CT
Latest News

New Analysis Forecasts Substantial Cost Savings with the Use of Photon Counting CT for CCTA

Imaging Findings Reveal 49 Percent Improvement in Progression-Free Survival for Ivonescimab in NSCLC Patients
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
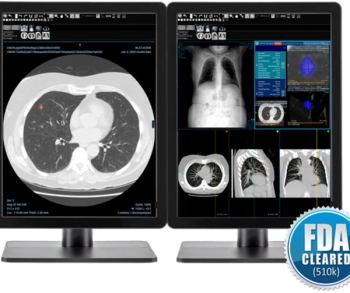
The F.A.S.T. aiCockpit CT Lung Nodule reportedly facilitates enhanced CT workflow and automated reporting for evaluation of lung nodules

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in February 2025.

In a recent interview, Abhinav K. Jha, Ph.D., discussed key challenges with the use of SPECT MRI and how an emerging deep learning model may facilitate attenuation compensation without the need for an additional computed tomography (CT) scan.
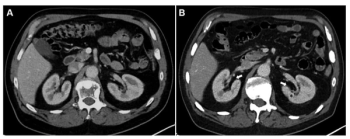
In patients who had at least four cycles of 177Lu-PSMA-I&T for mCRPC, new research shows that a 10 percent or greater decrease in total kidney volume on CT at six months has a 90 percent AUC for predicting estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFRs) of 30 percent or greater at one year.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
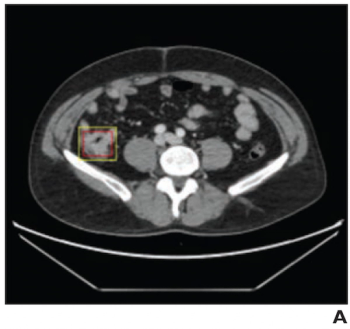
For the assessment of contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT exams, an artificial intelligence model demonstrated equivalent or better sensitivity than radiologist readers, and greater than 90 percent specificity for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
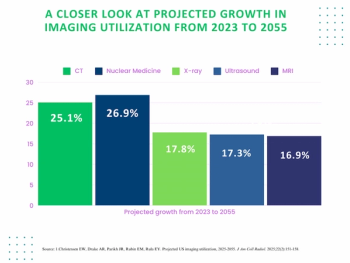
Reviewing current and emerging trends in imaging utilization and the impact of attrition rates and radiology residency positions on the field, researchers explore the future of radiology with two new provocative studies.
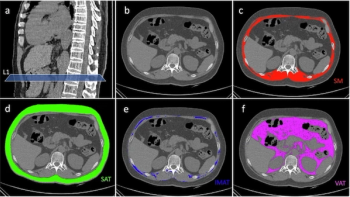
A high intermuscular adipose index has a 49 percent increased likelihood of being associated with lower overall survival in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to new research.
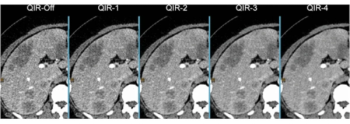
The advanced reconstruction algorithm offers optimal noise reduction, artifact correction, detailed spectral data and streamlined radiation dosing across cardiac, pulmonary and oncologic imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a video interview from the International Stroke Conference (ISC), Jeremy Heit, M.D., Ph.D., discussed new research revealing over 90 percent sensitivity and specificity rates for AI detection of subdural hematomas on non-contrast-enhanced head CTs.
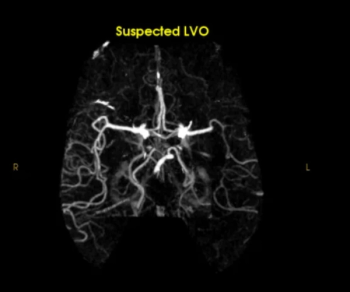
The Rapid LVO AI software detected 33 percent more cases of large vessel occlusion (LVO) on computed tomography angiography (CTA) than Viz LVO AI software, according to a new comparative study presented at the International Stroke Conference (ISC).
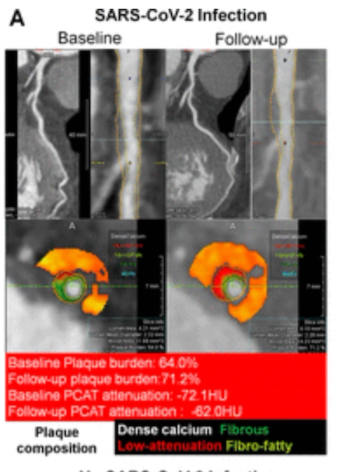
Prior COVID-19 infection was associated with a 28 percent higher progression of total percent atheroma volume (PAV) annually and over a 5 percent higher incidence of high-risk plaque in patients with coronary artery lesions, according to CCTA findings from a new study.

Emphasizing the role of radiologists in facilitating timely diagnosis of Marfan syndrome, Alan Braverman, M.D. discussed the use of echocardiography, CT, and MRI in evaluating patients with this genetic aortic condition.
The artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software Lumina 3D reportedly provides reconstructions of computed tomography angiography (CTA) images of the head and neck in minutes.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
A predictive model for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) recurrence, based on clinical parameters and CT findings, demonstrated an 85.2 percent AUC and 83.3 percent sensitivity rate, according to external validation testing in a new study.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in January 2025.
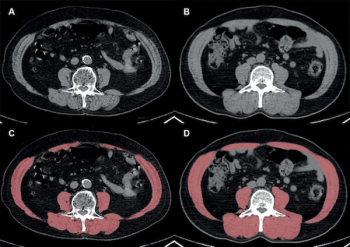
For those without low skeletal muscle mass on CT and myosteatosis, obese patients have a 23 percent lower risk of death than non-obese patients after undergoing curative resection for non-small cell lung cancer, according to newly published research.
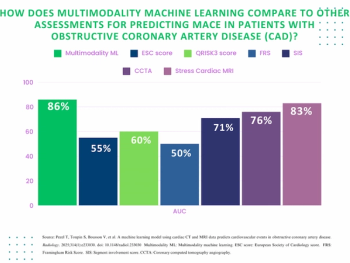
For patients with newly diagnosed obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), a multimodal machine learning model offered an 86 percent AUC for predicting MACE, which was 10 percent higher than CCTA alone and over 35 percent higher than the Framingham Risk Score.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
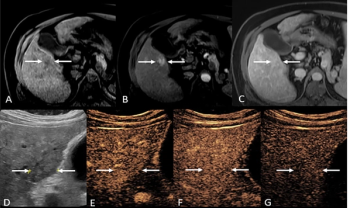
For patients previously assessed with LI-RADS LR-4 and LR-M presentations based on MRI or CT findings, the use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound led to 30 percent of these patients having LR-5 assessments definitive for hepatocellular carcinoma.