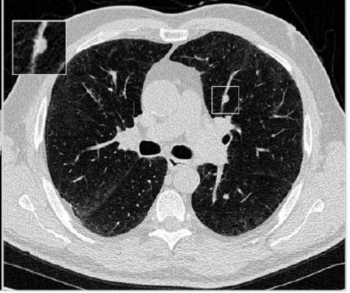
Researchers suggest that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered risk stratification tool for lung nodules identified on computed tomography (CT) scans may identify likely malignancies more than one year prior to definitive diagnosis.
Senior Editor, Diagnostic Imaging

Researchers suggest that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered risk stratification tool for lung nodules identified on computed tomography (CT) scans may identify likely malignancies more than one year prior to definitive diagnosis.
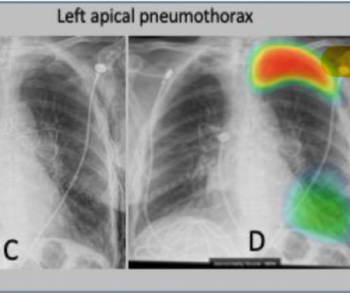
Researchers found that stand-alone use of an artificial intelligence (AI) model led to a 24.9 percent increase in sensitivity for diagnosing pulmonary nodules and a 21.4 percent increase in sensitivity for diagnosing pneumonia.

The automated measurement of heart ventricle diameters and detection of potential dilation in the right ventricle may facilitate quicker intervention in cases of pulmonary embolism.
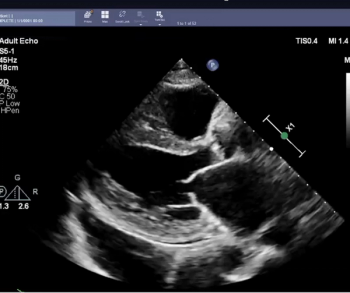
In comparison to initial sonographer assessment of echocardiograms, cardiologists are over 10 percent less likely to change initial artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), according to new research recently presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress in Barcelona, Spain.

In a new study of over 7,200 women with no history of breast cancer, researchers found that women who scheduled health-care appointments online were more likely to have annual mammography exams but only 18 percent of the study population scheduled appointments online.
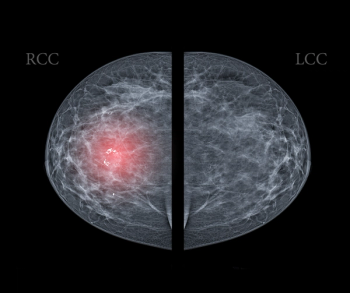
Emerging research suggests a higher prevalence of positive breast arterial calcification (BAC) rates among Hispanic and Black women, and a lower rate of BAC in women with dense breasts or breast implants.
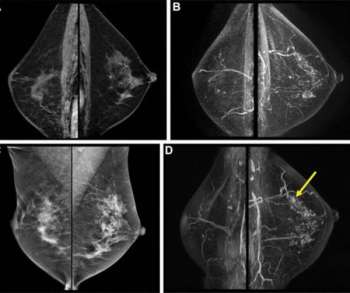
Mild, moderate, or marked background parenchymal enhancement on surveillance magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reportedly doubles the risk of second breast cancer in women who have had surgery for primary breast cancer.
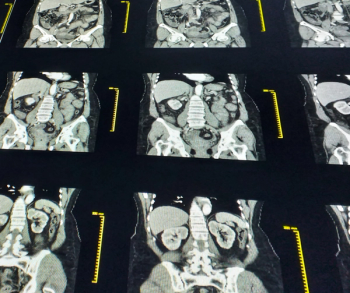
Emerging research findings suggest the use of single-encounter thoraco-abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) per 1,000 trauma-related emergency department (ED) visits more than quadrupled for minor injuries and more than doubled for intermediate injuries from 2011 to 2018.
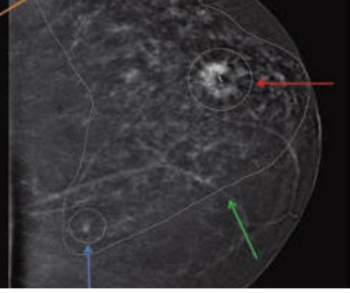
Researchers found the combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and contrast-enhanced mammography was nearly 22 percent more effective at detecting breast lesions than MRI-directed ultrasound.
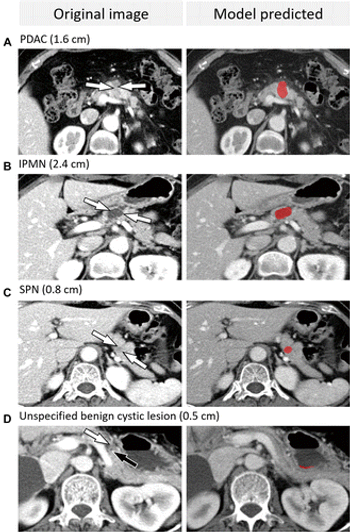
Researchers showed the deep learning system had an area under the curve (AUC) ranging from 87 percent to 91 percent in two test sets for diagnosing solid pancreatic lesions of any size and cystic lesions 1 cm or larger on high-contrast computed tomography (CT).

