
Typically when someone presents to the emergency department with acute chest pain, the patient is admitted for further workup.

Typically when someone presents to the emergency department with acute chest pain, the patient is admitted for further workup.

Typically when someone presents to the emergency department with acute chest pain, the patient is admitted for further workup.

Radiologists can predict cardiovascular disease using incidental findings from routine diagnostic CT, according to a study appearing in Radiology.
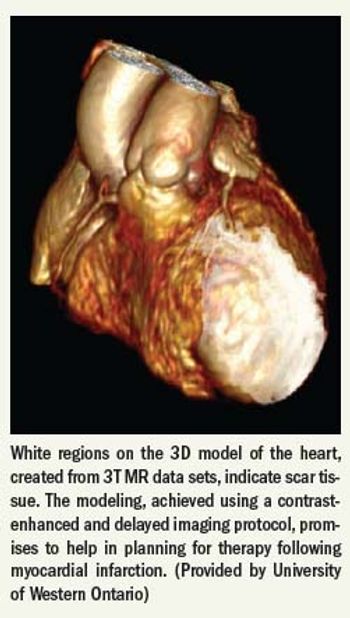
Experts have long suggested that the clinical promise of 3T, with its improved signal-to-noise ratio compared with 1.5T, might eventually be expressed in cardiac imaging, one of the least approachable clinical areas of MR.

MRI was able to reveal changes to the heart and vessels of athletes who trained for triathlons, according to research conducted at the University of Erlangen- Nuremburg in Germany.

MRI was able to reveal changes to the heart and vessels of athletes who trained for triathalons, according to a study conducted at the University of Erlangen-Nuremburg in Germany.

Stress cardiac MRI reduced incident cost without missing any acute coronary syndrome cases in patients with chest pain at a North Carolina facility.
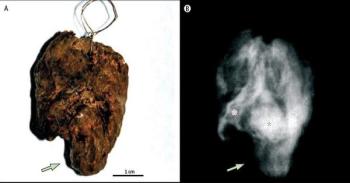
An x-ray taken centuries after her death proves a well-known saint died from a cardiac embolism instead of tuberculosis, as was previously thought. The body of Santa Rosa, an 18- or 19-year old girl, was naturally mummified in the 13th century.

A new SPECT cardiac imaging system that uses a cadmium zinc telluride-based high-speed, high-resolution camera dramatically reduces imaging time for patients while also reducing radiation exposure.

Computer-aided detection software developed especially for coronary CT angiography could boost imagers' ability to rule out clinically relevant stenosis in patients at low to moderate risk of coronary artery disease, according to researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina.
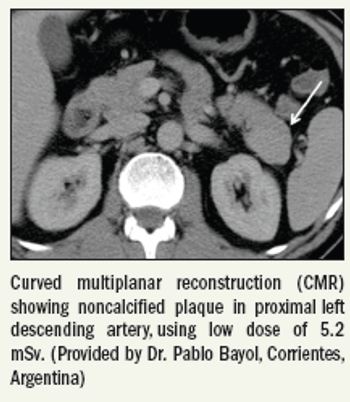
Electrocardiogram-gated tube modulation is essential to lower radiation dose in fusion imaging.

Coronary artery calcium scanning predicts the risk of myocardial infarction and sudden death accurately enough to guide the selection of diagnostic tests for symptomatic patients, according to a multicenter prospective study.

Increasing CT scanning speeds and image resolution combined with automated injection and optimized protocols tailored to specific patient features could reduce iodinated contrast media needed for coronary CT angiography by at least half, according to several papers presented at the 2009 RSNA meeting.

Bracco Diagnostics sees opportunity in the latest decision by the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services to reimburse more for PET procedures in 2010.

Cardiac imaging researchers are expanding the scope of topics considered at the 2009 RSNA meeting to include iodinated contrast media administration as a safety issue and clinical outcomes studies that weigh the relative merits of cost and clinical efficacy.

Electrocardiogram-gated tube modulation is essential to lower radiation dose in fusion imaging.

Findings from a large multicenter study by U.S. researchers suggest 64-slice CT angiography is better suited to detect nonobstructive but otherwise clinically relevant coronary artery plaques in patients with diabetes than are other cardiac diagnostic tests.
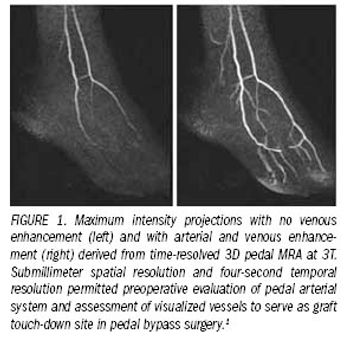
Cardiovascular MR imaging has become a valuable diagnostic modality.

Results from the first Cardiac CT Board Examination suggest that clinical experience is what counts the most toward making the grade.

Findings from a Washington, DC, study suggest that cardiac CT performed before repeat cardiac surgical revascularization may lead to safer and more cost-effective operations. Preoperative CT was also linked to a higher likelihood of improved peri- and postoperative outcomes in these patients.

Radiologists and cardiologists who meet image interpretation requirements for cardiac CT competence certification do equally well on the test, according to results of the first Cardiac CT Board Examination. Board exam results also hint that actual clinical experience counts more toward passing scores than does medical education.

The last decade has seen rapid advances in our technological capability to image the heart noninvasively.
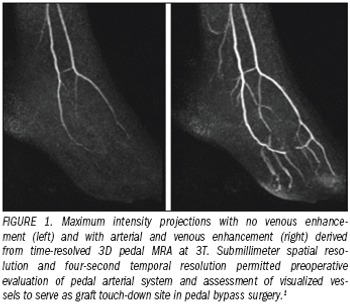
Cardiovascular MR (CVMR) imaging has become a valuable diagnostic modality.
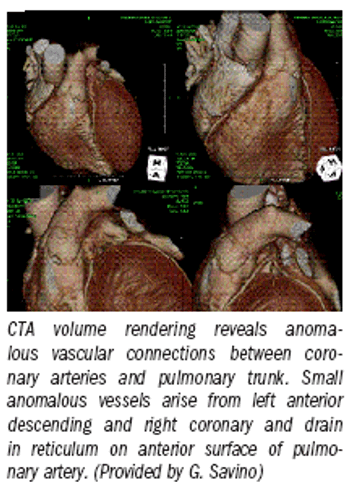
Multislice CT angiography can save lives by identifying occult congenital cardiac anomalies and disease that could lead to sudden cardiac death among competitive athletes.

Carestream slates CR cassette debut