higher sensitivity rate for lung nodule detection in comparison to radiologists without AI.
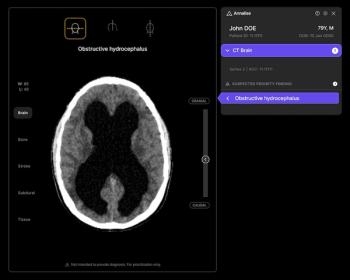
The first radiology triage modality to garner a Breakthrough Device Designation from the FDA, Annalise-Obstructive Hydrocephalus has reported sensitivity and specificity rates of 97.5 percent and 95.3 percent respectively.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
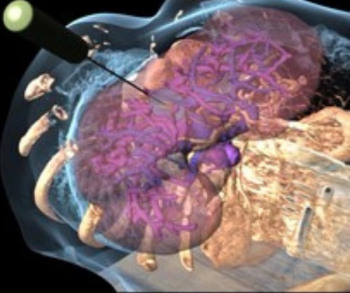
Featuring the previously FDA-cleared BioTraceIO Vision and BioTraceIO Precision modalities, the BioTrace software suite combines real-time ultrasound guidance and advanced AI technology to help bolster outcomes with liver tumor ablation therapy.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in July 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
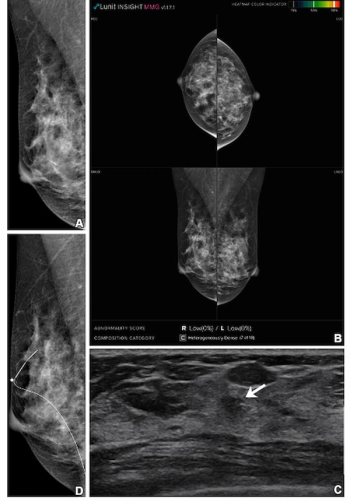
For women with dense breasts, the combination of mammography and supplemental breast ultrasound had a 36.4 percent higher sensitivity rate for detecting breast cancer in comparison to the combination of mammography and adjunctive AI, according to a new study.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
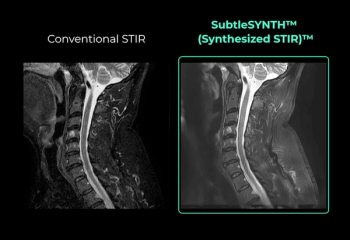
The deep learning SubtleSynth software creates synthetic STIR images that are reportedly interchangeable with conventional sequences obtained from T1 and T2-weighted MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
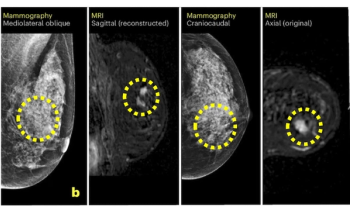
The AISmartDensity software facilitated a cancer detection rate (CDR) with breast MRI that was nearly four times higher than the CDR previously reported in trials involving traditional breast density assessment.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The EchoGo Heart Failure platform is reportedly the only AI-powered technology to receive a CPT reimbursement code for echocardiography detection of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.