Well known for her education and advocacy on the use of computed tomography (CT) colonography for colorectal cancer screening, Dr. Yee is also widely recognized for her leadership, mentoring skills and being a champion for diversity in the field of radiology.

In a new study comparing 2017 and 2019 Medicare claims submission data, researchers noted a 40 percent increase in evaluation and management (E&M) services, and a 74 percent increase in imaging services performed by radiology-employed nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs).
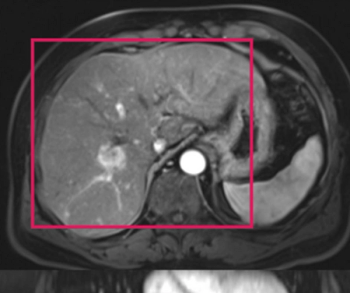
Noting that the machine learning model incorporating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had a higher mean area under the curve (AUC) than a model based solely on clinical features for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence, researchers said the study findings could have implications for refining liver transplant criteria.
In comparison to neuroradiology assessment of brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans for tumor diagnosis, researchers found that adjunctive use of a deep learning system improved diagnostic accuracy by 12.4 percent and sensitivity by 33.5 percent in one test set of 300 patients.
Emerging research from a positron emission tomography (PET) study suggests that prior COVID-19 infection can lead to a 30 percent increased risk of lower myocardial flow reserve in patients with cardiovascular risk factors ranging from diabetes to coronary artery disease.
Emerging research revealed that Asian patients, Black patients, and those who identified their race as “other” were nearly 1.5 times more likely than White women to have more than two-month delays with follow-up imaging after BI-RADS 0 screening mammography.
In a recent survey of nearly 2,000 women in their 40s who had no history of breast cancer, researchers found that over 38 percent of survey respondents said they had no reason to get a mammogram or had never thought about it.
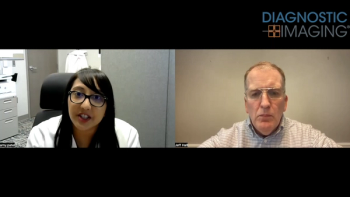
With ongoing gaps in mammography screening and patient anxiety that often accompanies screening exams and a possible diagnosis of breast cancer, patient education is critical. Accordingly, in a recent video interview, Amy K. Patel, M.D., discussed the potential impact of new patient-oriented breast cancer screening guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
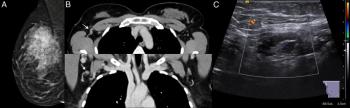
The combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) had a 63.83 percent sensitivity rate for tumor-infiltrated axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer in comparison to a 36.11 percent sensitivity rate for the combination of mammography and sonography.
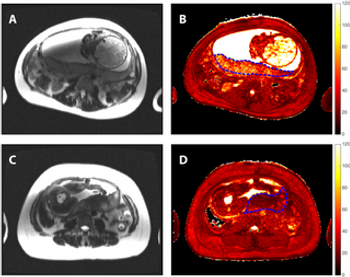
Emerging research suggests a robust association between pregnancy outcomes and placental measurements assessed via blood oxygen-level dependent magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-MRI).
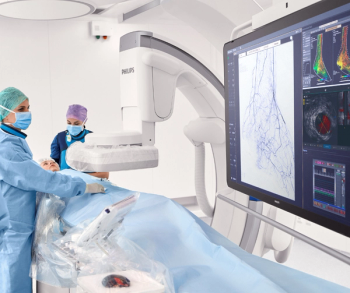
Published by the American College of Cardiology, the expert recommendations offer insights on the role of intravascular ultrasound for diagnosing and treating peripheral vascular disease in the lower extremity.
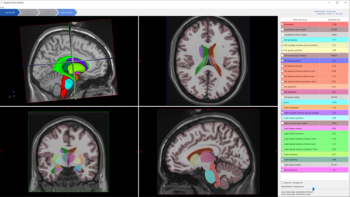
The Maestro Brain Model reportedly provides automated identification, quantification and labeling of brain structures on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

