
Digital mammography is better for detecting life-threatening breast cancers than is screen film mammography, without increasing overdiagnosis.

Digital mammography is better for detecting life-threatening breast cancers than is screen film mammography, without increasing overdiagnosis.

Adding digital breast tomosynthesis to digital mammography significantly increases the accuracy of the mammography, compared with full-field digital mammo.

GE Healthcare and RadNet have partnered to identify the most efficient, cost-effective approaches for breast cancer detection.

Breast cancer mortality can drop significantly among women who undergo screening.

Women with mutations to the BRCA1/2 genes who undergo diagnostic chest radiation before age 30 are at a higher risk of developing breast cancer.

Breast Imaging and Reporting Data Systems terminology is useful in predicting malignancy in breast lesions that are detected by MRI.

The non-radiation based imaging modality is not a reliable breast cancer screening tool and mammography should remain the standard of care.

Preoperative MRIs should be done on all newly diagnosed breast cancer patients, regardless of breast density.

Digital breast tomosynthesis plus mammography provides a 40 percent reduction in patient recalls, reducing anxiety and potentially cutting cost and overall radiation dose.

Radiation doses from digital breast tomosynthesis is comparable to and could be lower than conventional two-view full-field digital mammography.

In this podcast, Stephen Rose, MD, president and CEO of Houston Breast Imaging and a principal investigator of the 3-D tomosynthesis clinical trials in 2010, discusses the benefits of the new technology and what his practice learned when implementing the screening program.

Giotto USA will be demonstrating at RSNA 2011 its 3D and 3DL digital mammography systems, which recently received FDA 510(k) clearance.
Philips will highlight its newly released MicroDose Mammography System at RSNA 2011. The Philips unit will go head to head with other new entries in the mammography space including Hologic’s 3-D breast tomosynthesis product, Selenia® Dimensions, whole breast ultrasound from U-Systems, Dilon’s 6800 MBI scanner, and GE’s Discovery MB750b, a molecular breast imaging system.

In this podcast, Tom Gentile, president and CEO at GE Healthcare Systems, explains that “the whole focus of imaging is moving beyond the quality of the image.” Patient care, physician productivity and reimbursement take on a renewed focus in light of healthcare reform efforts internationally, he says.

Calling the results flawed, many in the radiology community are protesting a study released last week that suggested mammography hasn’t played a major role in the drop in breast cancer-related deaths.

Thermography not a replacement for mammography

Imagine a faster, inexpensive method for breast cancer screening. That’s some of the promise behind a new innovation from doctoral student, Sevan Goenezen, who has discovered a way to use ultrasound and advanced algorithms to differentiate between benign and malignant tumors.

HealthDay News - Mammogram's sensitivity lower in the initial five-year period after the first cancer

Breast imaging has gone 3-D. The FDA announced today the approval of Hologic Inc.’s Selenia Dimensions System, the first X-ray mammography device that provides 3-D images for breast cancer screening and diagnosis.

A 34-year-old Hispanic woman presented to her primary-care physician with a palpable left breast mass in June of 2009. She first noticed the mass 15 years prior, but never sought medical care.

Radiologists at Cambridge University Hospital found that more experienced radiologists are far better at detecting breast malignancy.
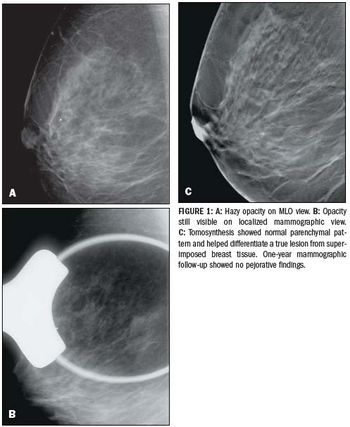
Mammography is the only screening modality that has been proven to reduce mortality from breast cancer.

Yearly mammograms greatly reduce the risk of mastectomy following breast cancer in women between the ages of 40 and 50, according to a study presented Wednesday at the RSNA meeting.

Hologic has pursued breast tomosynthesis as a commercial modality for the last five years, recruiting luminaries with track records in tomo going back a decade or more. Now, at RSNA 2010, the company is on the brink of achieving that objective.

Screening MRI should be an adjunct to screening mammography in women with a personal history of breast cancer, researchers at the 2010 RSNA scientific assembly in Chicago said.