
The Piur tUS Infinity system reportedly reduces operator dependency with ultrasound through upgrading of two-dimensional ultrasound devices and access to 3D multiplanar image reconstructions of thyroid conditions.

The Piur tUS Infinity system reportedly reduces operator dependency with ultrasound through upgrading of two-dimensional ultrasound devices and access to 3D multiplanar image reconstructions of thyroid conditions.
Providing automated TI-RADS classifications and worksheets, the new AI-enabled software may facilitate improved efficiency with thyroid ultrasound exams.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
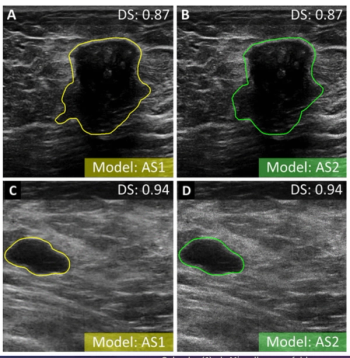
Developed with breast ultrasound data from nearly 1,200 women, a model with mixed radiomic and autoencoder features had a 90 percent AUC for diagnosing breast cancer, according to new research.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in August 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
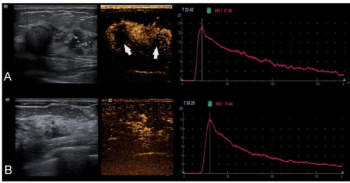
Adding two key findings from contrast-enhanced ultrasound to a predictive model of mammography, conventional ultrasound and clinicopathological findings led to a 86.1 percent AUROC for predicting the upgrading of ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer, according to new research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
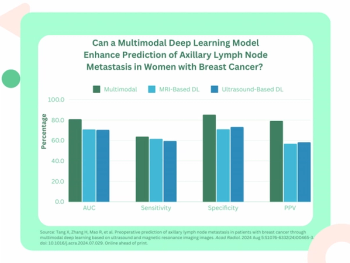
External validation testing revealed a deep learning combination of breast MRI, ultrasound and clinical factors had a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis than sole use of MRI- or ultrasound-based deep learning models in patients with breast cancer.
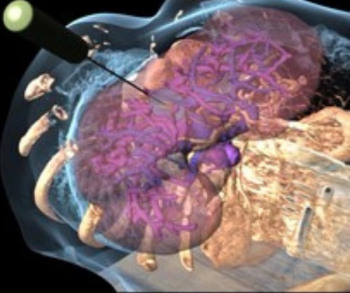
Featuring the previously FDA-cleared BioTraceIO Vision and BioTraceIO Precision modalities, the BioTrace software suite combines real-time ultrasound guidance and advanced AI technology to help bolster outcomes with liver tumor ablation therapy.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in July 2024.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
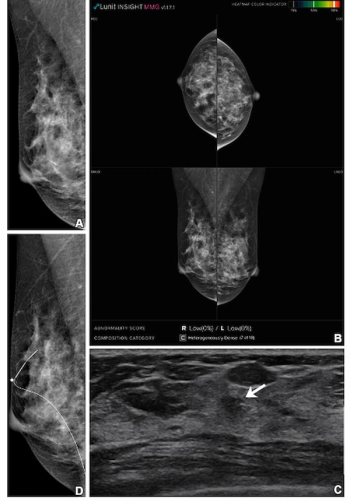
For women with dense breasts, the combination of mammography and supplemental breast ultrasound had a 36.4 percent higher sensitivity rate for detecting breast cancer in comparison to the combination of mammography and adjunctive AI, according to a new study.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Utilizing a threshold of less than 5 mm of ultrasound-measured endometrial thickness, the authors of a new study noted an 11.4 percent false-negative probability for endometrial cancer in Black patients.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
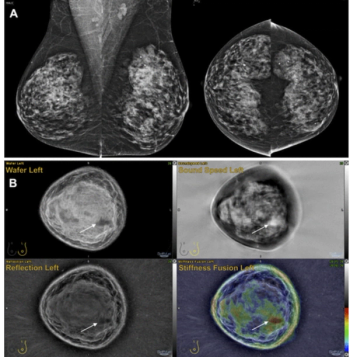
Emerging research suggests that combining full-field digital mammography and whole-breast ultrasound tomography provides superior sensitivity in detecting BI-RADS 4 lesions and superior specificity in diagnosing BI-RADS 3 lesions than mammography alone in women with dense breasts.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In recognition of National Women’s Health Month, Dana Bonaminio, MD, Amy Patel, MD, and Stacy Smith-Foley, MD, shared their thoughts and perspectives on the recently updated breast cancer screening recommendations from the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).
The package of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) applications can reportedly facilitate rapid implementation of POCUS into imaging workflows.

The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered module provides a prostate segmentation tool for MRI-guided transurethral ultrasound ablation (TULSA) procedures in patients with prostate cancer.

While radiologists and other providers may be discouraged by insurer denials saying the use of a technological advance is “unproven and investigational,” 82 percent of appeals for prior authorization denials were approved in 2021.
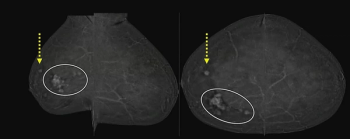
In a recent lecture at the 2024 ARRS Annual Meeting, Jordana Phillips, MD, discussed the role of contrast-enhanced mammography in staging breast cancer, evaluating response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and recalls from screening.