Emerging MRI research suggests that brain age is nearly two years older than chronological age for people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and increased alcohol intake.
Senior Editor, Diagnostic Imaging

Emerging MRI research suggests that brain age is nearly two years older than chronological age for people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and increased alcohol intake.
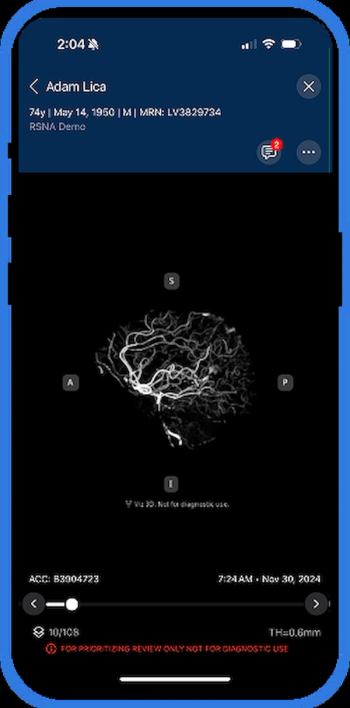
Offering automated conversion of computed tomography angiography (CTA) into 3D images, Viz 3D CTA reportedly facilitates real-time insights into complex neurovascular anatomy.
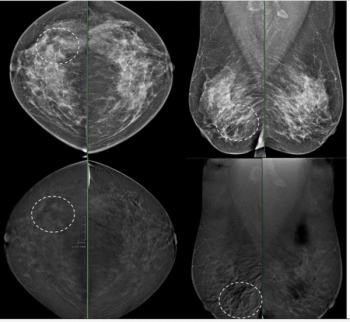
In comparison to minimal or mild background parenchymal enhancement on contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM), researchers found that moderate or marked BPE was associated with a 12 percent lower AUC for breast cancer detection.
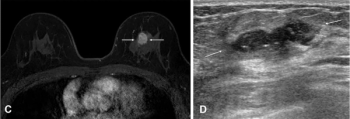
Preoperative breast MRI had no impact upon recurrence-free survival and overall survival for women with HER-2 positive, hormone receptor-negative breast cancer, according to a multivariable analysis of a new study involving nearly 1,100 women.
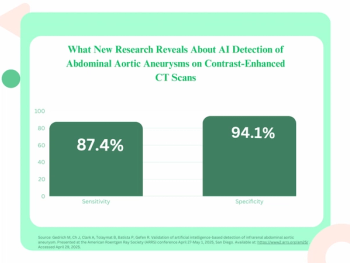
The AI software Viz AAA offered a sensitivity of 87.5 percent in detecting abdominal aortic aneurysms on contrast-enhanced CT, according to new retrospective research presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.
In a recent interview, Wayne Brisbane, M.D., discussed new research, presented at the American Urological Association (AUA) conference, which revealed a 15 percent higher AUC for an emerging AI software in detecting seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) in comparison to prostate MRI alone.
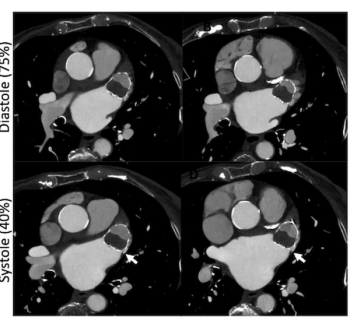
Cardiac CT angiography may provide insights on common post-op complications of left atrial appendage closure, ranging from peri-device leaks to device-related thrombus, according to research presented at the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) conference.

In a recent interview, Manisha Bahl, M.D., discussed key findings from a new study on AI and digital breast tomosynthesis that she presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.
