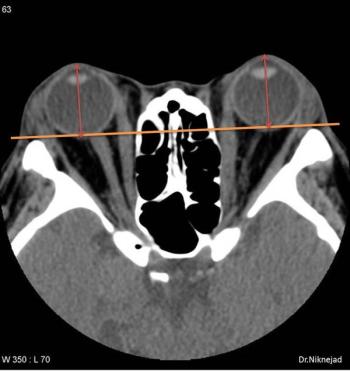
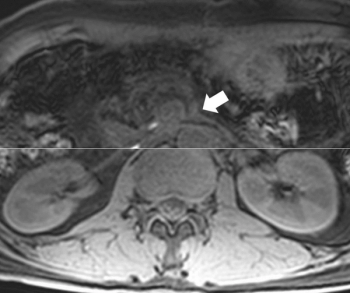
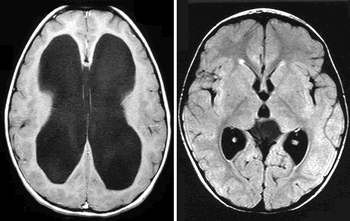
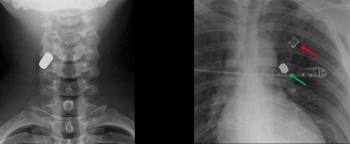
In a recent video interview on the current iodinated contrast media shortage, neuroradiologist Sean Bryant, MD discussed imaging alternatives, emphasized communication with referring physicians on optimal studies, and discussed the ongoing need to prevent “protocol creep” with timely updates of imaging protocols.