
For the first time in a year and a half, orders for Philips medical imaging equipment edged up in North America. It is the first tangible glimmer of hope that the great imaging recession may finally be over.

For the first time in a year and a half, orders for Philips medical imaging equipment edged up in North America. It is the first tangible glimmer of hope that the great imaging recession may finally be over.
A new CT generation takes shape as vendors introduce designs that cut dose and increase resolution.

The annual joint scientific meeting of the Singapore Radiological Society and the College of Radiologists, Singapore, was expanded this year to include the Singapore General Hospital nuclear medicine update. This allowed a greater inclusion of topics pertaining to nuclear medicine and radiation oncology, with the theme of the meeting being “imaging and therapy in the area of molecular medicine.”
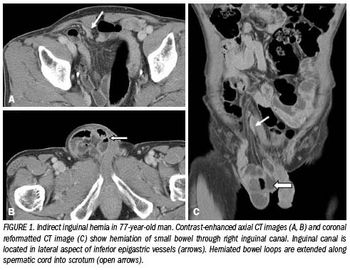
Although most hernias involving the anterior abdominal wall or groin can be diagnosed easily by inspection and palpation, imaging is the principal means of detecting internal, diaphragmatic, and other nonpalpable or unsuspected hernias.1,2

Imaging studies at the 2010 Winter Olympic Games increased 65% from when they were last held, in Torino, Italy.

The amount of data obtained in a single MR or CT scan is mind-boggling. At least some of the data radiologists throw away could save patients money while reducing their exposure to radiation and risk of complications from invasive procedures.

The 19th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Singapore Radiological Society was jointly organized with the College of Radiologists, Singapore, from Feb. 25 through 28. I have attended this meeting the past three years as it gives me ample opportunity to interact with my colleagues and feel the pulse of radiology in and around the region. Each year, the focus is on a hot topic, and this year’s topic was nuclear medicine and molecular imaging.
It is widely accepted that reducing time from admission to definitive care saves lives, but usually imaging is one of the major sources of delays. This means radiologists play a vital role in prioritizing patients and selecting the correct modality.

CT protocols used by researchers at Loma Linda University decreased radiation dose up to 95% when de-tecting distal ureteral calculi.
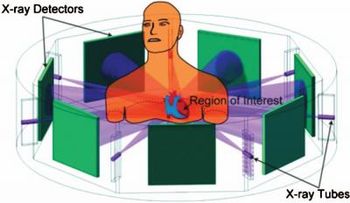
Radiology is a medical specialty created by a fertile marriage between biology and physics. But it is an entirely different academic discipline that is the focus of the research by major vendors of CT technology on show this year at the ECR’s technical exhibition. Their studies have centered on the subject that the illustrious 19th century German scientist Carl Friedrich Gauss called “the queen of sciences”: mathematics.

It’s not enough that sidelined nuclear reactors are restricting the supply of technetium for cardiac SPECT. Or that reimbursements for SPECT procedures are falling. Now the besieged modality has to contend with a challenge from CT.
Multimodality imaging is rapidly becoming an essential tool, particularly in oncology, where many publications have focused on a role for PET/CT.

In news from the nuclear medicine front, there’s a new twist in the technetium situation and equipment sales look to boom in Europe over the next decade.

CT colonography can pinpoint cancerous colorectal segments more accurately than colonoscopy, according to Italian investigators.
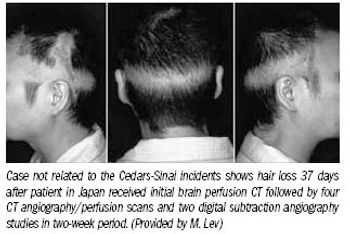
In the aftermath of CT-related radiation accidents at the prestigious Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, the FDA, healthcare providers, and manufacturers are taking action to avoid suffering through similar situations themselves.
CT vendors have responded to public concerns about radiation dose with innovations that promise to cut patient exposure substantially without affecting imaging service operations.

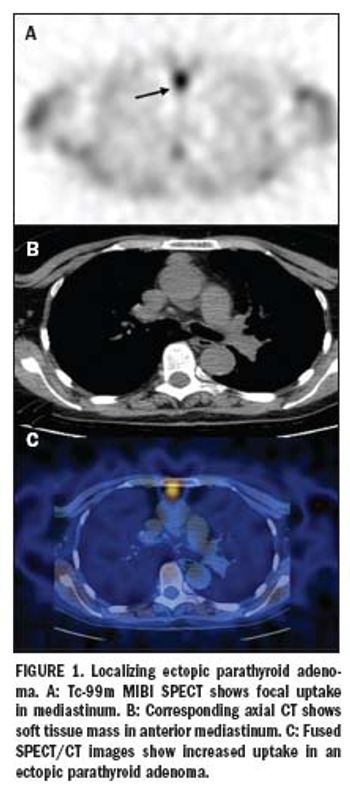
Standard nuclear scintigraphy of parathyroid cancer produces enough false positives for patients with multigland disease to lead researchers to recommend rapid intraoperative parathyroid hormone assay along with preoperative technetium-99m sestamibi imaging to assure that all lesions have been removed.

Endocrinologists are biting into radiology’s control over the management of nuclear imaging procedures involving an administration of radioiodine.

GE Healthcare announced at RSNA 2009 an effort to develop the next generation of software designed to cut patient x-ray dose from CT.

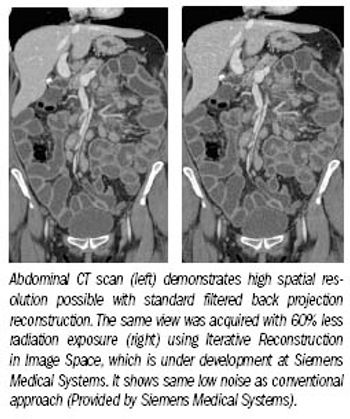
New software shown by Siemens at the RSNA meeting promises to cut patient exposure to x-rays by as much as 60% for a wide range of CT applications.

Over the last several months, Philips has been dropping hints that the company would unveil at RSNA 2009 a high-powered technique for cutting CT dose. The company did not disappoint.

A preliminary study suggests that CTA can play the role cardiac MRI has been playing for detecting and quantifying myocardial infarction to estimate the potential success of coronary bypass graft surgery.

Siemens unveiled a new information technology at RSNA 2009: software that promises to do the tedious and time-consuming tasks involved in reading MR and CT exams. The new product, a work-in-progress pending FDA clearance, is an outgrowth of the syngo platform that Siemens has used for years to provide consistency in data processing among its modalities.
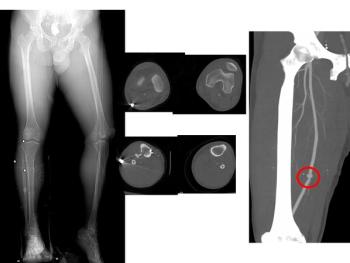
Findings of a study released Sunday at the 2009 RSNA meeting by researchers in Boston suggest CT angiography could help radiologists identify the factors that keep some types of lower extremity fractures from healing faster and better than other, similar lesions.

Mild skin reactions are a not infrequent delayed adverse outcome of contrast-enhanced CT, according to a prospective study from the University of California, Davis.