
Radiologists have the opportunity to identify women suffering intimate partner violence by detecting a specific type of forearm fracture.
Whitney J. Palmer has been with Diagnostic Imaging since 2011, serving as the Senior Editor since November 2019. She has 20 years experience in healthcare and academic medicine reporting.

Radiologists have the opportunity to identify women suffering intimate partner violence by detecting a specific type of forearm fracture.
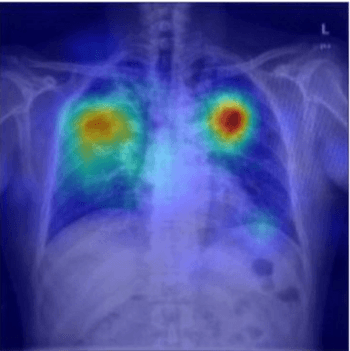
Applying a deep-learning model to a photograph of a chest X-ray can help providers in resource-poor areas diagnose the disease.

A model that uses biomarkers pulled from a woman’s mammogram does produce a more accurate breast cancer risk assessment.
By incorporating non-imaging data, the algorithm can effectively pinpoint which patients will need ICU intervention.

fMRI scans show that babies’ brain activity can be influenced through associative learning, presenting a potential strategy for promoting the development of life-long skills in infants who have injured brains.
Low-dose CT for lung cancer screening offers significant benefits for detection and follow-up, but utilization, to date, has been low. Debra S. Dyer, M.D., chair of the American College of Radiology's Lung Cancer Screening 2.0 Committee discusses what the screening provides and the challenges to more widespread implementation.
Optically pumped magnetometer sensor detects magnetic signals that could augment the detection of traumatic brain injury and disease.
Left atrial diameter and fibrosis differences between African American and white patients could play a role the risk of ischemic stroke.

CT scans reveal impaired lung function in individuals who use biomass, such as wood or wildfires, to cook.
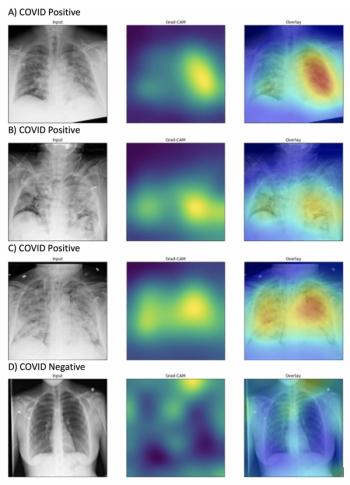
Investigators from Northwestern University have developed an algorithm that can identify evidence of COVID-19 on chest X-rays in a fraction of the time.
Brain MRI scans reveal that anxiety is independently associated with a faster progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease.
Images reveal that adolescents experienced a loss in volumetric bone mineral density after sleeve gastrectomy and extreme weight loss.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Swabs created with a 3D printer produce virtually identical diagnostic results, effectively addressing the shortage of nasopharyngeal swabs.
Basic photographs paired with AI technique can pick up on retinal changes that are early signs of the progressive central nervous system disorder.

This mathematical algorithm can reduce dose in pediatric CT scans by 52 percent.

Trends for CT scans for abdominal pain in pediatric patients are down, but they are up for adults. Still, the scan is integrally involved in appendicitis diagnoses.
Third annual report from the American Lung Association reveals 94 percent of high-risk eligible patients are not getting screening with LDCT, and access and outcomes are worse for racial and ethnic minorities.
Rapid COVID-19 Diagnosis with CT and CO-RADS; Cooled Radiofrequency Ablation for Pain Relief; Inappropriate Abdominal CT and Ultrasound Scans; and Lead Shielding Guidance
New research shows radiologists – regardless of experience level – fall victim to inattentional blindness, overlooking obvious unrelated findings when they are trying to answer a specific diagnostic question.
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals neurochemical abnormalities that shed light on how the virus impacts the brain.

Older women exposed to higher levels of air pollution can experience a 24-percent increase in Alzheimer’s risk.
Women who experience food or housing insecurities are more likely to take longer between imaging and follow-up, putting them at greater risk for undiagnosed breast cancer.

For patients who have had viral symptoms for more than 48 hours, combining chest CT findings and CO-RADS classifications can effectively diagnose COVID-19-positive patients.

Study finds 84 percent of CT and ultrasounds in the emergency department do not follow ACR appropriateness criteria and cause downstream problems for patient care.

Approximately half of all patients who experience stroke, brain bleeds, or blocked blood vessels, identified on MRI or head CT in this study, had high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes.

In this episode, Dr. Michael Recht, chair of the radiology department at New York University Langone Health, discusses the partnership between NYU and Facebook AI that has created an accelerated MRI that is four times as fast as a standard MRI.
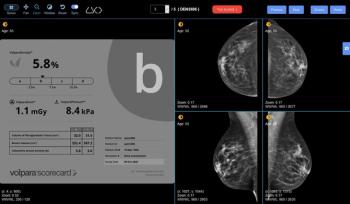
Volpara Health and DetectED-X are collaborating to make a breast density categorization training tool available to radiologists worldwide.

Scans show increased knee degeneration in overweight or obese patients who play fast-paced racket sports.
Cooled radiofrequency ablation (c-RFA) for moderate-to-severe hip and shoulder arthritis could help some patients avoid surgery and reduce the risk of opioid addiction.