
Italian doctors launched a study when introducing handheld ultrasound diagnosis into their hospital, comparing diagnostic accuracy for both trainees and experts against the accuracy of standard Doppler ultrasound imaging.

Italian doctors launched a study when introducing handheld ultrasound diagnosis into their hospital, comparing diagnostic accuracy for both trainees and experts against the accuracy of standard Doppler ultrasound imaging.

Transvaginal ultrasound demonstrates good sensitivity and specificity for detecting endometrial cancer, a study from the University College, London. finds. But that doesn’t mean it’s suited for use in the general population just yet. The researchers found transvaginal ultrasound is better for high-risk groups prone to endometrial cancer, and especially in the management of postmenopausal women undergoing pelvic scans for reasons other than vaginal bleeding.
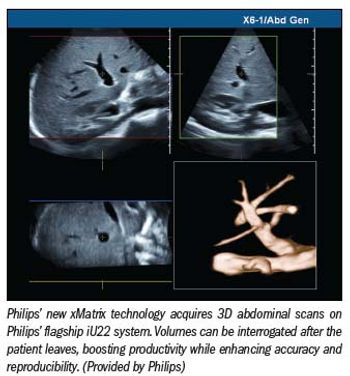
Sonography aspires to pushbutton simplicity, but the nature of the technology stands in the way.

U.S. hospitals could save nearly $22 million annually by deemphasizing CT in favor of diagnostic ultrasound as the frontline imaging test for suspected appendicitis. Such a change would also spare many patients unnecessary exposure to ionizing radiation from CT, according to financial evaluation and meta-analysis by Laurence Parker, Ph.D., an imaging economics researcher at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.

Siemens demonstrated Sie-Reality at this year’s RSNA conference. The new ultrasound technology displays fetal images that take on a third dimension when viewed through 3D glasses.

Dr. Ellen Mendelson is a co-author on a paper exploring the use of shear wave elastography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. In an interview with Diagnostic Imaging, she explains what shear wave elastography is and why it could become a standard element of breast imaging.

The use of ultrasound needle guidance improves the performance, outcomes, and cost-effectiveness of knee injections in people with osteoarthritis, according to research presented last week at the American College of Rheumatology Annual Scientific Meeting in Atlanta.

Not only is it possible to detect aneuploidy and structural fetal anomalies with sonography during the first trimester, but doing so allows for better treatment options, according to a study published in the Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.

Debate continues in the medical community about how many exams it takes before a physician is proficient in identifying ectopic pregnancy with ultrasound. The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine recommends at least 300 sonographic examinations for obstetric indications. The American College of Emergency Physicians recommends a minimum of 25 exams in each emergency bedside sonography indication. A new study finds 25 exams are not enough, but 300 are probably too many.
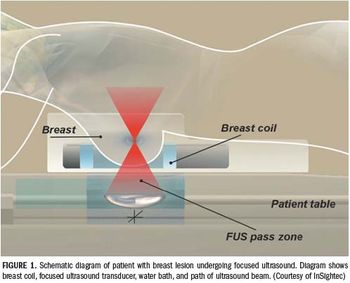
The therapeutic potential of focused ultrasound was first appreciated almost 70 years ago.

An ultrasound-guided diffuse optical technique may lower the rate at which women undergo breast biopsies for suspicious lesions, according to a study published in Radiology.

It may be possible to use ultrasound as a reliable, low-cost form of male contraception, according to ongoing research at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in the U.S.

When it comes to the transducers that power ultrasound, less is more. As they have gotten smaller, more has been packed into the handheld probes that host them, providing more information, allowing easier access to the body’s acoustic windows, and offering easier handling by operators. Now this triad of benefits might be in line for a further boost, a big one.

Sales of ultrasound equipment fared better last year than those of other, more costly, imaging products such as MR and CT. The reason, according to InMedica, the medical research division of IMS Research, may be as simple as the price tag.

Royal Philips Electronics announced it has acquired Shanghai Apex Electronics Technology, a leading Chinese manufacturer of ultrasound transducers, key determinants of image quality for ultrasound systems. The acquisition strengthens Philips’ portfolio of high-quality transducers specifically aimed at the value segment in emerging markets.

While the dramatic effects of the economic recession have been felt in the Western European and North American markets for ultrasound imaging equipment, the Chinese market has seen tremendous growth over the last two years. Driven by China’s ongoing healthcare reform, strong economic growth, and the Chinese population’s increasing awareness of healthcare issues, the second edition of InMedica’s study The China Market for Ultrasound Imaging Equipment – 2010 Edition predicts the Chinese market for ultrasound imaging equipment will exceed $1 billion by 2014, growing at a compounded average growth rate of 9.3%.

Ultrasound can help tissue grafts to survive and thrive following surgery, according to research in the Journal of Tissue Engineering.

Using transcranial Doppler ultrasound to detect asymptomatic cerebral emboli can identify patients who are at a higher risk of stroke and transient ischemic attack as well as those with a low absolute stroke risk, according to an international study.
A pilot study involving eight community midwives from Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust suggests that portable ultrasound has the potential to reduce hospital admissions for predelivery scans. This would eliminate the need for patients in remote areas to travel to appointments.

Synexus, a Manchester-based multinational company dedicated to the recruitment and running of clinical trials, has recently invested in Doppler ultrasound equipment for each of its seven U.K.-based dedicated research centers. After training for all Synexus’ doctors, the facilities are now being used as part of the drive to recruit patients to a new diabetes study.

Certain complex ovarian tumors may be safely monitored using ultrasound without raising the risk of ovarian cancer, according to a new study.

Radiation safety standards are becoming increasingly stringent. Ultrasound systems, however, present no such safety threats, and manufacturers are trying to enhance the versatility of these devices, both in primary and secondary diagnosis. Elastography and therapeutic and contrast-enhanced ultrasound are poised to herald new and more effective means of diagnosis.
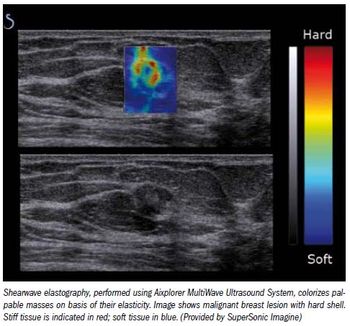
Reducing the number of breast biopsies by better classifying suspicious lesions noninvasively could improve healthcare and cut healthcare costs, laudable goals in the current era of healthcare-and economic-reform.

It may be possible to use ultrasound as a reliable, low-cost form of male contraception, according to ongoing research at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
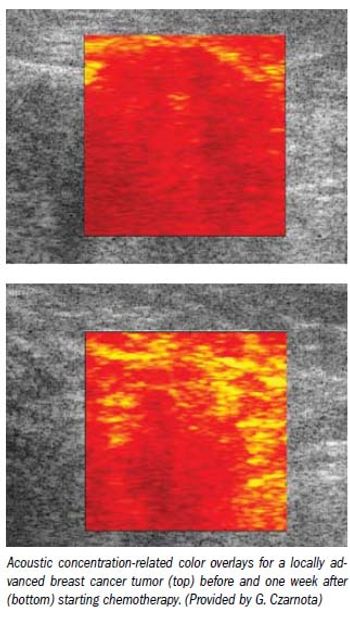
A new ultrasound technique that measures cell death, tumor elastography, and vascular patterns can better predict how well cancer patients are responding to chemotherapy, Canadian researchers report.