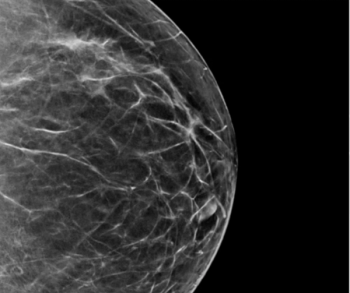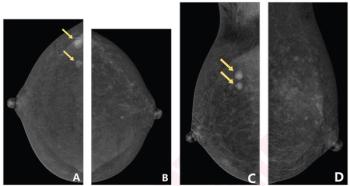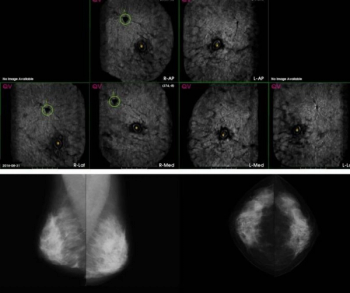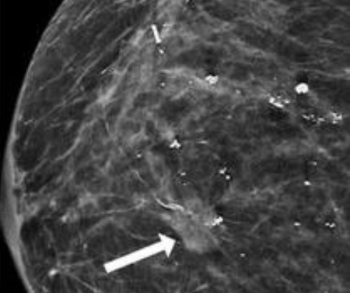
As part of updates to the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) of 1992, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued a final rule that requires the inclusion of breast density assessment in mammography reports starting on September 10, 2024.