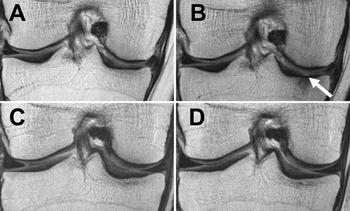
Effect of diet, exercise on people who are overweight or obese who lose weight to help decrease knee cartilage deterioration.

Effect of diet, exercise on people who are overweight or obese who lose weight to help decrease knee cartilage deterioration.

Images showing body composition have shown that where body fat is stored is more of a factor in cardiovascular and metabolic risks than the type of fat.
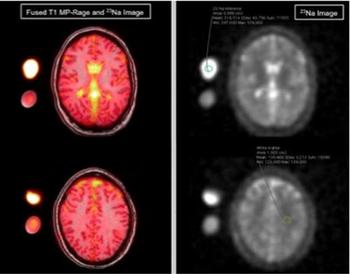
Researchers used MRI to detect higher levels of sodium in the CSF of patients who have migraines.
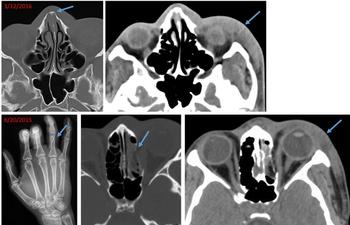
Images that show specific types of injuries and old injuries could help radiologists identify victims of domestic and sexual abuse.
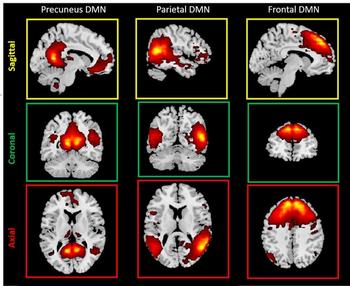
Imaging shows lasting brain damage among children who play high-impact sports like football.
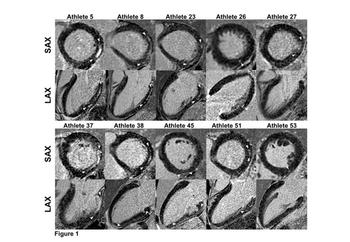
MRI shows evidence of higher risk for elite male triathletes.
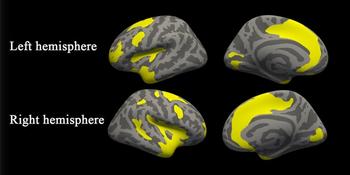
MRIs show common structural abnormalities among patients with depression and anxiety.

The effect of high BMI on breast cancer screening frequency.

Abdominal CT studies can help clinicians accurately evaluate the lumbar spine.
Use of imaging for musculoskeletal extremities has increased significantly over the past 20 years.

Adding automated breast US to regular screening of women with BRCA mutation and cancer detection.
Older patients with brain PET results showing elevated amyloid have many questions.

MRI shows damage to brain tissue among adolescent athletes may continue after they have been cleared to return to sports.

The PanCan approach to lung cancer detection utility in lung cancer screening.

A machine learning module may help predict which high-risk breast lesions are least likely to progress to cancer.
Effect of breath holding during lung PET/CT.

Nuclear medicine radiologic technologists may be at risk for developing cataracts.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain may help physicians predict patient outcomes following a cardiac arrest.
Multiple CT scans for young adults with non-traumatic acute abdominal conditions increase radiation exposure.

More patients and providers are aware of CT dose in 2015 than they were in 2004.

Macrocyclic GBCAs in nonenhanced T1 signal intensity pediatric brain tissue.
MRI for evaluation of breast masses in lactating women.

Information in the EMR may suggest which patients may not show up for scheduled radiology examinations.

FDA approves Philips’ ‘Small Parts’ ultrasound transducer.

Disparities in radiation doses from CT scans in different countries.

MRI may still be possible for some patients with non-conditional cardiac implantable electronic devices.

MRI in the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium meets most BI-RADS benchmarks.
Utility of both PI-RADS version 2 and MRI-ultrasound fusion biopsy for diagnosing prostate cancer.
Routine mammography does not detect more cancers among high-risk women who undergo annual screening with MRI.

There are significant differences between women who use mobile units for breast cancer screening compared with those who attend cancer centers.