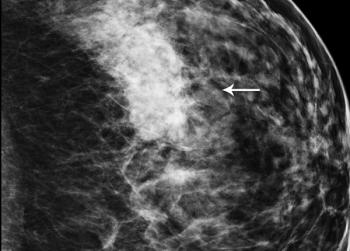
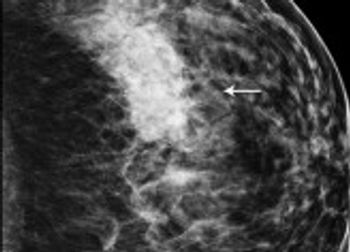
Mammography
Latest News
CME Content


Breast lesions rated as category 3 (BI-RADS) on ultrasound could wait 12 months for re-evaluation.

Women with breast cancer who undergo preoperative MRI have a higher rate of bilateral mastectomies and contralateral prophylactic mastectomies than women who aren’t scanned.

Women with some breast tissue abnormalities may avoid surgery if they undergo yearly mammograms plus MRI and ultrasound to monitor for changes.

Digital tomosynthesis results in fewer false positives and reduces recall rates, but has higher radiation doses than mammography.
Mammography recall rates may be influenced by factors outside of radiologists’ control, and rates might not be a great measure of quality.
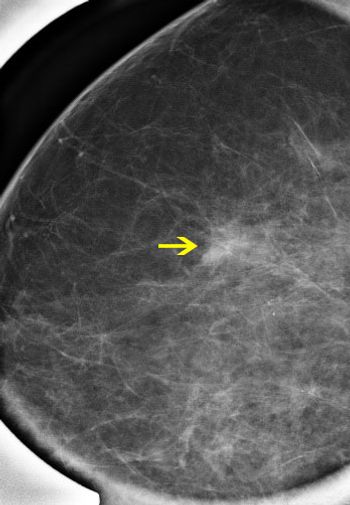
What’s your diagnosis?

Siemens Healthcare has received FDA clearance for their MAMMOMAT Inspiration Prime Edition lower dose mammography system.

Digital chest tomosynthesis used as a screening tool for lung cancer shows comparable rates of detection to low-dose CT.

Digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer screening reduces recall rates and biopsies, and detects more cancers.

Maryland became the seventh state to enact breast density patient notification laws.
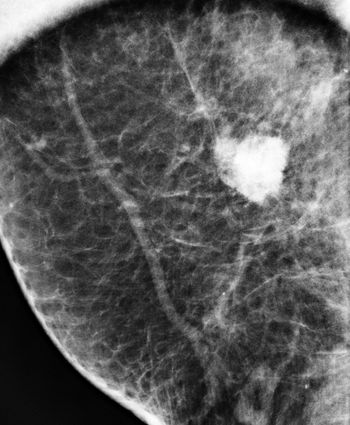

Digital radiography (mammography) detects as many breast cancers as screen film mammography and more cancers than computed radiography.

Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI is a useful tool in aiding detection of residual disease following excisional biopsy for breast cancer.

Electronic bone suppression programs used in addition to CAD allow radiologists to detect more lung nodules than with chest X-rays alone.

Integrating 2D and 3D screening increases breast cancer detection and may lower reports of false positives.

Screening mammograms enhanced by CAD trigger more false alarms than non-CAD screenings and detect more early cancers that may never have needed treatment.

Better communication between radiologists and patients undergoing image-guided breast biopsies results in lower anxiety before and after the procedure.

CAD with chest X-ray to screen for lung cancer may reveal abnormalities, but more study is required.

The ACR and SBI took issue with a recent study on the long-term mental anguish caused by false-positives from mammograms.

CAD may help highlight nodules the clinician may have otherwise missed, but its use is not without legal ramifications. What do you think? Take this survey.
The tides are turning for breast imagers. After several years of declining demand and facility closures, the market is rebounding and more growth is expected.

The man meets machine era is here, and harnessing the power of the machine-man interaction will be key to effective implementation of CAD. So get ready.

Philips received FDA 510(k) clearance for MicroDose SI, a full-field digital mammography system that enables future Single-Shot Spectral Imaging applications.