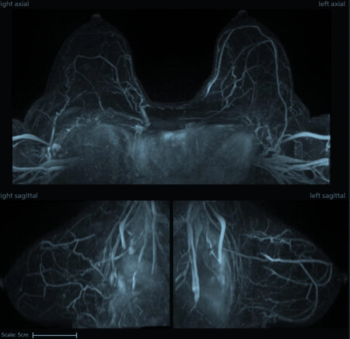
An artificial intelligence algorithm for dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI offered a 93.9 percent AUC for breast cancer detection, and a 92.3 percent sensitivity in BI-RADS 3 cases, according to new research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference.
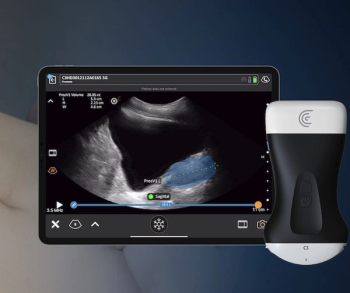
Offering expedited calculation of prostate volume, Clarius Prostate AI is reportedly the first AI-enabled prostate measurement tool to garner FDA clearance for use with handheld ultrasound.
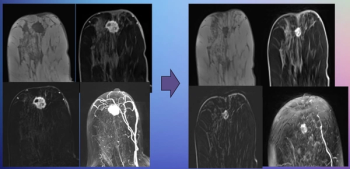
New research presented at the Society for Breast Imaging (SBI) conference suggests that abbreviated MRI is comparable to full MRI in assessing pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
In a recent interview, Benjamin Kann, M.D., discussed the use of an emerging AI model that can assess longitudinal MR imaging to help predict postoperative recurrence risk for gliomas in pediatric patients.
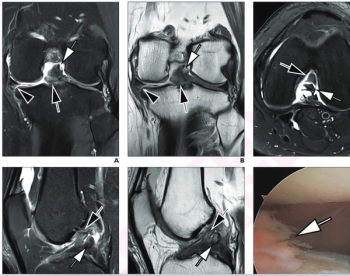
Employing deep learning image reconstruction, parallel imaging and multi-slice acceleration in a sub-five-minute 3T knee MRI, researchers noted 100 percent sensitivity and 99 percent specificity for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears.
In a recent interview, Arjun Sahgal, M.D., discussed current and emerging research examining the potential of MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy for treating glioblastomas.
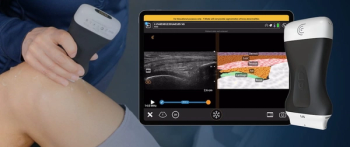
The T-Mode Anterior Knee feature reportedly offers a combination of automated segmentation and real-time conversion of grayscale ultrasound images into color-coded visuals that bolster understanding for novice ultrasound users.
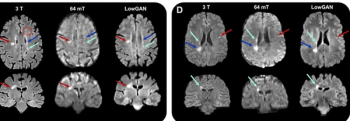
In comparison to native 64-mT MRI, the deep learning generative model LowGAN offered enhanced white matter lesion conspicuity and image quality in a study involving patients with multiple sclerosis.
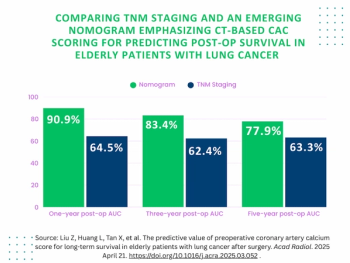
For elderly patients with lung cancer, a preoperative CT-based coronary artery calcium score > 40 was associated with a 53 percent higher risk of all-cause mortality after surgery, according to new study findings.

In a recent interview, Syam Reddy, M.D., discussed the rising incidence of colon cancer and a clinical pathway resource with Radiology Partners that facilitates the integration of computed tomography colonography (CTC) into radiology practice.
Recently published research projected that 103,000 future cases of radiation-induced cancer would result from 93 million computed tomography (CT) exams performed in the United States in 2023.