In a new study, researchers examined trends with diversity in the radiology workforce, offering a closer look at the gender, race and ethnic makeup of radiology residency programs and academic faculty.
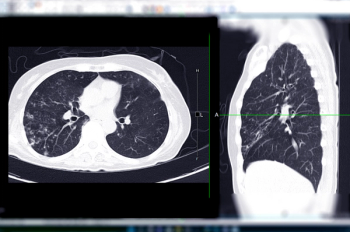
While recent recommendations from the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) to lower lung cancer screening thresholds significantly expanded eligibility for screening tests such as low-dose computed tomography (CT), differences in education, health-care insurance and proximity to health-care facilities continue to be key drivers of racial and socioeconomic disparities limiting access to appropriate preventive care.
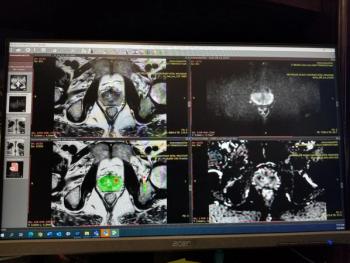
The ProstatID, an adjunctive artificial intelligence software that radiologists can utilize with traditional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), reportedly measures prostate gland volume, and suggests PI-RADS scoring of suspicious lesions.
Researchers discuss key parameters for the assessment, implementation and post-implementation monitoring of emerging artificial intelligence (AI) tools in radiology practices large and small.

A recent study found the use of an alert and a request for more clinical information in a multisite health system’s electronic health record (EHR) system led to a 12 percent reduction in contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) exams per day and a 15.2 percent reduction in orders for CT with contrast media per day.
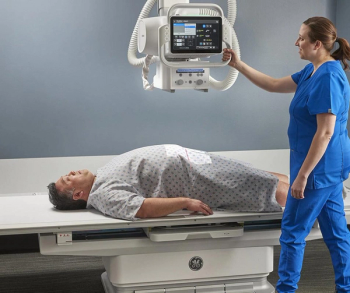
The Definium 656 HD fixed X-ray system reportedly features enhanced, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven image processing, facilitates radiology workflows, and reduces patient positioning time.
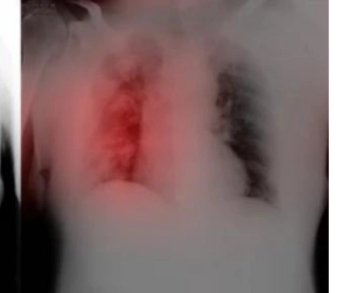
Preliminary research revealed an area under the curve (AUC) of 85 percent for an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm in diagnosing COVID-19 on initial chest X-rays in comparison to a consensus 71 percent AUC for five radiologists.
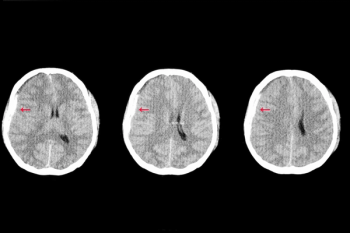
Viz.ai said the Viz Subdural Hematoma (SDH) artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm provides automatic detection of acute and chronic subdural hemorrhages, facilitating timely triage and treatment of patients.