CT
Latest News

Study Assesses Lung CT-Based AI Models for Predicting Interstitial Lung Abnormality
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
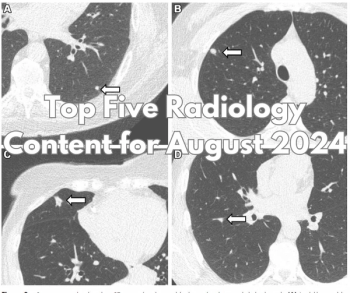
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in August 2024.

Catch up on the latest research in neuroradiology over the past month.

Review the case and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
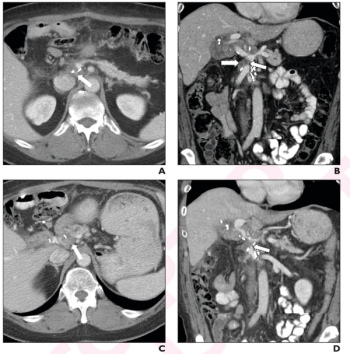
For patients who had post-op recurrence after a Whipple procedure for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), between 80 to 86 percent of follow-up CT exams revealed new or increased soft tissue.
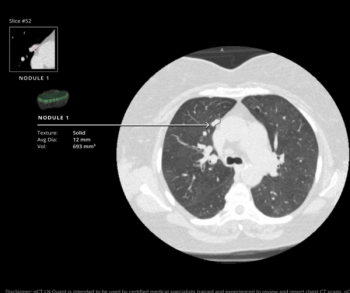
The AI-powered qCT LN Quant software reportedly generates 2D and 3D reconstructions and facilitates assessment of morphologic data across multiple thoracic studies.
Key features of the HealthCCSng V2.0 software include numerical coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a new zero CAC category and user customization of upper and lower limits for CAC scoring categories.
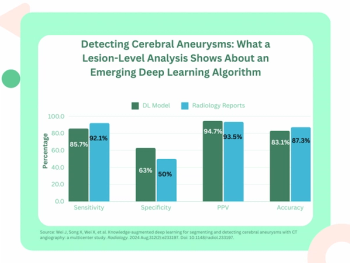
Providing an 85.7 percent sensitivity rate for detecting cerebral aneurysms on computed tomography angiography (CTA), the deep learning model also offered a similar AUC (93 percent) in comparison to radiology reports (91 percent).
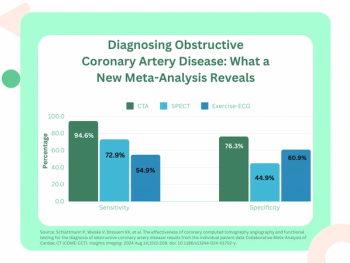
For patients with stable chest pain, CT angiography demonstrated a nearly 40 percent higher sensitivity rate than exercise electrocardiography and over an 18 percent higher sensitivity rate than SPECT for detecting obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
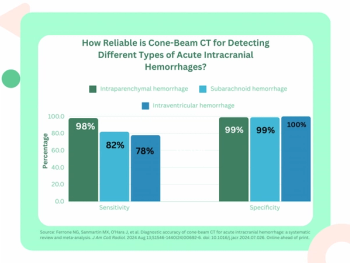
While cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) demonstrated high pooled sensitivity and specificity rates for intraparenchymal hemorrhage in the systematic review, researchers noted higher false-negative rates for subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhages.
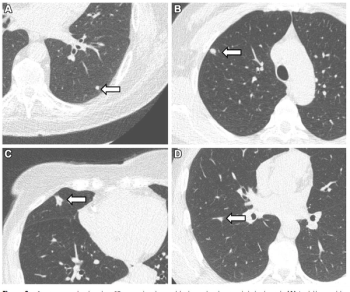
Utilizing low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans for a cohort of over 10,000 non-smokers, researchers found that over 11 percent of study participants had clinically relevant lung nodules.

Review the case and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
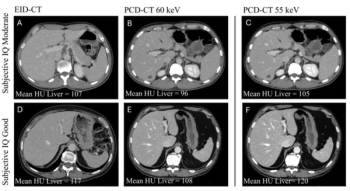
In addition to a 20.1 percent reduction in iodine load, photon-counting CT offered higher signal-to-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios than energy-integrating detector CT in a new study.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Automated CT-derived assessments may provide stronger stratification of diabetes and cardiometabolic risks than conventional predictive models, according to a new study of over 32,000 adults in Korea.
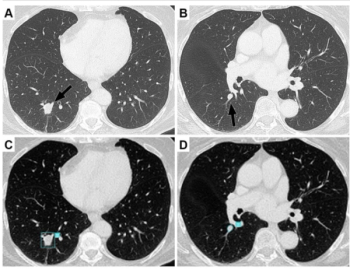
New research shows the use of adjunctive AI resulted in a 12 percent higher sensitivity rate for lung nodule detection in comparison to radiologists without AI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
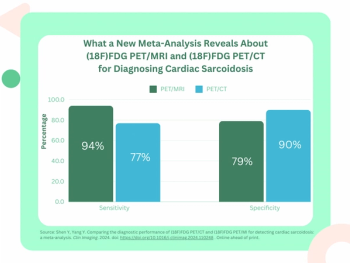
The researchers found that (18F)FDG PET/MRI had a 17 percent higher pooled sensitivity rate for cardiac sarcoidosis in contrast to (18F)FDG PET/CT.
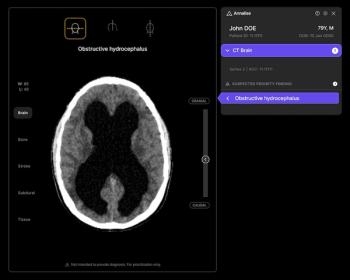
The first radiology triage modality to garner a Breakthrough Device Designation from the FDA, Annalise-Obstructive Hydrocephalus has reported sensitivity and specificity rates of 97.5 percent and 95.3 percent respectively.
While contrast media extravasation is a rare complication, there can be varying degrees of severity. Accordingly, this author reviews possible causes of this complication, prevention principles and pertinent considerations in addressing this complication when it does occur.
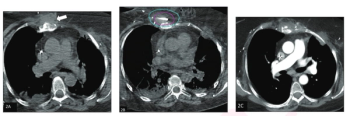
In a study involving 217 percutaneous cryoablation procedures for treating recurrent or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma in 141 patients, researchers noted an 86 percent rate of local progression-free survival and a 2 percent complication rate.
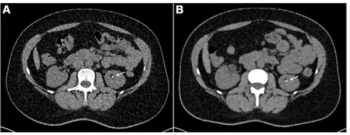
New research shows that photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) at an effective dose of 0.79 mSv provided significantly higher signal-to-noise ratios for urinary calculi (kidney stone) detection than energy-integrating detector CT at 1.39 mSv.

Review the case and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.