Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: June 12, 2020
Whitney J. Palmer has been with Diagnostic Imaging since 2011, serving as the Senior Editor since November 2019. She has 20 years experience in healthcare and academic medicine reporting.

Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: June 12, 2020
Guidelines, supported by several medical societies, offer direction for post-operative and “definitive” settings.
Three-stage system can help providers assess patients, as well as guide future treatment and research efforts.
Symptoms of digital eye strain are felt more among women and trainees.
Navigating the need for new workflow strategies and protocols has revealed opportunities for women to take on more leadership roles.

Small daily techniques can help you avoid burnout as imaging volumes swell to process the backlog of scans.
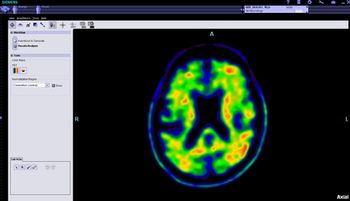
Scans show greater amyloid accumulation in the brains of older adults who get less than six hours sleep nightly.

More than 75 percent of breast imaging environments are close to re-capturing pre-pandemic imaging volumes.

Cryoablation offers patients with early-stage kidney cancer comparable results to surgery.
UTE-MRI can be a valuable alternative in situations where repeated radiation exposure is of concern.
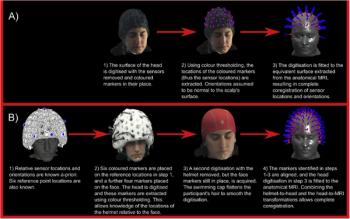
49-channel device tracks the brain’s electrophysiological processes and can be an effective imaging option for children or patients who have difficulty being still.
Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: June 5, 2020
Duke researchers determined task-fMRI does not produce reliable predictions individuals will respond in particular circumstances or future mental health.

Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers see “untapped potential” for artificial intelligence tools.
When added to exercise electrocardiography, CTA can improve five-year risk prediction.
The modality is an effective, reliable alternative to chest CT or chest X-ray in this vulnerable population.
A five-tiered approach to cross-sectional interventional procedures can help radiologists determine which patients to treat first, minimizing likelihood of viral transmission.
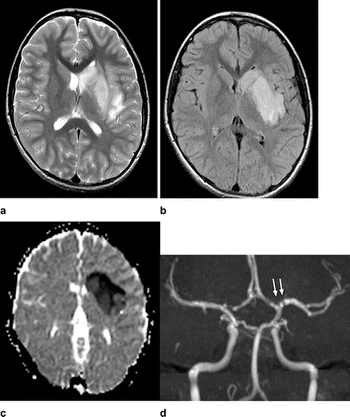
Iranian researchers diagnosed ischemic stroke in COVID-19-positive child with no other symptoms.
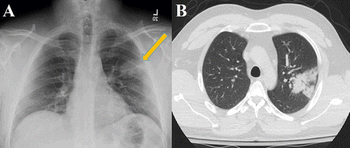
Researchers from Mount Sinai examine and assess the imaging modalities used to evaluate patients positive for the virus.

Knowing what will impact image volumes can help put practices on the fastest road to imaging stability.

Johns Hopkins shares its experience with hosting live events, garnering international participation.

American College of Radiology President Geraldine McGinty, M.D., MBA, FACR, discusses the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on female radiologists and their colleagues.
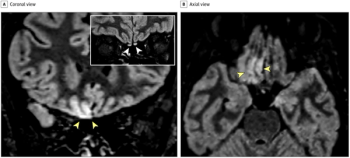
Technologist positive for the virus experienced a loss of smell and altered sense of taste.
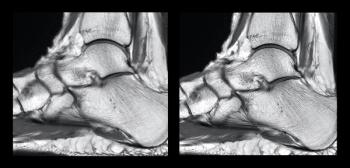
New technology designed to provide shorter scan times, better image quality.

Diagnostic Imaging's Weekly Scan: May 29, 2020
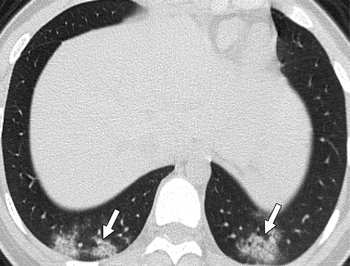
Research shows 77 percent of children who are confirmed positive for the virus have no findings via chest CT.
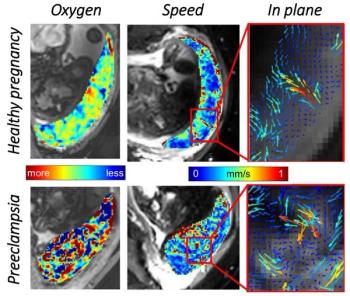
Independent contractions of uterine wall and placenta sends more oxygen-rich blood to unborn child.

Patient isolation bag could not only reduce risk of viral transmission, but could also streamline CT workflow.
Additional steps further reduce risk of viral transmission in MRI suites.
New York’s largest health system experiences 88-percent decrease in outpatient imaging between 2019 and 2020, indicating potential national trend.