
Siemens’ computed tomography (CT) iterative reconstruction protocol has been cleared by the FDA, the company announced Wednesday.
Once limited to research and use by eye specialists, optical coherence tomography (OCT) is emerging as a major imaging modality. OCT is more sensitive than ultrasound, experts said, and now researchers and clinicians are now finding ways to use OCT to guide esophageal and cervical biopsies.

Siemens’ computed tomography (CT) iterative reconstruction protocol has been cleared by the FDA, the company announced Wednesday.

Patients voting with their feet strongly preferred noninvasive CT colonography over traditional colonoscopies, Dutch researchers have found.

Coronary artery calcification (CAC) scores of zero don’t give patients a pass from obstructive coronary artery disease, according to a study using coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) on patients with symptoms of coronary artery disease.
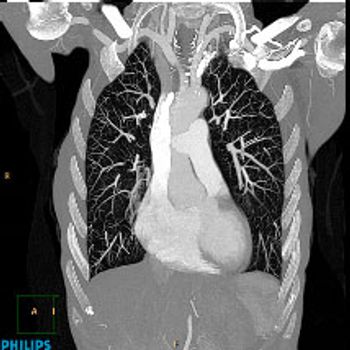
Scott Smith, director of project management, CT, Philips Healthcare, describes low-dose CT as nearly a given in the marketplace now. What’s more important is maintaining the speed and quality of the image while using iterative reconstruction to keep the dose low.


Agreement is lacking - both across institutions and within departments - for the management of six commonly encountered incidental findings on body CT, concludes a study in the November issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology. Departments should develop guidelines to ensure consistent patient recommendations, authors said.

New custom-designed patient shielding devices should supplant traditional lead aprons for chest CT scans - and possibly every scan, regardless of body part. That’s according to the authors of a new study published in the British Journal of Radiology.

CT angiography works as well as conventional digital subtraction angiography for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease (PAD), researchers reported online in the journal Radiology.

Diagnostic Imaging spoke with Dr. Johnsey Leef III, a radiologist with Charleston Area Medical Center in Charleston, WV, about how the industry is responding to the call for lower dose imaging and what his department is doing to address the issue.

Heavy smokers screened for lung cancer with low-dose helical CT scans had a 20 percent lower mortality risk than those screened with standard X-ray, according to a large scale study recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine. So should the lung cancer screening policy change?
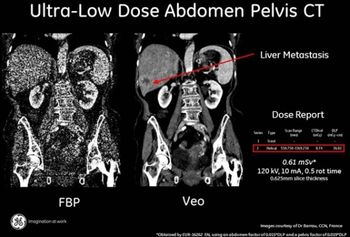
Radiologists have been struggling to balance image noise with radiation dose in computed tomography (CT) scans for decades. But the competition just went up a notch (or perhaps many notches) with the recent FDA approval of GE Healthcare’s Model Based Image Reconstruction (MBIR) technology, Veo. While MBIR is the most recent of the iterative reconstruction technologies, top manufacturers offer their own software answers to the noise versus dose argument.

Radiologists can boost patient safety without significantly affecting the quality of the images by cutting the dose of contrast media in coronary CT angiography, according to a new study in the American Journal of Roentgenology.

Careful consideration of CT scanning protocols can cut breast radiation burden by 50 percent, according to a new study in the American Journal of Roentgenology.

Adenosine stress 128-slice dual source computed tomography perfusion imaging (CTP) with a high pitch factor appears to provide faster, more accurate heart scans for both viewing blood vessels in the heart and measuring blood supply to the heart muscle - while exposing patients to less radiation, researchers report in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging, a journal of the American Heart Association.

Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores based on cardiac CT scans can stratify the risk of heart disease among those without symptoms, a new study reports.

A study assessing CT angiographs of nearly 25,000 patients presumed to be free of coronary artery disease (CAD) has shown both obstructive and nonobstructive forms of the disease to increase the risk of death.

Increasing use of CT scanning in emergency departments has corresponded with fewer hospital admissions, according to a new study published online in the Annals of Emergency Medicine.

Optical Coherence Technology (OCT), a favored tool of eye specialists for nearly two decades, may soon be coming to an esophagus or colon near you.

Computed tomography (CT) scans beat traditional spirometry in identifying lung damage associated with flare-ups of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, a study published online in the journal Radiology concludes.

Siemens Healthcare has received FDA 501(k) marketing clearance for a software package that helps in the assessment of cerebral blood flow during interventional procedures.

Quirks associated with CT measurement can give a false impression of lung-tumor growth, according to a new study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.

Even healthy patients with low cholesterol are at a greater risk of heart attack or stroke if their CT scans show calcium buildup in their coronary arties, a new study has found.

"Picturing Science: Museum Scientists and Imaging Technologies," an exhibition of more than 20 sets of striking large-format prints, showcases advanced imaging technologies used by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History and reveals once-hidden, intricate details of both natural phenomena and cultural artifacts.

The dramatic increases in the use of Multidetector CT scanners (MDCT) prior to surgery in cases of acute appendicitis appear justified by their diagnostic abilities, a new study suggests.

It's now possible to diagnose strokes from scans sent to a smart-phone, using a newly developed Candian app. Researchers found that the sensitivity and specificity of detecting intraparenchymal hemorrhage were 100 percent for the iOS device.