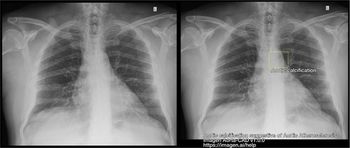
One study showed use of the Aorta-CAD cloud-based software led to a 62 percent reduction of missed aortic calcification that suggested aortic atherosclerosis.

One study showed use of the Aorta-CAD cloud-based software led to a 62 percent reduction of missed aortic calcification that suggested aortic atherosclerosis.
In a recent video interview, Susan Holley, MD discussed key findings from a large retrospective longitudinal study, presented at the recent Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, which found that an emerging artificial intelligence (AI) model was over 24 percent more consistent than radiologist assessment of breast density.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent video interview, Raymond Y. Kwong, MD, discussed his clinical experience with the Vista.ai (formerly HeartVista) One Click MRI software and recent research, presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, that revealed a 31 percent decrease in cardiac MRI scan times for patients with cardiomyopathy or structural heart disease.
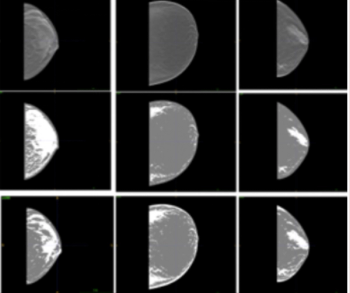
An emerging artificial intelligence algorithm, developed to estimate volumetric breast density from 3D-reconstructed digital breast tomosynthesis images, could potentially facilitate individual risk assessments for breast cancer.

Recently launched at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, the SIGNA Experience reportedly features synergistic technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) advances that help improve the efficiency and quality of magnetic resonance imaging.
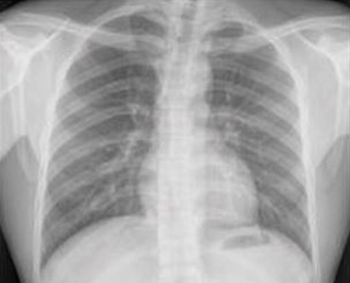
Based on a single existing chest X-ray image, the deep learning model predicts future major adverse cardiovascular events with similar performance to an established risk scoring system and may help identify people for preventive use of statin medication.
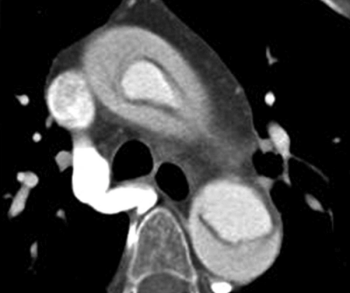
New research suggests the Viz Aortic Dissection Algorithm has a 94.2 percent sensitivity rate for detecting aortic dissection on computed tomography (CT) angiography.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a recently published article, researchers from Yale University discuss the pros and cons of current FDA regulations as they apply to the clearance and use of adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) software with conventional breast cancer screening modalities such as mammography.
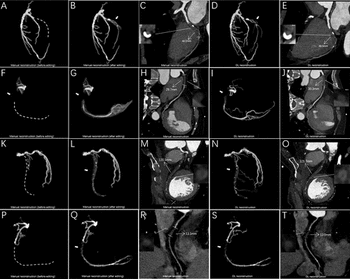
Emerging research revealed that a deep learning model had a nearly twofold increase in successful segmentation and reconstruction of coronary total occlusions (CTOs) on coronary computed tomography angiogram (CCTA) and a 73 percent reduction in post-processing and measurement time in comparison to a conventional manual approach.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
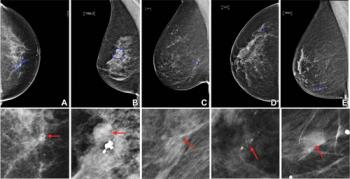
In separate test sets of Israeli women and United States women who had either ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive breast cancer, emerging artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms achieved an area under the curve (AOC) of 88 percent and 80 percent, respectively, for malignancy detection.

Catch up on the top AI-related radiology content of the past month.
Rads will always have to deal with forces outside of their control, but it’s how we address those forces that makes us the type of radiologist we can be proud of.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
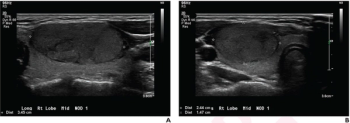
The retrospective study of patients 21 years of age or younger found that a deep learning algorithm and use of the American College of Radiology’s Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) both had more than a 26 percent greater sensitivity for differentiating thyroid nodules on ultrasound in comparison to radiologist assessment.
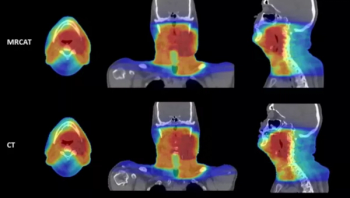
For physicians performing radiotherapy treatment of soft tissue tumors in the head and neck, the MRCAT Head and Neck offers an artificial intelligence (AI) application that allows the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as the primary or sole imaging for procedure planning.
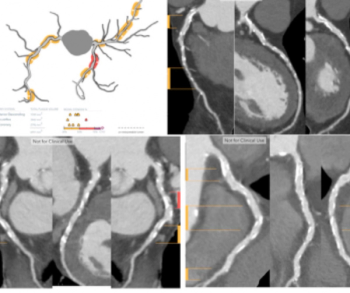
Plaque Analysis and RoadMap Analysis, two artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled assessment products, may enhance clinical evaluation of coronary artery disease (CAD) on cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
While artificial intelligence (AI) models have been acknowledged for aiding imaging analysis or facilitating workflow enhancements, this author envisions AI as a potential workstation conceierge capable of turning common venting and gripes into actionable items for significant improvements.
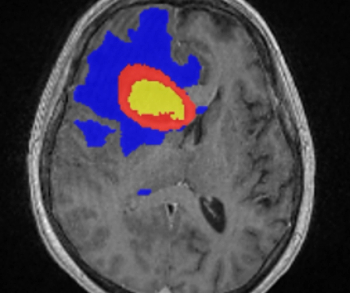
Incorporating artificial intelligence (AI)-based technology, Neosoma HGG reportedly demonstrated a 95.5 percent accuracy rate in measuring brain tumor volume on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans at various points during the treatment of patients with high-grade gliomas.

TeraRecon Neuro reportedly offers six automated and customizable computed tomography (CT) perfusion maps that facilitate assessment of brain function in hemorrhagic and ischemic neurological cases.
Addressing upgrades of traditional infrastructure used in everyday radiology practice may be a more practical use of resources than investment in artificial intelligence (AI) technology that is still evolving.
AIR Recon DL, a deep learning-based image reconstruction software, will now be available with 3D sequences as well as PROPELLER motion-insensitive sequences on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners from GE Healthcare.