
Breast-specific gamma imaging detects breast cancer in both dense and nondense breast tissue.

Breast-specific gamma imaging detects breast cancer in both dense and nondense breast tissue.

Annual mammography does not reduce risk of death from breast cancer for women between 40 and 59, according to a study the ACR faulted as misleading.

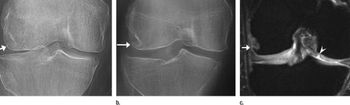
Tomosynthesis is better than radiography and almost as good as MRI in detecting bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.

Adding one-view tomosynthesis to digital mammography improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces recall rates, but adding two-view tomosynthesis provides even better results.

Digital mammography with a photon-counting system had higher cancer detection rates than traditional systems.

Cost of breast cancer screening mammography not as cut-and-dry as reported in a recent Annals of Internal Medicine article, according to the ACR and SBI.

Screening breast MRIs should be considered for women with a personal history of breast cancer.

Screening mammograms for women in their 40s may result in earlier high-risk breast cancer diagnosis, less chemotherapy, and lower future risk of subsequent breast cancer.

Tomosynthesis plus mammography images take 47 percent longer for radiologists to interpret than digital mammography alone.

Pulmonary emboli missed by CT angiography may be detected by computer aided detection programs.


After a decade of increased use of breast MRI for screening and surveillance, its use has stabilized.
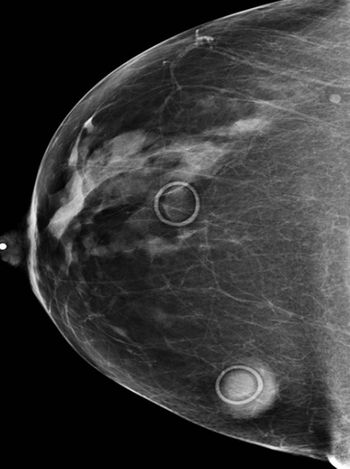
Breast density notification mandates exist in 18 states but there are still questions about their utility and implementation. Mary Lou Smith, JD, MBA, discusses the controversial topic.

Use of tomosynthesis for orthopedic and chest imaging offers greater study clarity and reduced dose.

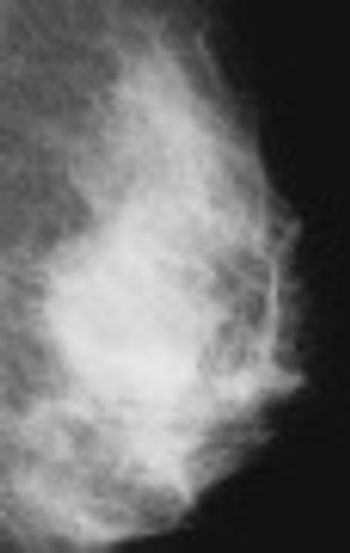
CHIGACO - Researchers continue to study the role of dense breast tissue. Knowing the risk factors, how to monitor it, and what to recommend as a next step is crucial.

CHICAGO - Screening mammograms done every year have a higher chance of detecting breast cancer before it spreads to the lymph nodes than do less frequent exams.

CHICAGO - More breast cancer detection, fewer false positives with digital tomosynthesis.
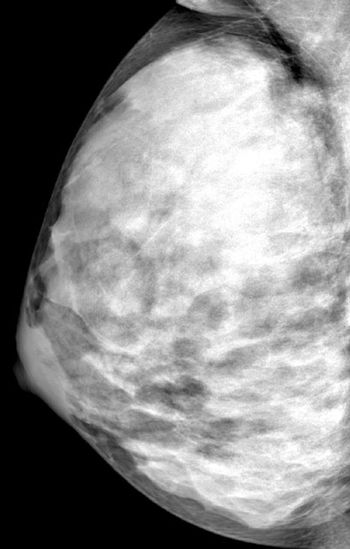
CHICAGO - Establishing early breast density through full-digital mammography may predict breast cancer among younger women.

More screening breast MRIs performed, but improvement in appropriate use still needed.
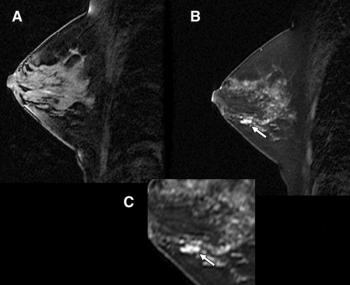
Breast cancer screening and surveillance MRI use increased significantly over a decade - but not among the women who need it most.
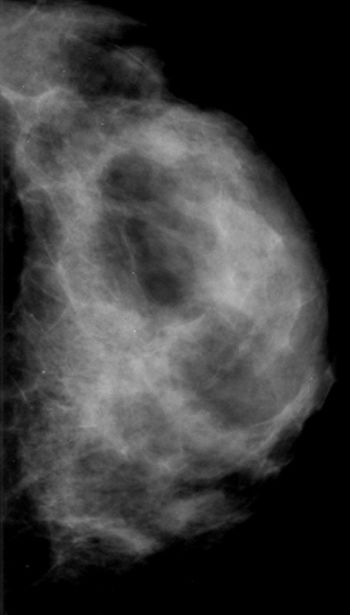

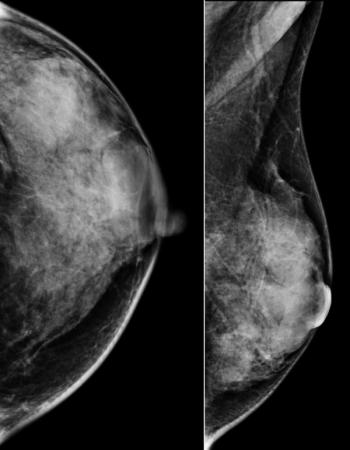
Digital mammography use has resulted in 3-fold increase in high-risk breast lesions rate; potential oversurveillance, overtreatment.