
Radiologists who believe that Washington insiders have targeted medical imaging for financial cutbacks can find plenty of evidence to raise concerns in a recent report on Medicare costs published by the Medicare Payment Advisory Committee.

Radiologists who believe that Washington insiders have targeted medical imaging for financial cutbacks can find plenty of evidence to raise concerns in a recent report on Medicare costs published by the Medicare Payment Advisory Committee.

A type of iterative reconstruction may reduce patient radiation dose from CT scans up to 65%, according to a study published in the September issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology.

The Canadian nuclear reactor that satisfies more than half of demand of molybdenum-99 for medical nuclear imaging services in North America will not return to service until the first quarter of 2010.
Radiologists may have to make only minor changes to their practices to adjust to the new international standards for lung cancer staging, but a lecture covering their implications was still controversial enough to send sparks flying Aug. 4 at the World Conference on Lung Cancer in San Francisco.

Blue Dog Democrats on the House Energy and Commerce subcommittee on health were credited Friday with combating liberal proposals arising during protracted deliberations that would have cut physician pay. No action was taken on an amendment that would have banned in-office imaging physician self-referral.

SNM’s Clinical Trials Network has expanded to include relationships with European PET radiopharmaceutical manufacturing sites to support molecular and nuclear imaging facilities on the continent that are gearing up to perform scientific studies for the program.

Other headlinesVarian allies with Calypso to track tumorsNucletron signs oncology outpatient networkFDA clears Chinese 16-slice CT

A study combining the work of two commercial health insurance plans and a Medicare Advantage managed care program indicates that imaging prior authorization dramatically slows the use of high-tech imaging in the short run, but its impact decreases over time.

Other headlinesSiemens evolves treatment planningSoftware analyses tumor blood supplyPhilips CT reaches milestone

The number of technologists taking primary certification exams has hit a plateau with the growth trend seen over the last eight years flattening out, according to the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists.

The window for giving tissue plasminogen activator is extended from three hours to four and a half hours after the onset of stroke under new guidelines recommended by the American Stroke Association. Results from two large multicenter trials led the group to advise expanding the time window for tPA delivery.

The nuclear reactor that serves as North America’s primary source of molybdenum-99 will not return to service before late 2009.

Experts are urging physicians to remain skeptical about controversial findings that show patients with compromised kidney function face a more than one in 10 chance of death, stroke, or myocardial infarction after experiencing contrast-induced nephropathy from coronary angiography.

Medicare reimbursement for high-tech imaging, including MRI and CT, could be cut by up to 40% if the Obama administration moves ahead with plans covered in proposed changes to the 2010 Physician Fee Schedule to shift funds to primary care physicians.

Diagnostic imaging is the focus of 11 of 100 priority research projects identified in an Institute of Medicine report released Tuesday that promises to revolutionize how the clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of emerging medical technologies and treatment regimens are determined in the U.S.

An article in the May 27 New England Journal of Medicine provides some interesting, and perhaps unintended, insights into the new world that is emerging as government takes a more active role in decisions about the relative value of medical procedures.

Results of a study by Italian and U.S. investigators suggest CT colonography can simultaneously spot colorectal cancer and abdominal aortic aneurysms.

Angry backers of CT colonography for colorectal cancer screening are regrouping after the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services repulsed their efforts to secure Medicare coverage for the procedure.
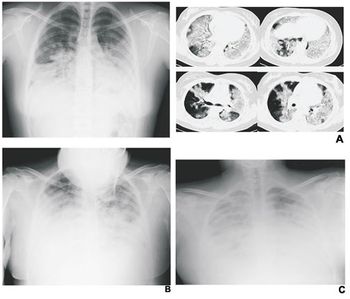
Mexican physicians have compiled a set of radiological findings that is helping local health agencies confirm the diagnosis of the swine A-H1N1 flu virus in humans. Some imaging patterns resemble those from the severe acute respiratory syndrome or ‘avian flu’ epidemic that struck mostly Asian countries in 2003.

A study by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission has confirmed what critics of in-office self-referred imaging have long claimed. Physicians who have a financial interest in medical imaging equipment are more likely to refer patients to use it, and they incur higher costs generally than physicians who do not have similar financial incentives.
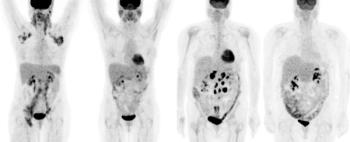
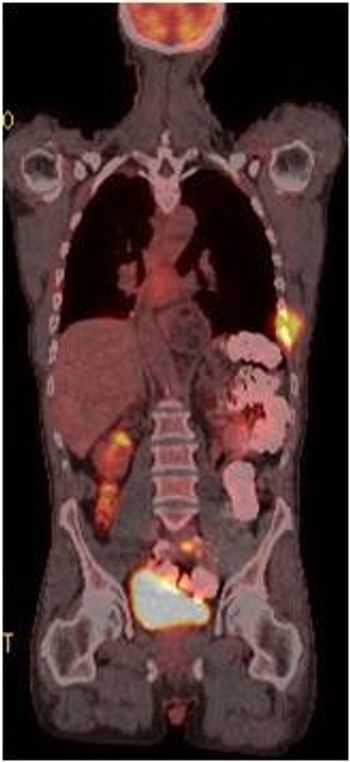
A study showing the promising effects of radioimmunotherapy with two different agents for treatment of patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma won the Image of the Year award at the 2009 SNM meeting in Toronto.

Patients who experience pain in the lower back are more likely to get an x-ray or CT scan within 28 days if their primary physician works in a larger practice as opposed to a smaller facility, according to a study by the Center for Studying Health System Change. The center also found that patient satisfaction incentives encourage unnecessary imaging.

The International Atomic Energy Agency and Brigham and Women’s Hospital have turned to YouTube to educate the public and physicians about the risks of exposure to CT-generated ionizing radiation and strategies to address them.

Low-dose CT lung cancer screening carries a high burden of false-positive results after only two rounds of testing, according to a presentation at the 2009 American Society of Clinical Oncology.

Nuclear medicine providers can expect molybdenum-99 shortages until at least September while North America’s primary source of medical isotopes is shut down for repairs.