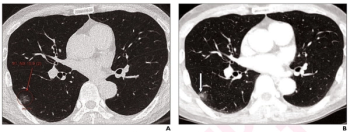
In comparison to radiologist assessment, the use of AI to pre-screen patients with low-dose CT lung cancer screening provided a 12 percent reduction in mean interpretation time with a slight increase in specificity and a slight decrease in the recall rate, according to new research.
The Nanox.ARC X system reportedly provides enhanced 3D imaging for a variety of indications, ranging from pulmonary imaging and intra-abdominal views to musculoskeletal assessment.
Seniors who had at least one prior screening mammography exam in the five years prior to breast cancer diagnosis were over a third less likely to die from breast cancer, according to new research.
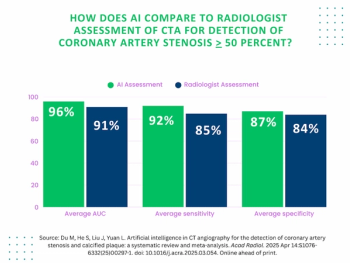
Artificial intelligence demonstrated higher AUC, sensitivity, and specificity than radiologists for detecting coronary artery stenosis > 50 percent on computed tomography angiography (CTA), according to a new 17-study meta-analysis.
The additional FDA 510(k) clearance for the AI-powered cmAngio platform covers use of the software for GE HealthCare mammography systems.
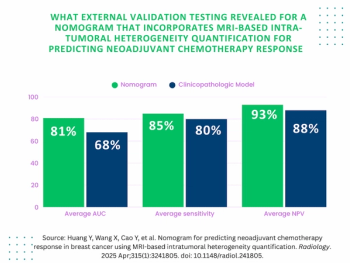
An emerging nomogram model for intra-tumoral heterogeneity quantification with breast MRI demonstrated an average 85 percent sensitivity in external validation testing for predicting pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
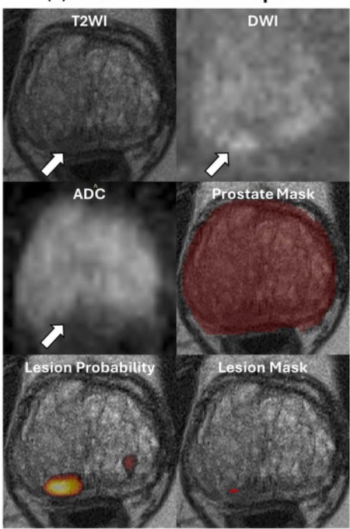
Demonstrating no significant difference with radiologist detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), a biparametric MRI-based AI model provided an 88.4 percent sensitivity rate in a recent study.
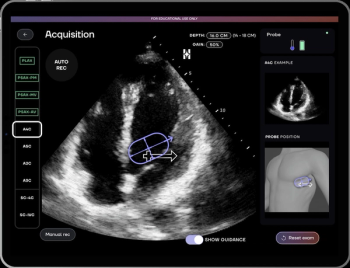
Recent research has demonstrated that the AI software HeartFocus enabled novice health-care providers to achieve greater than 85 percent agreement with expert sonographers in assessing echocardiographic parameters.

In a recent interview, Rebecca Smith-Bindman, M.D., offered key insights on new research examining the link between computed tomography scans and projected future cases of radiation-induced cancer.
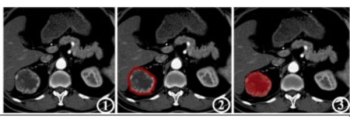
In comparison to a model based on clinicopathological risk factors, a CT radiomics-based machine learning model offered greater than a 10 percent higher AUC for predicting five-year recurrence-free survival in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
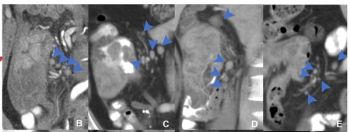
For patients with microsatellite instability-high colon cancer, distribution-based clinical lymph node staging (dCN) with computed tomography (CT) offered nearly double the accuracy rate of clinical lymph node staging in a recent study.