
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Utilized in conjunction with screening digital mammography or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered software cmAngio may help detect and localize breast arterial calcification (BAC), an incidental finding that has been linked to an elevated risk for heart disease and stroke.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a prospective study of over 55,000 women who had screening mammography, researchers found that double-reading by a radiologist and artificial intelligence (AI) was non-inferior to double-reading by two radiologists in detecting breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
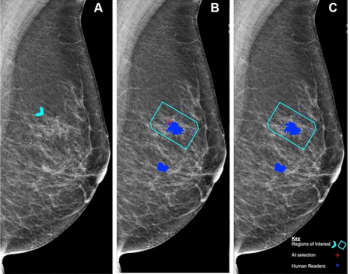
In separate test sets that included challenging mammography cases, researchers found that artificial intelligence (AI) demonstrated similar sensitivity and specificity for detecting breast cancer in comparison to assessments from over 500 clinicians.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In the third episode of a three-part podcast, Anand Narayan, M.D., Ph.D., and Amy Patel, M.D., discuss the challenges of expanded breast cancer screening amid a backdrop of radiologist shortages and ever-increasing volume on radiology worklists.
The study demonstrated that the combined model yielded improved risk assessment for both interval and long-term breast cancers.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In the second episode of a three-part podcast, Anand Narayan, M.D., Ph.D., and Amy Patel, M.D., discuss recent studies published by the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) that suggested moving to more of a risk-adapted model for mammography screening.
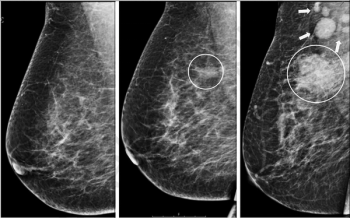
Primary diagnostic delays in mammography screening led to a greater than 10 percent higher incidence of lymph node metastasis with invasive breast cancer in comparison to women without a primary diagnostic delay, according to new research out of the Netherlands.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
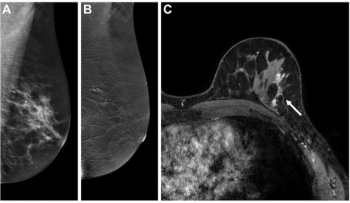
In a new study comparing standard breast MRI, abbreviated breast MRI and contrast-enhanced mammography in supplemental breast cancer screening, researchers found that MRI offered a greater than 14 percent higher cancer detection rate and a nearly 39 percent higher sensitivity rate than CEM.

In the first episode of a three-part series, Anand Narayan, M.D., Ph.D., and Amy Patel, M.D., discuss recently issued updates to breast cancer screening recommendations from the American College of Radiology and the United States Preventive Services Task Force and potential implications for health equity.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Reportedly the first randomized trial to examine the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on screening mammography, researchers found AI-aided screening led to a 20 percent increase in breast cancer detection and a 44.3 percent decrease in mammography screening workload.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
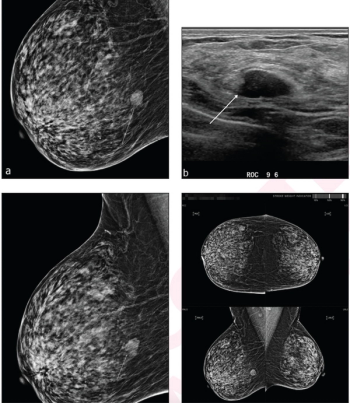
In a study of over 1.300 women with dense breasts, the combination of mammography and ultrasound had a recall rate of 11.7 percent, a specificity rate of 89.1 percent and an accuracy rate of 89.2 percent in comparison to a 21.4 percent recall rate, 79.4 percent specificity and 79.5 percent accuracy for the combination of mammography, ultrasound, and artificial intelligence (AI).
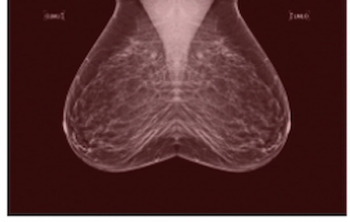
In a dataset enriched for African American women, BRCA mutation carriers and those with benign breast disease, a mammography-based deep learning model demonstrated a five-year AUC of 63 percent for predicting breast cancer in comparison to 54 percent for BI-RADS assessment.

Carch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
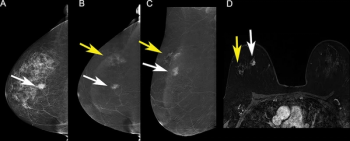
Ultravist is reportedly the first contrast agent to gain a specific indication for visualization of known or suspected lesions on contrast-enhanced mammography, which was recently recommended by the American College of Radiology as a supplemental imaging alternative to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in women with dense breasts at the age of 40 and other risk factors for breast cancer.
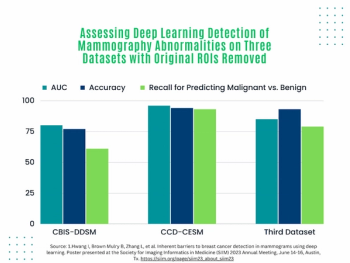
In multiple mammography datasets with the original radiologist-detected abnormality removed, deep learning detection of breast cancer had an average area under the curve (AUC) of 87 percent and an accuracy rate of 83 percent, according to research presented at the recent Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine (SIIM) conference.